您的位置:上海毫米网络优化公司 > 网站优化分享 >
相关推荐recommended
- 前端文件上传(文件上传,分片上传,断点续传)
- Java Spring Boot 写 API 接口
- Hive 排名函数ROW
- 【C语言】贪吃蛇【附源码】
- 23、Lua 学习笔记之一(初阶话题)
- 多模态之ALBEF—先对齐后融合,利用动量蒸馏学习视觉语言模型表征,学
- 数据结构 -> 时间复杂度和空间复杂度的计算(做题助推器)
- MySQL篇—启动或者关闭linux下MySQL数据库的多种方式
- centos系列:【 全网最详细的安装配置Nginx,亲测可用,解决各
- MySQL三表联合查询语法
- nginx重启失败:Job for nginx.service fai
- Mysql 提升索引效率优化的八种方法
- Springboot之自定义注解
- 「PHP系列」PHP E-mail 注入防止注入
- SpringBoot3整合Redis&基础操作
- Jenkins 命令无法后台运行,使用BUILD
- 5 万字 124 道MySQL经典面试题总结(2024修订版)
- MySQL INSERT插入条件判断:如果不存在则插入
- JavaWeb项目:航班信息管理系统(tomcat+jsp)
- SpringMVC基础篇(二)
- MySQL— 基础语法大全及操作演示!!!(上)
- Tc0.Springboot项目启动失败
- LLM-AI大模型介绍
- 【Nginx】Nginx启动显示80端口占用问题的解决方案
- 21、Lua 面向对象
- Mysql 报 java.sql.SQLException:null,
- Linux部署Sonarqube+Gogs+Jenkins(一)
- HashMap源码解读(中篇)
- Qt5.14.2 深入理解Qt多线程编程,掌握线程池架构实现高效并发
- k8s中,kubelet 出现问题, k8s-master node
rabbitmq基础教程(ui,java,springamqp)
作者:mmseoamin日期:2024-02-04
概述:安装看我上篇文章Docker安装rabbitmq-CSDN博客
任务一

创建一个队列

这样创建两个队列
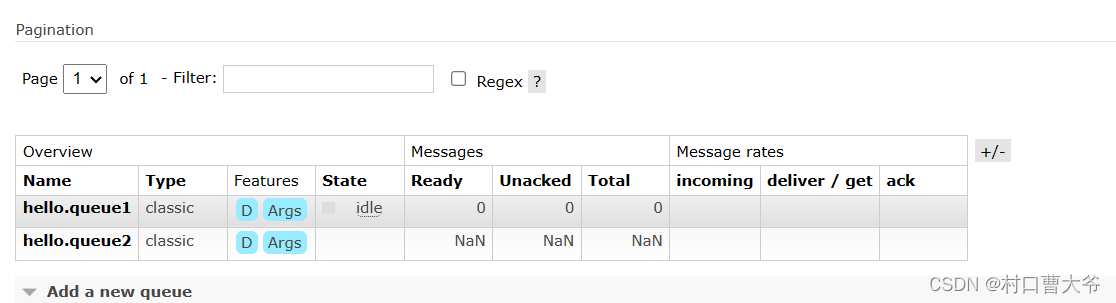
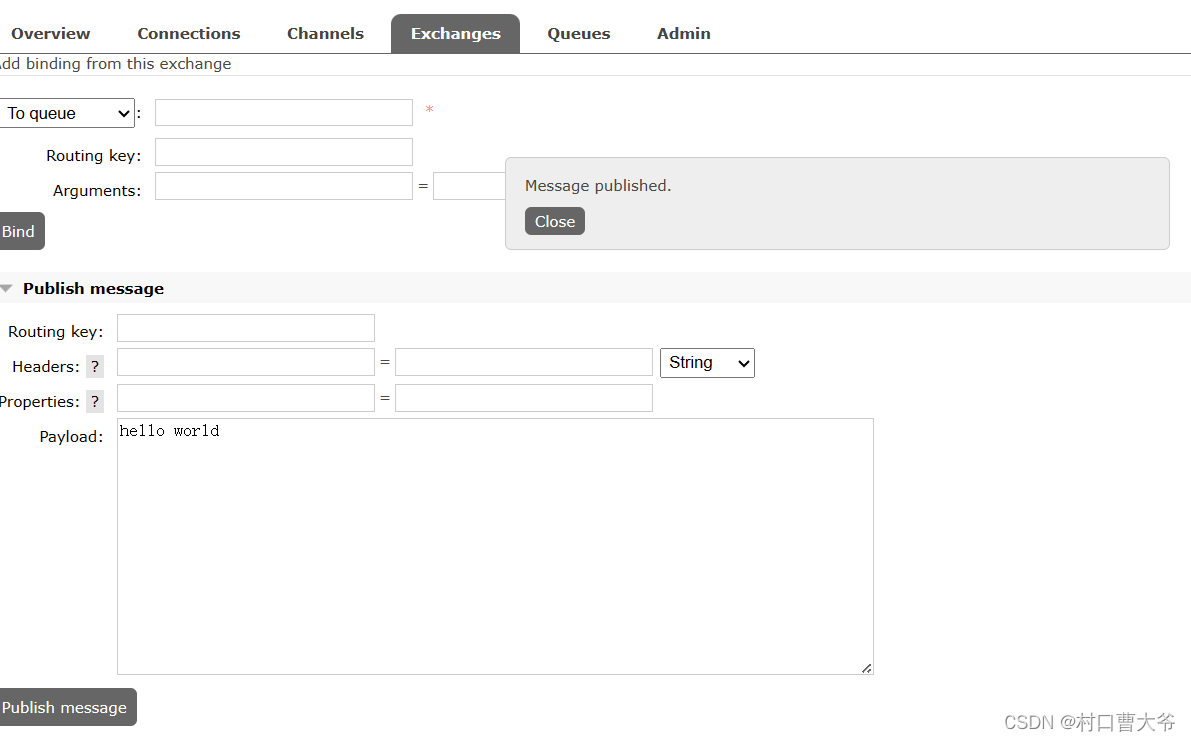
在amq.fanout交换机里面发送数据
模拟发送数据
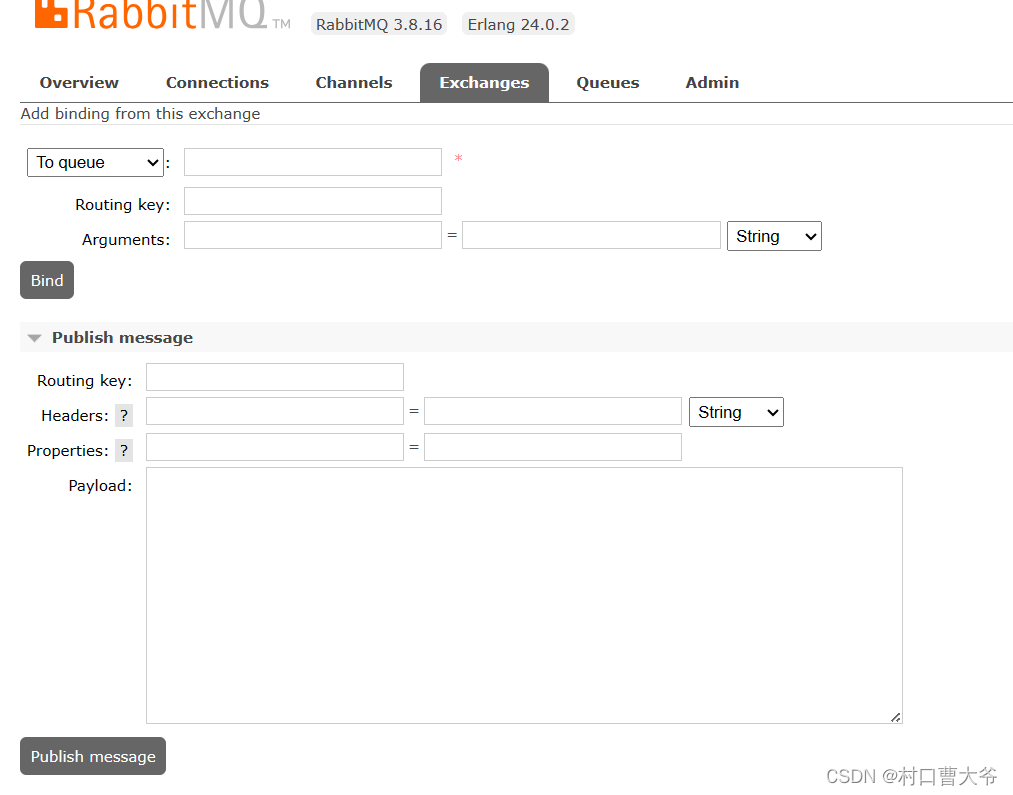
发送消息,发现一下信息:

所以得出理论,消息发送是先到交换机,然后由交换机路由到消息队列
交换机是负责路由和转发消息的,并没有存储的功能。
绑定队列
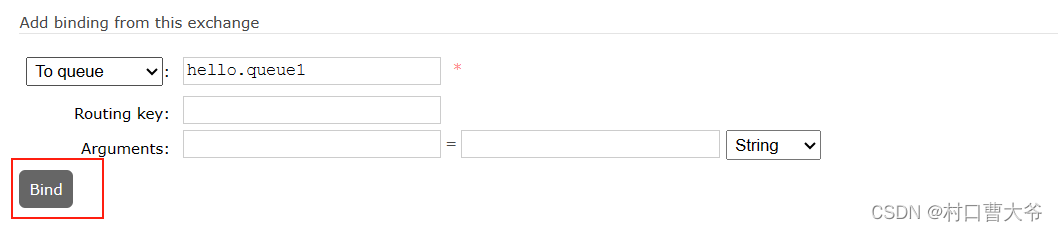 同理绑定queue2
同理绑定queue2
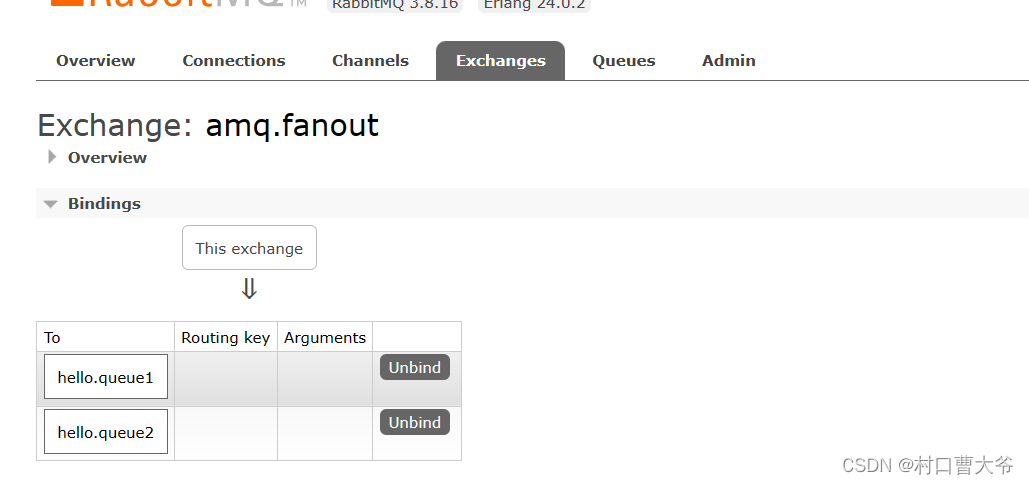
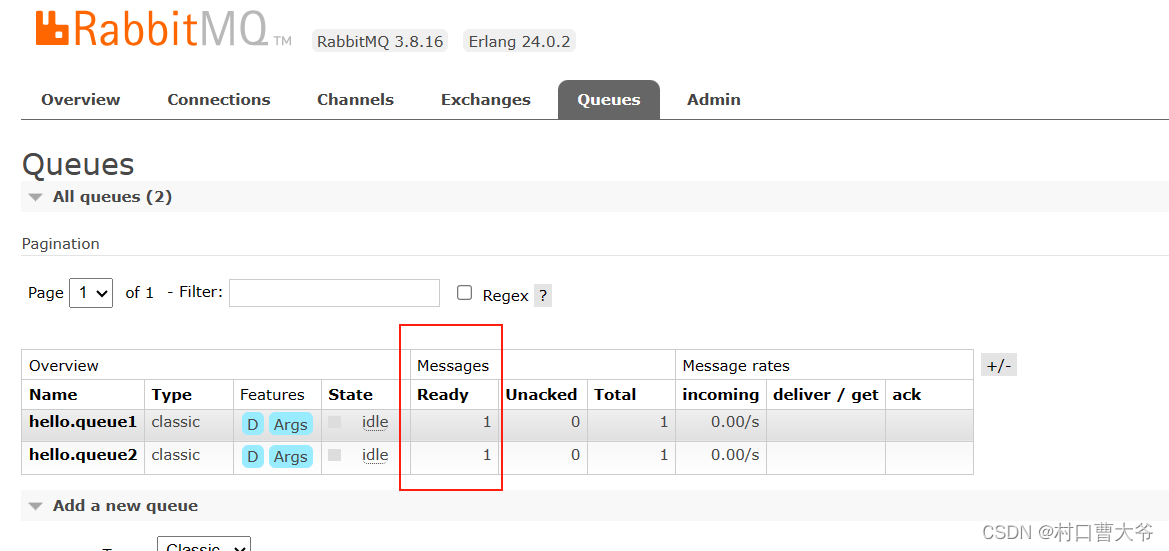
这时,再在交换机中发消息
查看结果:
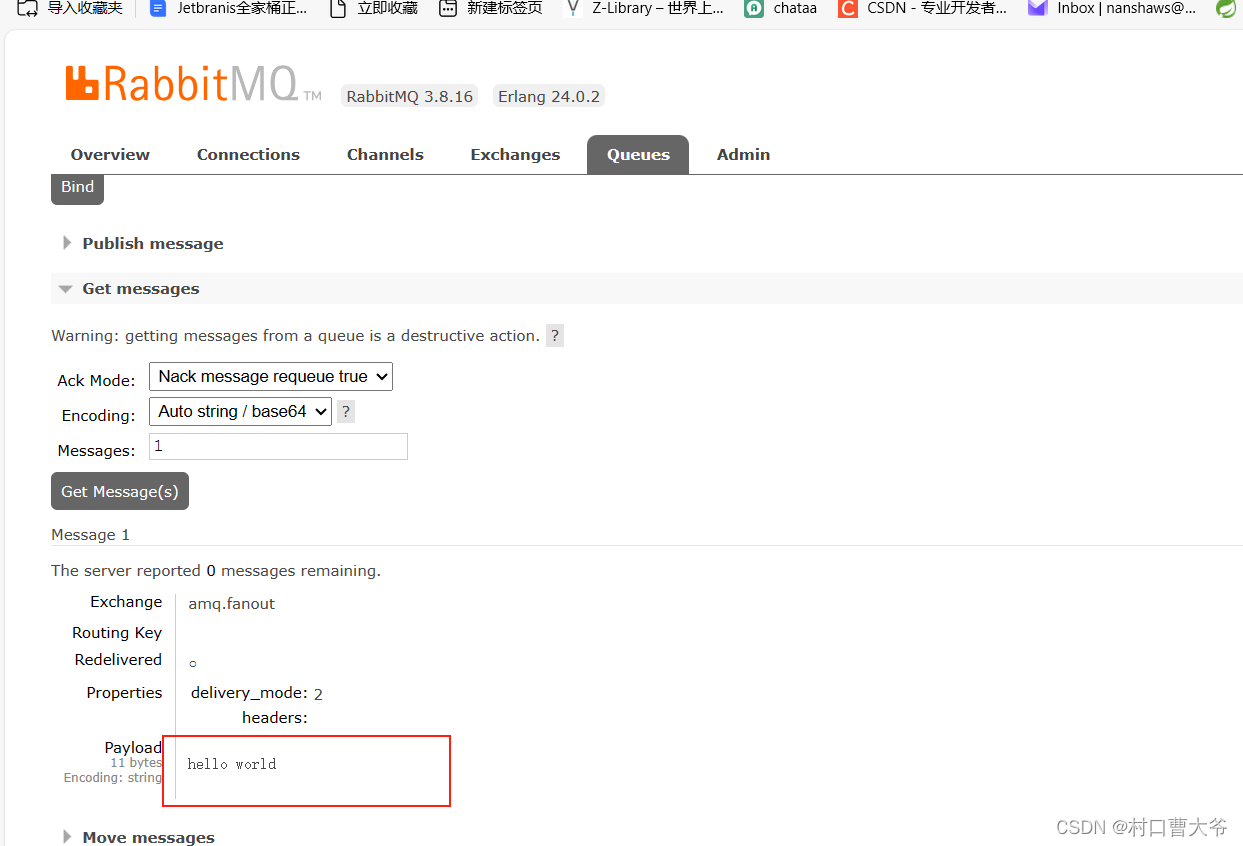
数据隔离
在rabbitmq中有虚拟主机的概念。

第一步:新添用户
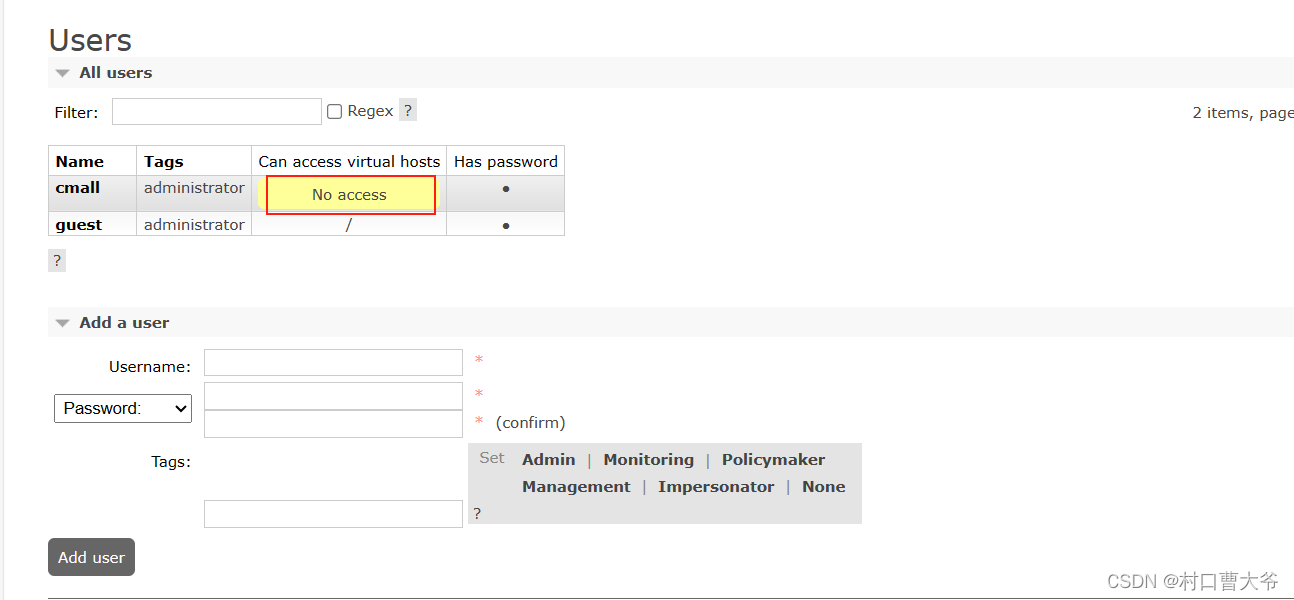
添加成功后,发现没有虚拟主机,也就是说,我用这个用户登录后,是不可以操作上面的数据的。
又因为,我是超级管理员,所以我能看到这些

所以只能看,不能操作。
第二步:创立自己的虚拟主机
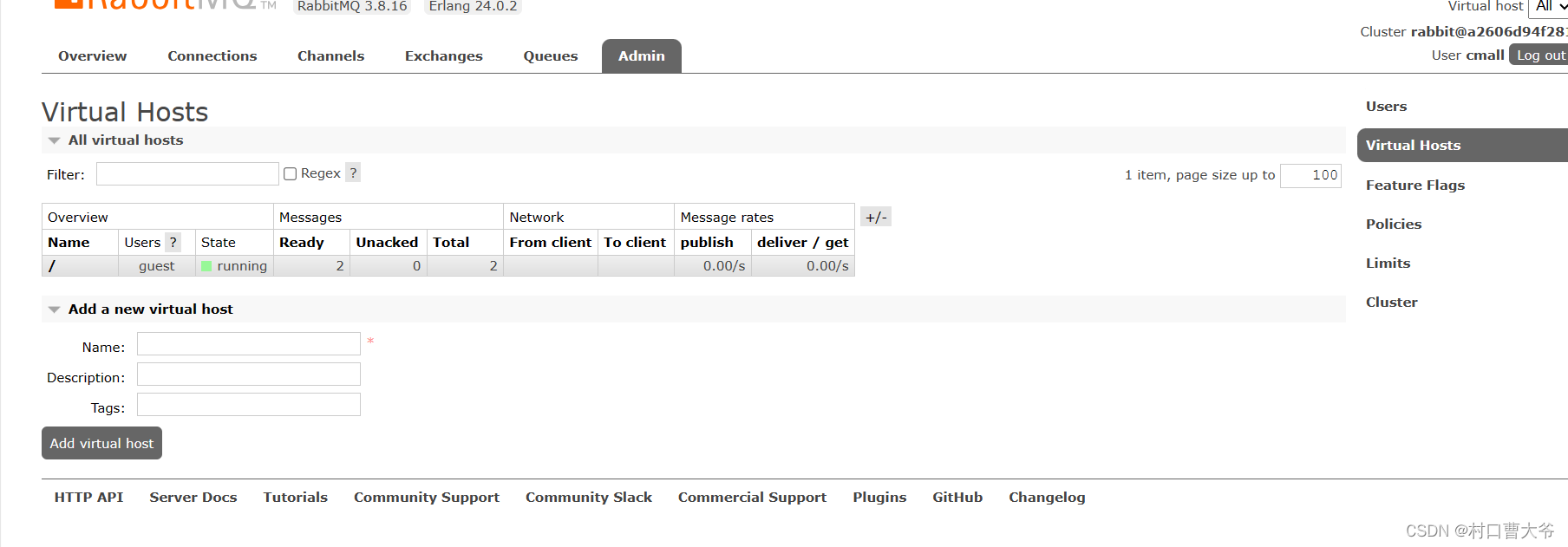

第三步:选自己的虚拟主机

选好后就只能看自己的了。
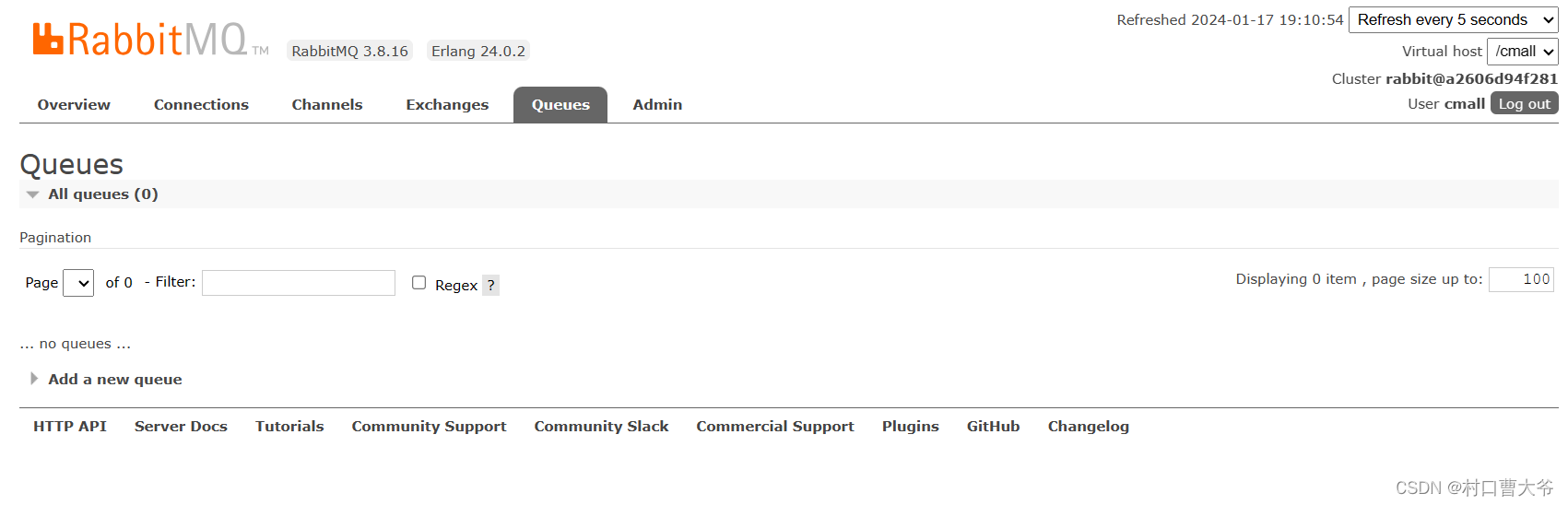
用Java代码操作
官网:RabbitMQ Tutorials — RabbitMQ
可以看到,官网上有案例,我们大多情况下用的是SpringAmqp,所以也就不讲那么多java简单调用的事情了。
用Spring AMQP操作


第一步:在控制台里面创建一个simple.queue队列

第二步:编写代码
pom文件
4.0.0 org.cyl test090.0.1-SNAPSHOT test09 test09 1.8 UTF-8 UTF-8 2.6.13 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-weborg.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-testtest org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-amqpcom.rabbitmq amqp-client5.13.0 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-dependencies${spring-boot.version} pom import org.apache.maven.plugins maven-compiler-plugin3.8.1 1.8 1.8 UTF-8 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-maven-plugin${spring-boot.version} org.cyl.test09.Test09Application true repackage repackage
配置mq服务端消息
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.56.10
port: 5672
virtual-host: /cmall
username: cmall
password: 123456
发送方:
package org.cyl.test09.demos;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SendMessageService {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
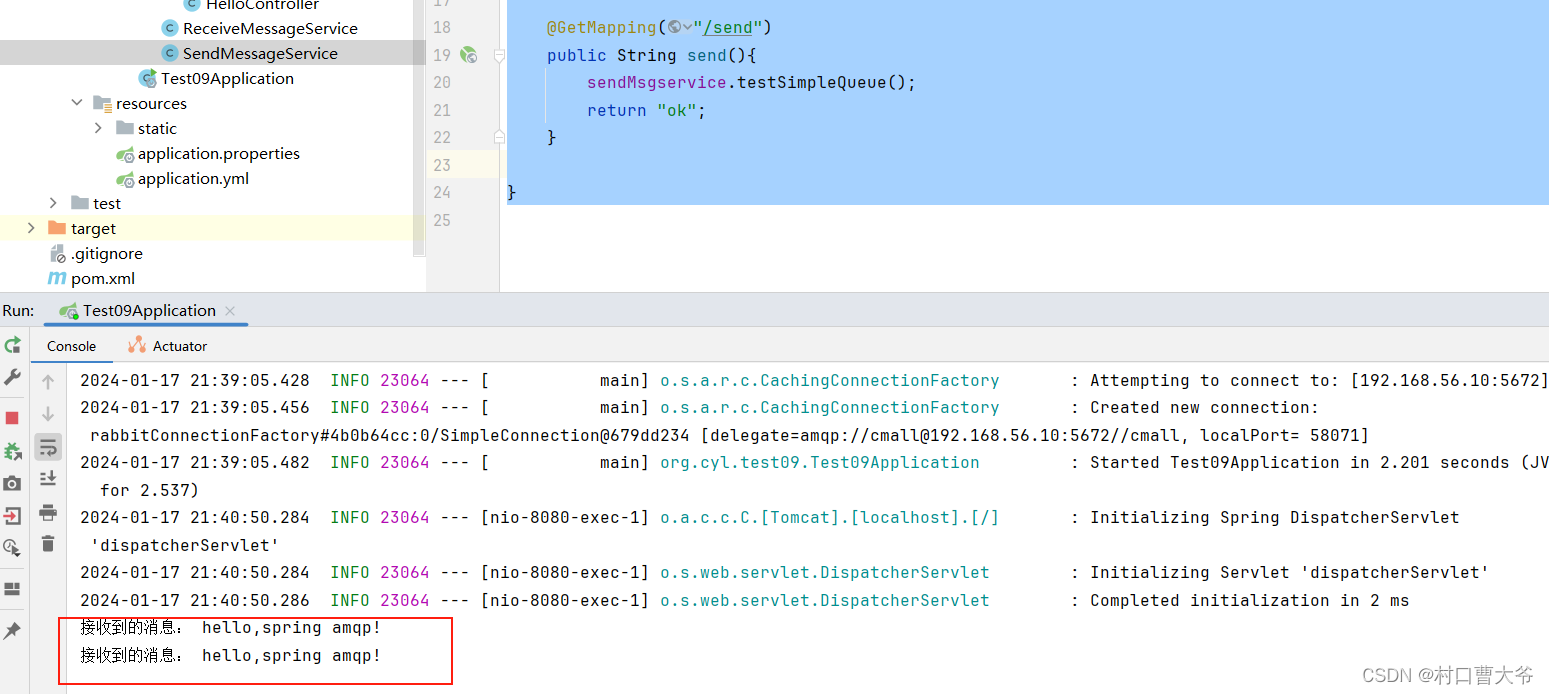
public void testSimpleQueue(){
String queueName="simple.queue";
String message="hello,spring amqp!";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName,message);
}
public void sendMessage(String exchange, String routingKey, Object message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, message);
}
}
接收方:
package org.cyl.test09.demos;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ReceiveMessageService {
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void receiveMessage(String message) {
System.out.println("接收到的消息: " + message);
}
}
controller类:
package org.cyl.test09.demos.controller;
import org.cyl.test09.demos.ReceiveMessageService;
import org.cyl.test09.demos.SendMessageService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
SendMessageService sendMsgservice;
@Autowired
ReceiveMessageService receiveMsgService;
@GetMapping("/send")
public String send(){
sendMsgservice.testSimpleQueue();
return "ok";
}
}
展示结果:
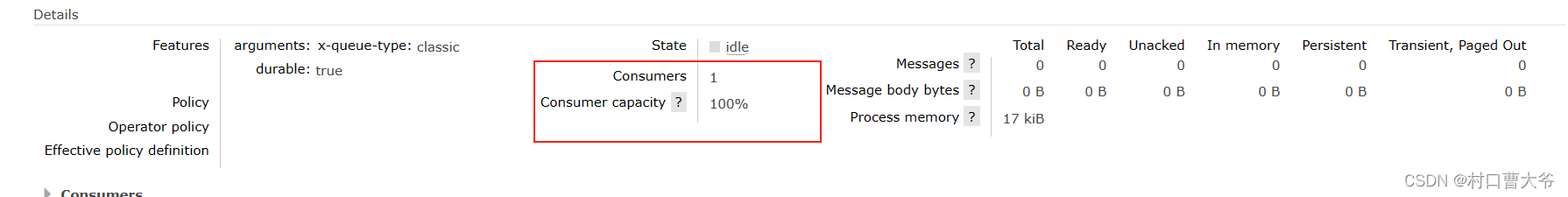
Work模型


第一步:创建一个队列

第二步:编写代码
发送:
package org.cyl.test09.demos;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SendMessageService {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void testSimpleQueue() throws InterruptedException {
String queueName="work.queue";
for (int i=1;i<50;i++){
String message="hello,spring amqp!_"+i;
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName,message);
Thread.sleep(20);
}
}
public void sendMessage(String exchange, String routingKey, Object message) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, message);
}
}
接收:
package org.cyl.test09.demos;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ReceiveMessageService {
@RabbitListener(queues = "work.queue")
public void receiveMessage1(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到的消息: " + message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "work.queue")
public void receiveMessage2(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到的消息: " + message);
}
}
结果展示:
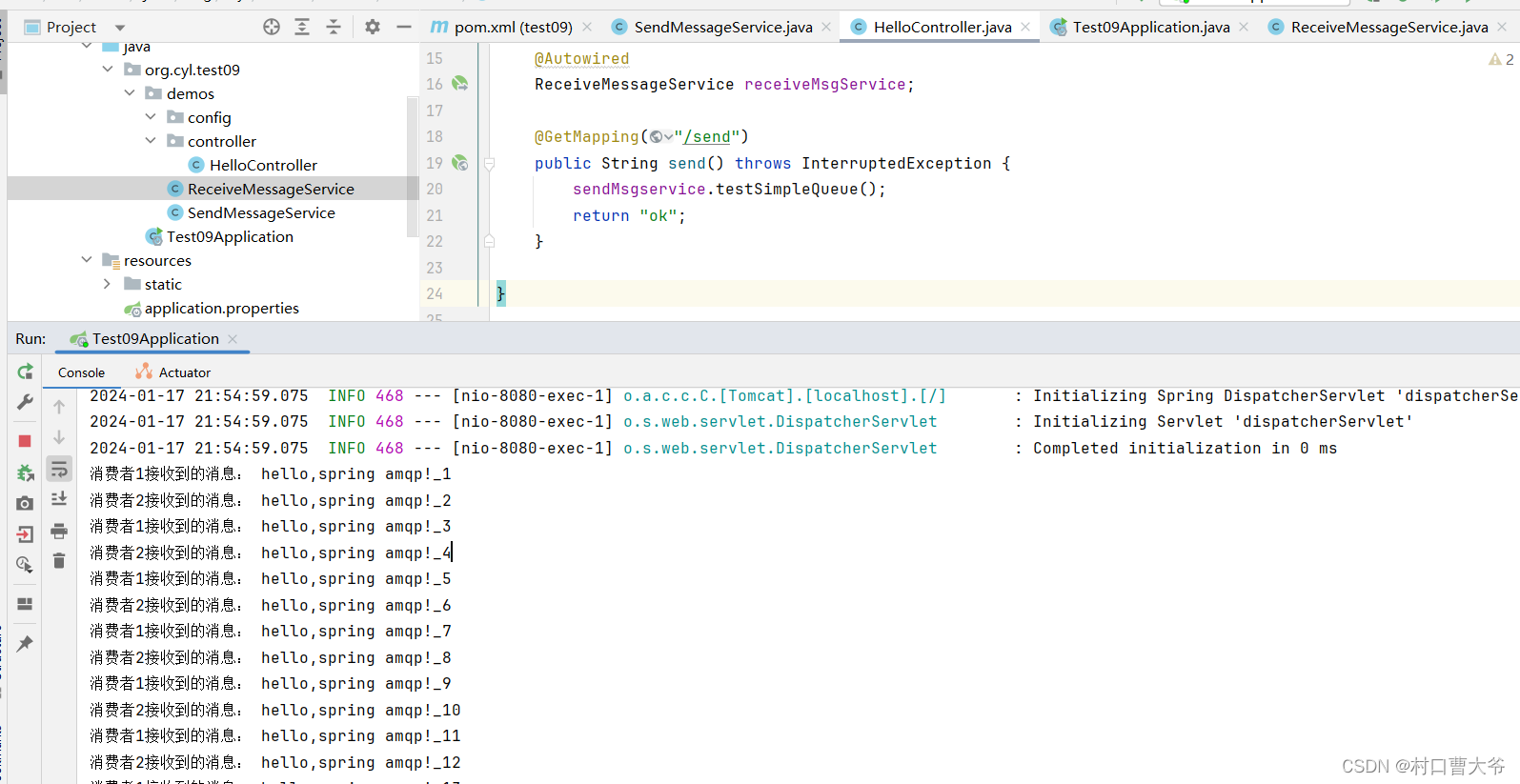
消费者一和消费者二是轮询效果。
Fanout交换机
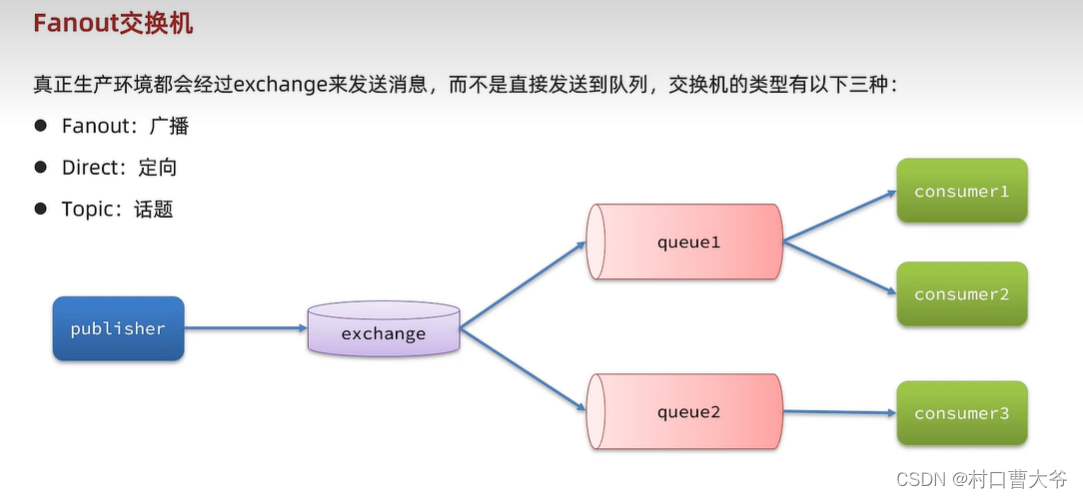
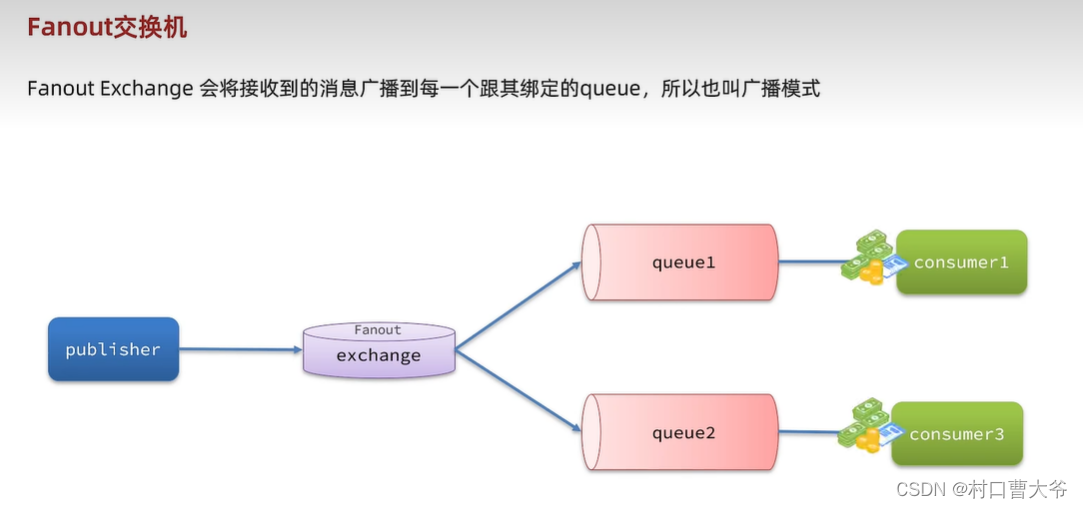

第一步:创建队列

第二步:创建交换机并绑定
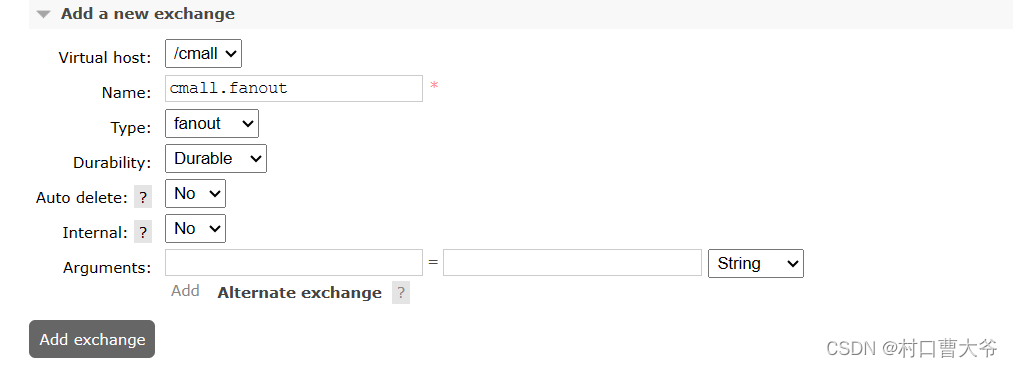
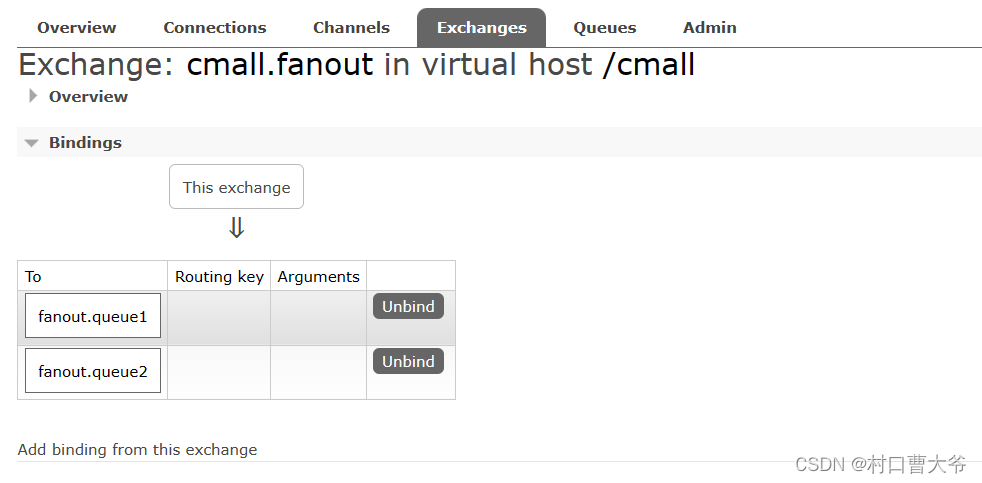
第三步:编写代码
发送端:
public void testFanout() {
String exchangeName="cmall.fanout";
String message="hello,spring everyone";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,null,message);
}
接收端:
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
public void receiveMessage3(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到的消息: " + message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void receiveMessage4(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到的消息: " + message);
}
展示结果:

私发给不同的人:Direct交换机
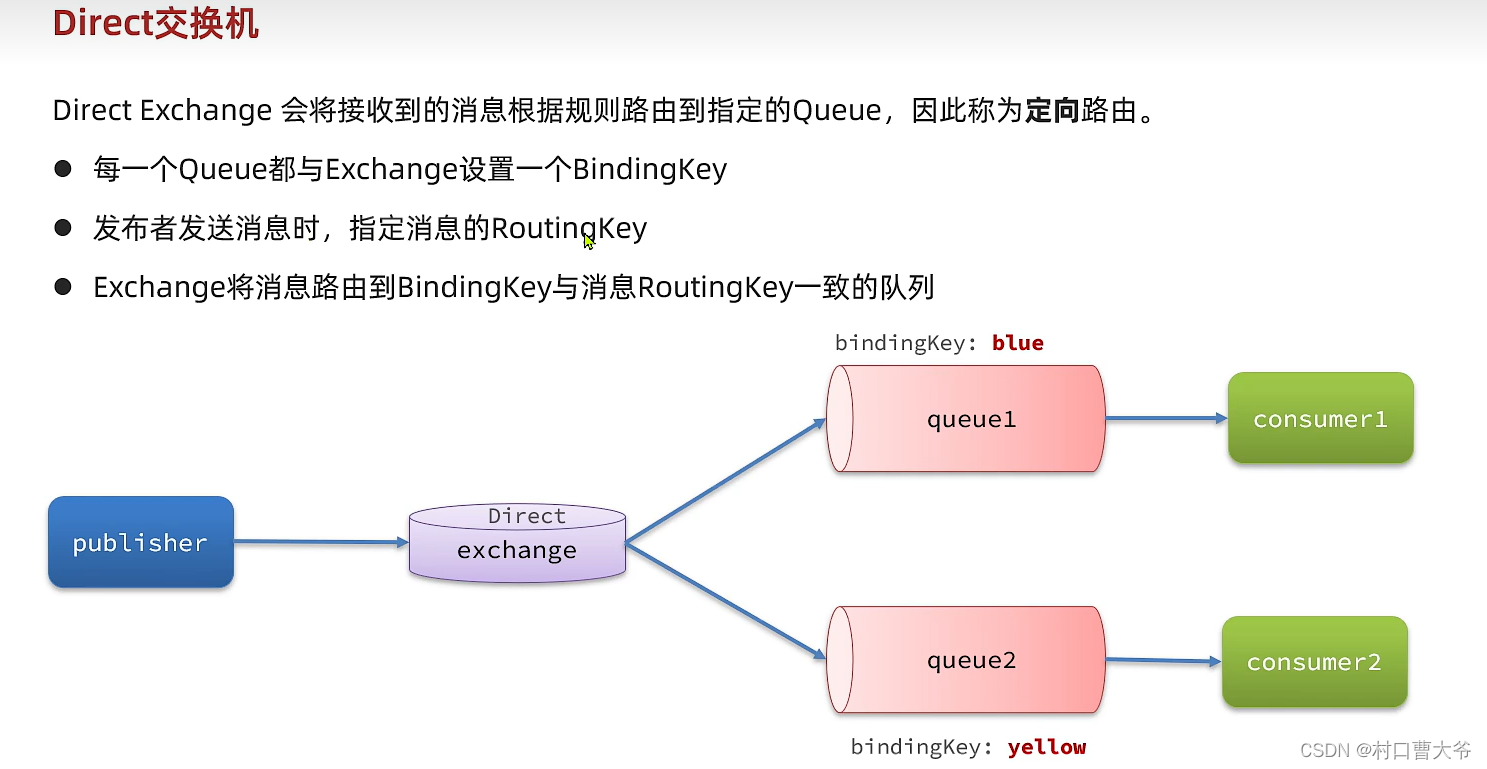
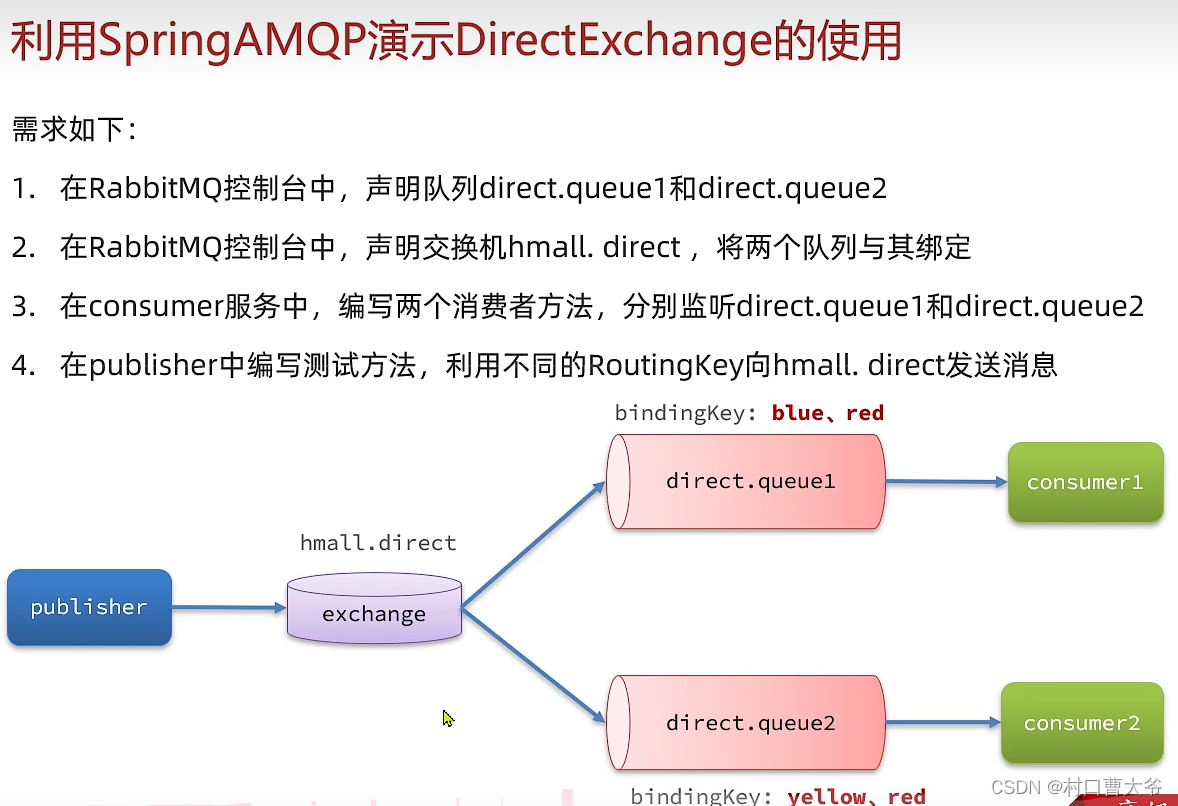
第一步:创建两个队列

第二步:声明交换机并绑定


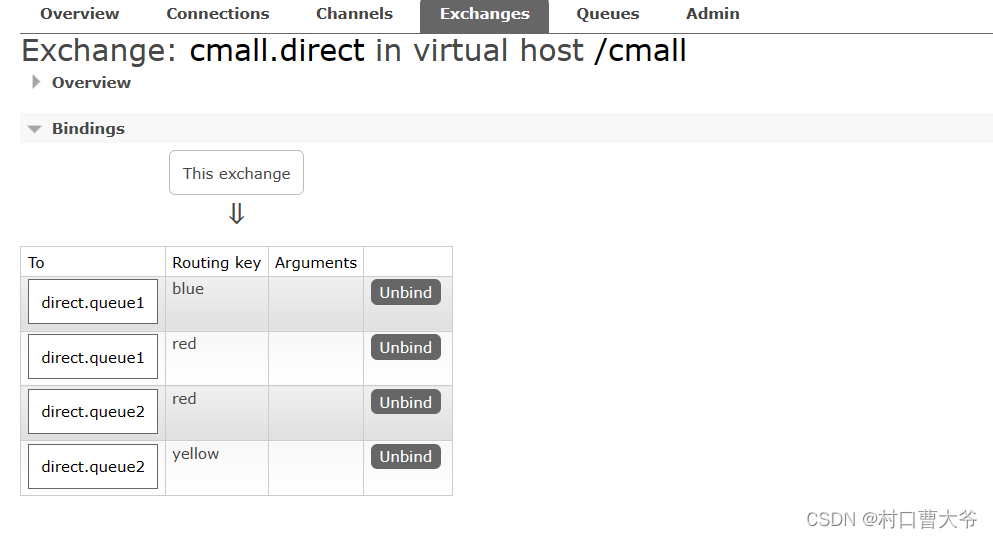
第三步:编写代码
接收方:
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue1")
public void receiveMessage5(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到的消息: " + message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue2")
public void receiveMessage6(String message) {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到的消息: " + message);
}
发送方:
public void testDirect1() {
String exchangeName="cmall.fanout";
String message="hello,spring everyone";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"red",message);
}
public void testDirect2() {
String exchangeName="cmall.fanout";
String message="hello,spring blue";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"blue",message);
}
public void testDirect3() {
String exchangeName="cmall.fanout";
String message="hello,spring yellow";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"yellow",message);
}
Topic交换机
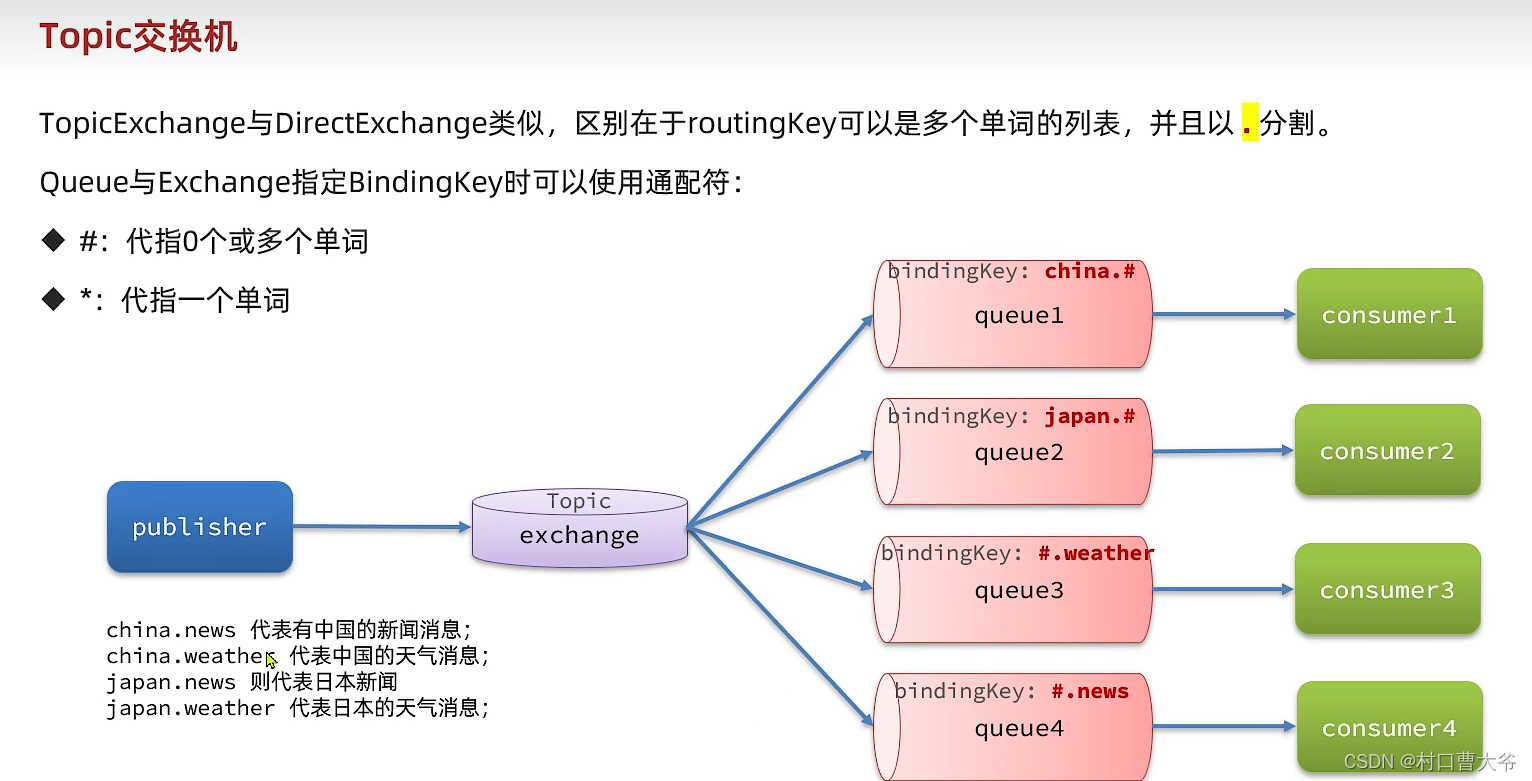

这个示例代码就懒得写了。
声明交换机和队列1

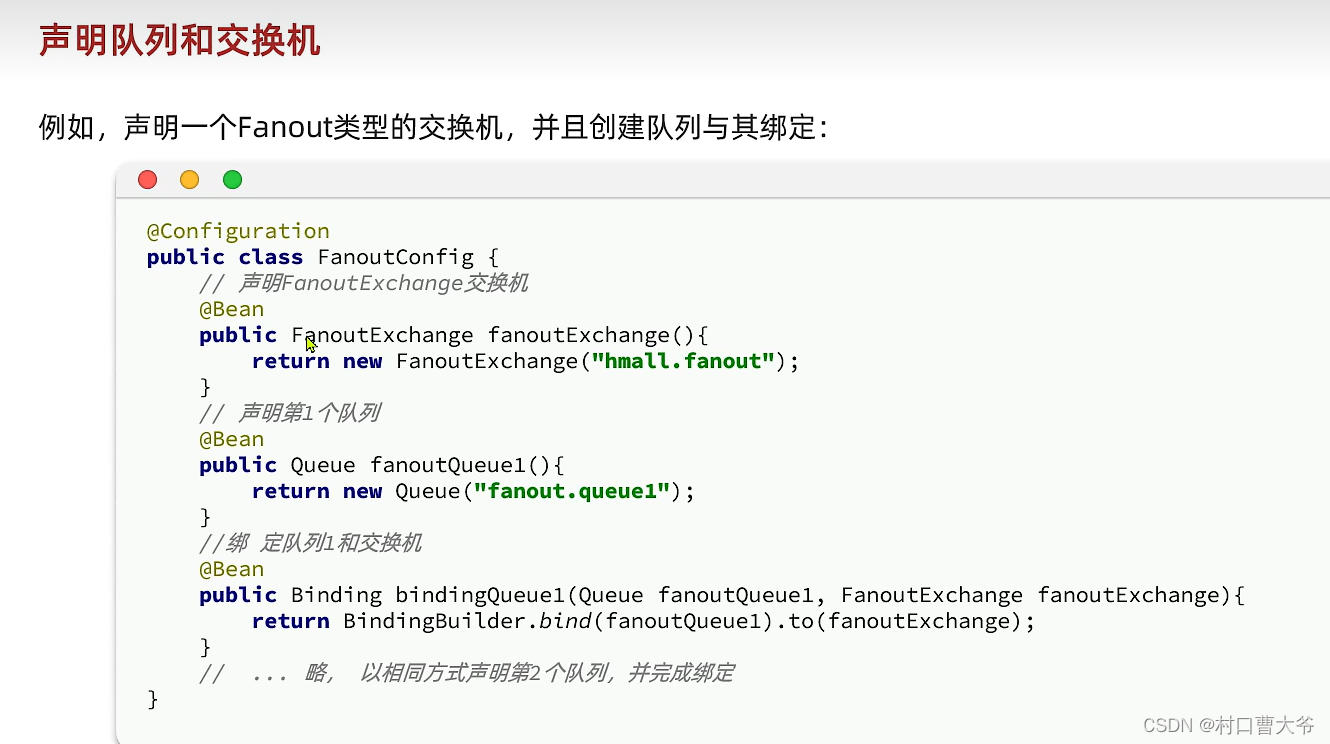
绑定队列到哪个交换机里面。
一般建立关系都是在消费者这边的。
声明交换机和队列2

基于注解式声明队列和交换机。
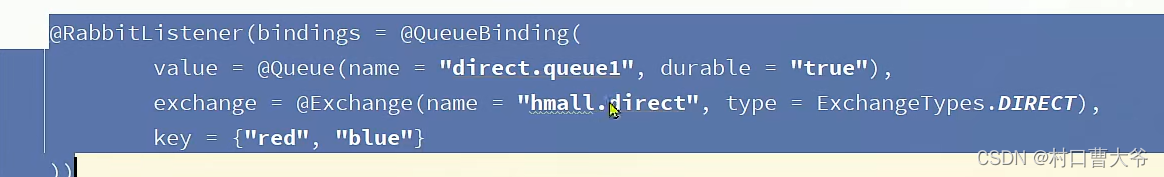
消息转换器

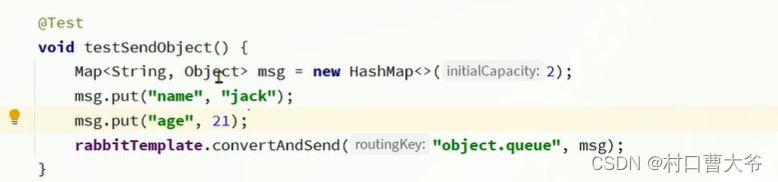
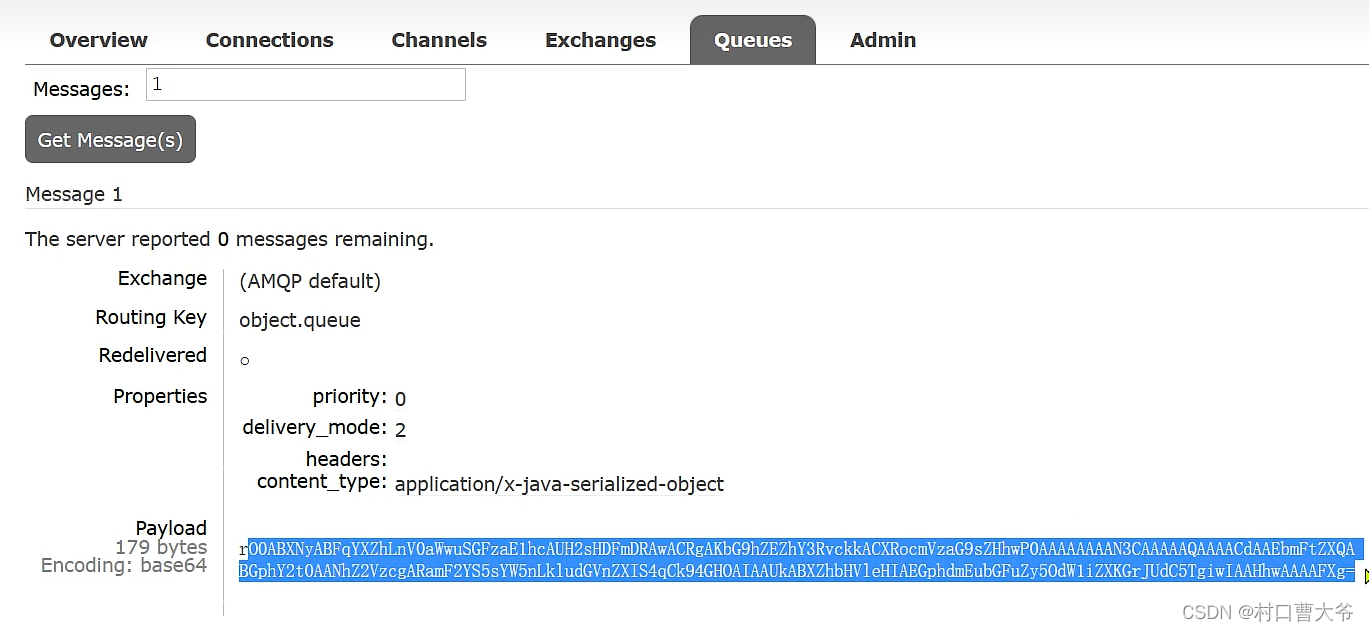
字节码可变,会有安全问题。

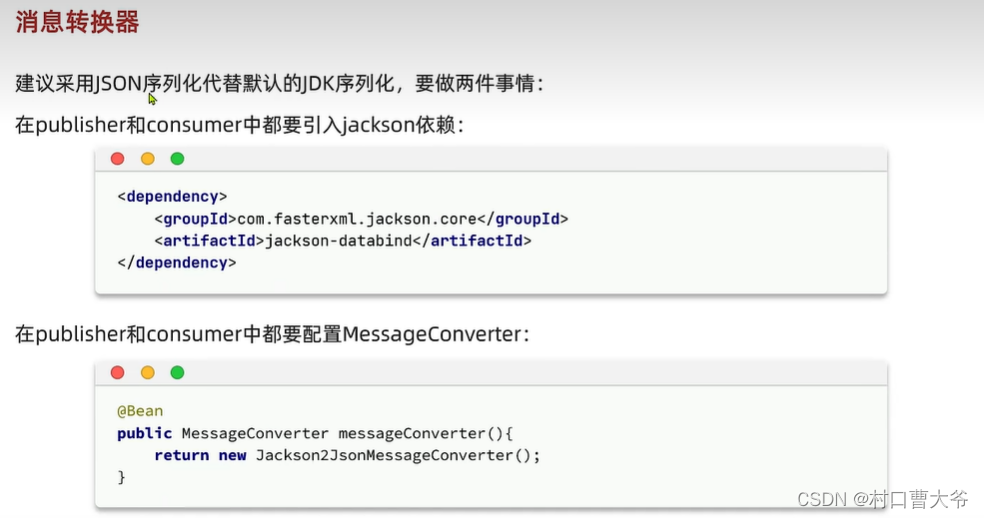
搞完以上东西,代码不用变,在发一次,即可为json。
好了,基础讲完。














