- 基于大模型的Text2SQL微调的实战教程(二)
- 【spring】 ApplicationListener的使用及原理简
- 【MyBatis Plus】初识 MyBatis Plus,在 Spr
- 【Docker】Docker比虚拟机快的原因、ubuntu容器、镜像的
- 如何使用phpStudy快速搭建一个网站
- 网络爬虫之爬虫原理
- 【数据库】数据库的介绍、分类、作用和特点,AI人工智能数据如何存储
- 【神经网络模型】——AI大模型学习
- 详解:-bash: mysql command not found (
- 推荐系统算法 协同过滤算法详解(三)Springboot 实现基于用户
- 若依(前后端分离版)部署全流程 | 宝塔部署SpringBoot项目踩
- SQL LIKE 运算符:用法、示例和通配符解释
- Scala 02——Scala OOP
- Spring Boot集成百度UidGenerator雪花算法使用以及
- SpringBoot3整合Redis&基础操作
- Mybatis之批量更新数据
- SQL笔记 -- 黑马程序员
- SpringBoot+Vue入门并实现前后端分离和数据库查询(入门笔记
- MySQL 中内连接、左连接、右连接有什么区别?
- SpringBoot-打印请求的入参和出参
- AI大模型探索之路-实战篇2:基于CVP架构-企业级知识库实战落地
- Vue实例挂载的过程
- 【docker】docker-compose部署mysql
- Mysql判断一个表中的数据是否在另一个表存在
- 什么是网络爬虫?认识网络爬虫
- 关于AI与资本市场的一些思考
- 输了,腾讯golang一面凉了
- SpringBoot使用OpenCV
- 【CSDN活动】人工智能:前沿科技中的创业机遇与挑战
- 链表基础知识详解(非常详细简单易懂)
Part2
- 一、Nginx配置文件
- 1.1 主配置文件详解
- 1.2 子配置文件
- 二、全局配置部分
- 2.1 修改启动的工作进程数(worker process) 优化
- 2.2 cpu与worker process绑定(优化三)
- 2.3 PID 路径修改 优化
- 2.4 修改工作进程的优先级 优化
- 2.7 调试工作进程打开的文件的个数
- 2.7.1 基本原理
- 2.7.2 配置过程
- 2.7.3 测试是否配置成功
- 2.8 关闭master-worker工作模式(仅测试用)
- 三、events部分
- 四、http设置 (http部分)
- 4.1 http部分详解
- 4.2 mime
- 4.3 server 下的 root指令
- 4.4 构建虚拟主机
- 4.4.1 基于域名的虚拟主机
- 4.4.2 基于端口
- 4.4.3 基于IP地址
- 4.5 路径别名-----alias
- 4.6 location模块
- 4.7 基于四层的访问控制-----access模块
- 4.8 验证模块
- 4.8.1 htpasswd命令
- 4.8.2 配置验证模块
- 4.9 关闭或修改版本信息
- 4.9.1 关闭版本信息显示
- 4.9.2 修改nginx 版本信息 优化
- 4.10 自定义 错误页面
- 4.11 修改日志的位置
- 4.12 检测文件是否存在-----try_files指令
- 4.12.1 原理部分
- 4.12.2 配置实例
- 4.13 长连接相关-----keepalive指令
- 4.13.1 原理
- 4.13.2 keepalive_timeout
- 4.13.3 keepalive_requests
- 4.14 用户上传资料
- 4.15 其他设置
一、Nginx配置文件
1.1 主配置文件详解
主配置文件:nginx.conf

#主配置文件格式 main block:主配置段,即全局配置段,对http,mail都有效 #配置Nginx服务器的事件模块相关参数 events { ... } #http/https 协议相关配置段 http { ... } #默认配置文件不包括下面两个模块 #mail 协议相关配置段 mail { ... } #stream 服务器相关配置段 stream {负载均衡 ... }
#以yum安装nginx后,nginx.conf为例 vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf

1.2 子配置文件
子配置文件: include conf.d/*.conf
子配置文件一般在主配置文件的http部分。
http块中可以包含多个子配置文件,常见的子配置文件
server块:用于配置HTTP服务器的具体行为,包括监听的端口、虚拟主机的配置、请求处理逻辑等。
location块:用于指定不同URL请求的处理方式,例如静态文件的服务、反向代理等。
upstream块:用于配置反向代理的目标服务器列表。
include指令:用于引入其他的子配置文件,可以将一些通用的配置项单独放在一个文件中,然后通过include指令引入。
二、全局配置部分
2.1 修改启动的工作进程数(worker process) 优化
通过使用 auto 参数,Nginx 可以根据系统的负载情况智能地分配工作进程,以提供更好的性能和资源利用率。
修改主配置文件中的 work_processes项
cd /apps/nginx/conf/ vim nginx.conf

nginx -s reload #重载
ps axo pid,cmd,psr,ni|grep nginx #查看工作进程的数量

2.2 cpu与worker process绑定(优化三)
在 Nginx 配置文件中,worker_cpu_affinity 指令用于控制 worker 进程与 CPU 的亲和性(affinity)关系
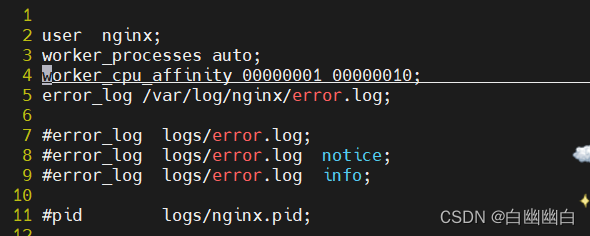
vim nginx.conf user nginx; worker_processes auto; worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010; #绑定到 第一 和 第二块cpu上 error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; #指定错误日志的路径和文件名
nginx -t #语法检查

ps axo pid,cmd,psr,ni|grep -v grep |grep nginx|sort -n
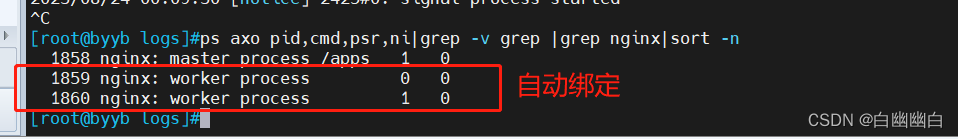
#补充说明# worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010; 这意味着每个 worker 进程将绑定到对应的 CPU 核心上,编号为 1 和 2。通过这种方式,可以手动调整 worker 进程与 CPU 核心之间的关系,以便更好地利用硬件资源
2.3 PID 路径修改 优化
修改主配置文件 vim nginx.conf

2.4 修改工作进程的优先级 优化
工作进程优先级,-20~20(19)
修改主配置文件 vim nginx.conf user nginx; worker_processes auto; worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010; error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; #添加优先级 worker_priority -20;

nginx -t nginx -s reload #语法无误后 重载
ps axo pid,cmd,psr,ni|grep nginx|sort -n #查看工作进程的优先级

2.7 调试工作进程打开的文件的个数
2.7.1 基本原理
所有worker进程能打开的文件数量上限,包括:Nginx的所有连接(例如与代理服务器的连接等),而不仅仅是与客户端的连接,另一个考虑因素是实际的并发连接数不能超过系统级别的最大打开文件数的限制.最好与ulimit -n 或者limits.conf的值保持一致,
2.7.2 配置过程
先修改主配置文件
vim nginx.conf 添加 worker_rlimit_nofile 65536

再修改系统默认项
方式一:临时修改
ulimit -n 70000 #修改单个进程能打开的最大文件数为 70000 #仅应用于当前会话即不会永久修改限制 ulimit -a #显示当前用户的所有资源限制信息

方式二:永久修改,修改pam认证模块
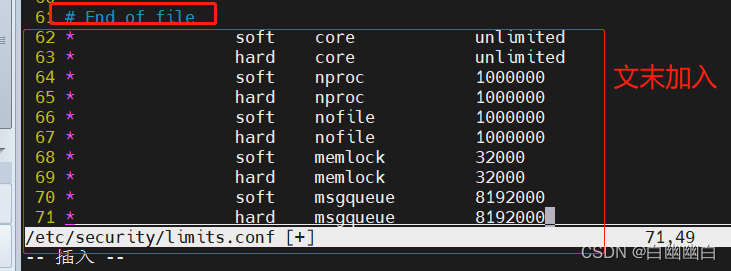
vim /etc/security/limits.conf #在最后加入 * soft core unlimited * hard core unlimited * soft nproc 1000000 * hard nproc 1000000 * soft nofile 1000000 * hard nofile 1000000 * soft memlock 32000 * hard memlock 32000 * soft msgqueue 8192000 * hard msgqueue 8192000 `nproc`(最大进程数限制)的软限制和硬限制都设置为 1000000,当前用户在单个会话中可以创建的最大进程数为 1000000 `nofile`(打开文件描述符限制)的软限制和硬限制都设置为 1000000,这意味着当前用户在单个会话中可以使用的最大文件描述符数将被限制为 1000000。软限制是软性限制,用户可以根据需要进行调整,而硬限制是硬性限制,一旦设定,用户无法超过该限制 `memlock`(锁定内存限制)的软限制和硬限制都设置为 32000,这意味着当前用户在单个会话中可以锁定的最大内存量为 32000KB `msgqueue`(消息队列限制)的软限制和硬限制都设置为 8192000,这意味着当前用户在单个会话中可以使用的最大消息队列大小为 8192000字节
reboot #重启生效
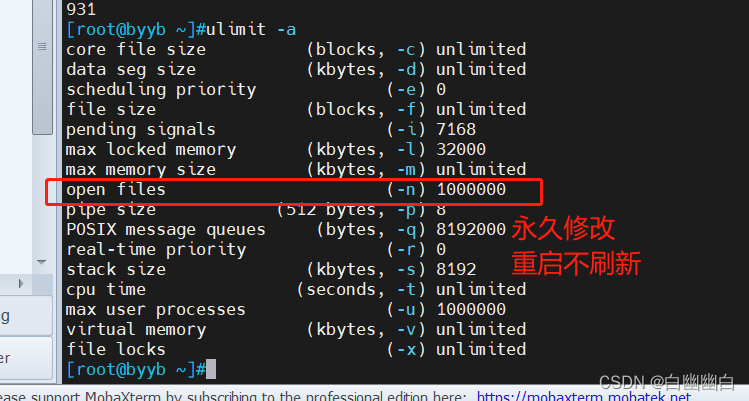
2.7.3 测试是否配置成功
#新建测试文件 dd if=/dev/zero of=big.img bs=100M count=1 yum install httpd-tools -y#安装压力测试的工具 #压力测试脚本 while : ;do ab -c 1000 -n 10000 http://192.168.2.100/big.img;sleep 1;done
没有修改时
ulimit -a

systemctl start nginx #开启服务 压力测试,观察反馈界面 while : ;do ab -c 10000 -n 10000 http://192.168.2.102/big.img;sleep 1;done #并发10000个请求,由于默认1024,观察失败的请求数

修改后
ulimit -a systemctl start nginx #开启服务

切换到另一台主机 ulimit -n 20000 压力测试,观察反馈界面 ab -c 10000 -n 10000 http://192.168.2.100/big.img #并发10000个请求,由于默认1024,观察失败的请求数

2.8 关闭master-worker工作模式(仅测试用)
master_process off|on; #是否开启Nginx的master-worker工作模式,仅用于开发调试场景,默认为on
三、events部分
在Nginx的主配置文件中,events部分用于配置Nginx服务器的事件模块相关参数,控制Nginx服务器在处理连接请求时的行为。
常见的events配置参数:
-
worker_connections:指定每个工作进程可以同时处理的最大连接数。
-
multi_accept:指定是否一次接受多个连接。默认情况下,Nginx在每个循环中只接受一个连接,但设置multi_accept为"on"后可以同时接受多个连接。
-
use:指定Nginx使用的事件模块。常见的事件模块有"epoll"、"kqueue"和"eventport"等。
#举个例子 events { worker_connections 1024; multi_accept on; use epoll; } #指定了每个工作进程可以处理的最大连接数为1024,启用了多个连接同时接受,以及使用了epoll事件模块四、http设置 (http部分)
4.1 http部分详解
include:引入其他配置文件,通常用于加载 MIME 类型配置文件。
default_type:指定默认的 MIME 类型。
server:定义一个或多个虚拟主机。
listen:指定该虚拟主机监听的端口。
server_name:指定域名,用于匹配请求的主机头。
root:指定虚拟主机的根目录。
location:用于匹配不同的 URL,并定义相关配置规则。
#基本格式 http { ... ... #各server的公共配置 server { #每个server用于定义一个虚拟主机,第一个server为默认虚拟服务器 ... } server { ... server_name #虚拟主机名 root #主目录 alias #路径别名 location [OPERATOR] URL { #指定URL的特性 ... if CONDITION { ... } } } }#详解 http { include mime.types; #导入支持的文件类型,是相对于/apps/nginx/conf的目录 default_type application/octet-stream; #除mime.types中文件类型外,设置其它文件默认类型,访问其它类型时会提示下载不匹配的类型文件 #日志配置部分 #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' refer是跳转的源地址,如果没有跳转 没有refer # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; #自定义优化参数 sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #在开启了sendfile的情况下,合并请求后统一发送给客户端。 #tcp_nodelay off; #在开启了keepalived模式下的连接是否启用TCP_NODELAY选项,当为off时,延迟0.2s发送,默认On时,不延迟发送,立即发送用户响应报文。 #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65 65; #设置会话保持时间,第二个值为响应首部:keepAlived:timeout=65,可以和第一个值不同 #gzip on; #开启文件压缩 server { listen 80; #设置监听地址和端口 server_name localhost; #设置server name,可以以空格隔开写多个并支持正则表达式,如:*.kgc.com www.kgc.* ~^www\d+\.kgc\.com$ default_server #charset koi8-r; #设置编码格式,默认是俄语格式,建议改为utf-8 #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; #定义错误页面 location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ \.php$ { #以http的方式转发php请求到指定web服务器 # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ \.php$ { #以fastcgi的方式转发php请求到php处理 # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /\.ht { #拒绝web形式访问指定文件,如很多的网站都是通过.htaccess文件 来改变自己的重定向等功能。 # deny all; #} location ~ /passwd.html { deny all; } } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { #自定义虚拟server4.2 mime
在Nginx中,“mime” 是一种配置指令,用于设置 MIME 类型与文件扩展名的映射关系。
vim /etc/nginx/mime.types #查看当前Nginx服务器配置的MIME类型列表
4.3 server 下的 root指令
在Nginx配置中,"root"指令用于设置服务器块(server block)的根目录,即指明软件的根目录。
通常,"root"指令位于Nginx配置文件中的服务器块(server block)中。
server { listen 80; server_name example.com; root /var/www/html; location / { ... } ... } #指定了服务器块的根目录为"/var/www/html" #访问该服务器的网站时,Nginx会在"/var/www/html"文件夹中查找并提供相应的静态文件4.4 构建虚拟主机
4.4.1 基于域名的虚拟主机
以手机端和电脑端为例
mkdir -p /apps/nginx/conf.d/#建立虚拟主机配置文件目录 cd /apps/nginx/conf #主配置文件所在目录 #添加到http模块中 vim nginx.conf include /apps/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; #声明子配置文件的位置,需要写在最上面 nginx -t #保存后检查语法

cd /apps/nginx/conf.d/ #编写电脑端的配置文件 vim computer.conf server{ listen 192.168.2.100:80; server_name www.computer.com; location / { root /data/nginx/html/pc; } } #编写手机端的配置文件 vim mobile.conf server { listen 192.168.2.100:80; server_name www.mobile.com; root /data/nginx/html/mobile/; }#构建数据文件夹 mkdir /data/nginx/html/pc -pv mkdir /data/nginx/html/mobile -pv

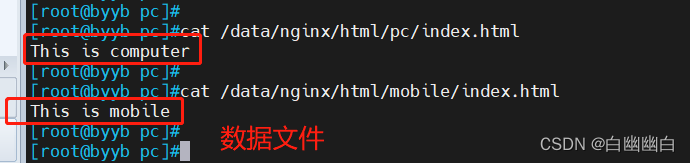
#构建数据文件 echo This is computer > /data/nginx/html/pc/index.html echo This is mobile > /data/nginx/html/mobile/index.html
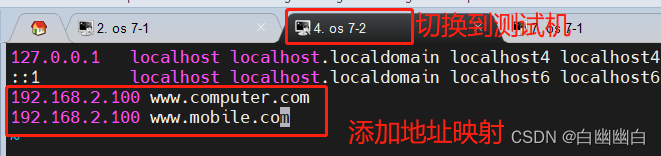
#切换到测试机 #修改本地hosts文件 添加对应映射 vim /etc/hosts 192.168.2.100 www.computer.com 192.168.2.100 www.mobile.com
#测试 curl www.computer.com curl www.mobile.com

4.4.2 基于端口
服务端 #编辑子配置文件 mobile.conf,修改端口号 server{ listen 192.168.2.100:8080; server_name www.mobile.com; root /data/nginx/html/moblie; } #computer.conf 不变 server{ listen 192.168.2.100:80; server_name www.computer.com; root /data/nginx/html/pc; }
切换到客户端 curl 192.168.2.100:8080 curl 192.168.2.100:80

4.4.3 基于IP地址
服务端 添加新网卡并配置
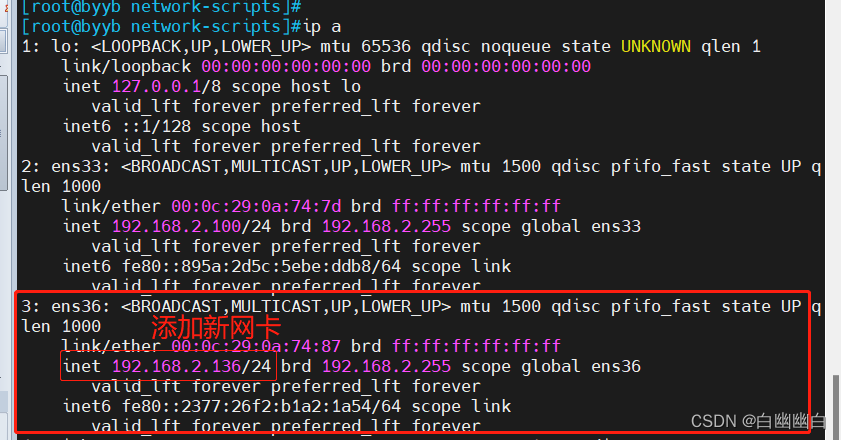
#编辑子配置文件mobile.conf,修改IP地址 cd /apps/nginx/conf.d/ vim mobile.conf server{ listen 192.168.2.136:80; server_name www.mobile.com; root /data/nginx/html/mobile; } #computer.conf不变 server{ listen 192.168.2.100:80; server_name www.computer.com; root /data/nginx/html/pc; }
客户端 vim /etc/hosts

#测试 curl 192.168.2.136 curl 192.168.2.100

4.5 路径别名-----alias
在 Nginx 中,alias 用于创建一个路径别名的指令。
别名可以用于将文件或目录从一个位置映射到另一个位置,提供更灵活的访问控制。
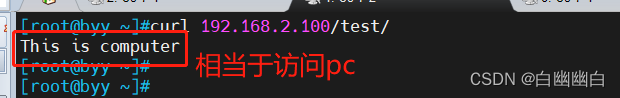
服务端 #编辑子配置文件mobile.conf,使用alias server { listen 80; server_name www.computer.com; location /test{ alias /data/nginx/html/pc; #相当于替换,访问/test/就是访问/data/nginx/html/pc; } }
客户端 curl 192.168.2.100/test/ #访问test目录
4.6 location模块
在Nginx中,location 是一个用于匹配请求 URL 路径的指令。它在 Nginx 配置文件中使用,在不同的 location 块中定义不同的行为或处理规则。
#官方帮助文档 http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#location
#基本语法 location [修饰符] 匹配的路径 { ... 配置指令 ... } ```修饰符 功能 = 精确字符串匹配 ^~ 前缀匹配,如果URL路径以指定的字符串开始,则停止查找其他匹配。 ~ 使用正则表达式进行匹配,区分大小写 ~* 使用正则表达式进行匹配,不区分大小写 不带符号 匹配起始于此uri的所有的uri \ 表示包含正则表达式并且转义字符 优先级(从高到低):=, ^~, /*, 不带符号
#举个例子 1 location { ... 处理根路径的配置 ... } location /static { ... 处理 /static 路径的配置 ... } location ~ \.(png|jpg)$ { ... 处理以 .png 或 .jpg 结尾的请求的配置 ... } location = /favicon.ico { ... 处理 favicon.ico 请求的配置 ... } ```#举个例子 2 location = / { [ configuration A ] } location / { [ configuration B ] } location /documents/ { [ configuration C ] } location ^~ /images/ { [ configuration D ] } location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ { [ configuration E ] } 访问路径是 / # A B 能匹配,A优先级高 ,A 访问路径是 /index.html #只有B 访问路径是 /documents/document.html #B C能匹配 C精确度高 所以C 访问路径是 /images/1.gif # B D E 能匹配,D的优先级高,D 访问路径是 /documents/1.jpg # B C E 能匹配, E#做个题目 如下请求内容,会匹配哪个 Location? http://www.example.com/gallery/images/cat.png A.Location /gallery {} B.Location ~* ^/.(png|jpg)${} C.Location ^~ /gallery/images {} D.Location / {} 我选C4.7 基于四层的访问控制-----access模块
Nginx的access模块允许用户定义基于IP地址、请求方法、URI等条件的访问规则,以控制客户端对NGINX服务器上特定资源的访问。
1)IP地址访问控制:允许或拒绝特定IP地址或IP地址范围的访问。
拒绝特定IP地址的访问 location / { deny 192.168.2.102; }允许特定IP地址段的访问 location / { allow 192.168.2.0/24; deny all; }2)请求方法访问控制:允许或拒绝特定HTTP请求方法(如GET、POST等)的访问。
仅允许GET请求 if ($request_method != GET) { return 403; }3)URI访问控制:允许或拒绝特定URI或URI模式的访问。
拒绝特定URI的访问 location /admin { deny all; }允许特定URI模式的访问 location ~ ^/api/ { allow all; }4)条件组合访问控制:根据多个条件的组合来实施访问控制策略。
仅允许特定IP地址段的GET请求访问特定URI模式 #举个例子 location ~ ^/api/ { if ($request_method != GET) { return 403; } allow 192.168.1.0/24; deny all; }4.8 验证模块
4.8.1 htpasswd命令
安装 yum install httpd-tools -y
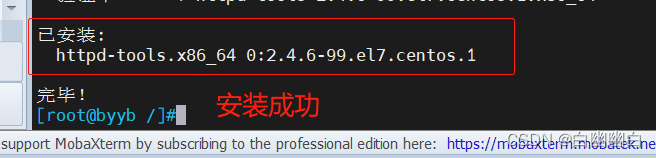
常用命令 #第一次生成文件 htpasswd -c 文件路径 姓名 交互式生成密码 htpasswd -bc 文件路径 姓名 密码 直接将密码跟在 -c 代表新建用户名和密码对应的文件 -b 将密码跟在用户名后
#非第一次生成文件 htpasswd 文件路径 姓名 交互式生成密码 htpasswd -b 文件路径 姓名 密码 直接将密码跟在后面
4.8.2 配置验证模块
#编辑配置文件 vim computer.conf server { listen 80; server_name www.byyd.com; location / { root /data/nginx/html/pc; } location /admin{ root /data/nginx/html/pc; auth_basic "admin site"; #提示信息,不是所有浏览器都有用 auth_basic_user_file /apps/nginx/conf.d/.httpuser; #密码文件存放位置 } }使用 Basic 认证(基本认证)对用户进行身份验证
htpasswd -bc /apps/nginx/conf.d/.httpuser byyd 123456 #创建一个.htpasswd文件,并添加一个使用Basic认证的用户名和密码

cat /apps/nginx/conf.d/.httpuser

打开虚拟机内置浏览器 访问 192.168.2.100/admin

4.9 关闭或修改版本信息
4.9.1 关闭版本信息显示
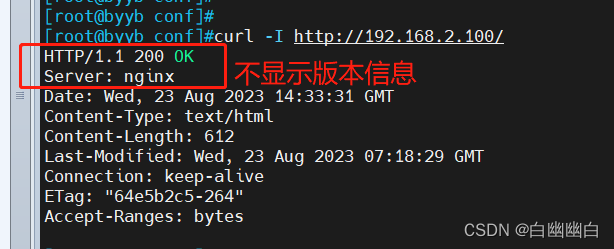
思路 修改主配置文件,将 server_tokens off;放在http语句中
cd /apps/nginx/conf/ vim nginx.conf

保存退出后 nginx -s reload #应用修改 curl -I http://192.168.2.100/ #将请求发送到IP地址为192.168.91.100的服务器上的根路径,并返回服务器的响应头信息 #响应头信息包括服务器类型、内容类型、响应日期和连接状态等。

4.9.2 修改nginx 版本信息 优化
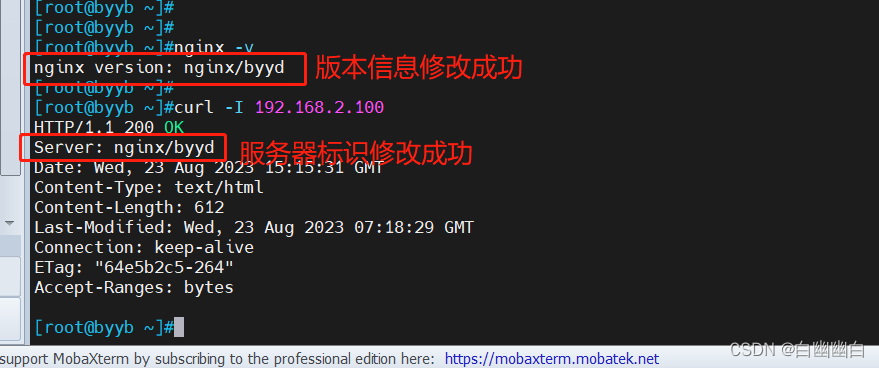
思路: 修改安装包里源码, 再重新编译 源码路径 /nginx-1.18.0/src/core/nginx.h
cd /test11 #源码包所在路径 vim ./nginx-1.18.0/src/core/nginx.h


vim ./nginx-1.18.0/src/http/ngx_http_header_filter_module.c #修改模块的源代码文件


##然后重新编译安装 ./configure --prefix=/apps/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module make -j2 && make install
编译安装完成后,重启 nginx -v #查看版本信息 curl -I 192.168.2.100
4.10 自定义 错误页面
原理部分

修改错误页面的主要目的是为了提供更友好的用户体验和品牌一致性。
也可以用指定的响应状态码进行响应。
#部分响应状态码 400 Bad Request:请求不正确或无效的错误页面。 401 Unauthorized:未授权访问的错误页面。 403 Forbidden:禁止访问的错误页面。 404 Not Found:页面未找到的错误页面。 500 Internal Server Error:服务器内部错误的错误页面。 502 Bad Gateway:错误的网关请求的错误页面。 503 Service Unavailable:服务不可用的错误页面
配置文件中的可用位置:http, server, location, if in location。
配置部分
#基本格式 error_page code ... [=[response]] uri; #构成详解 error_page 固定写法 code 响应码 = 可以将响应码转换 uri 访问连接
新建错误页面和错误页面目录 mkdir /data/nginx/html/pc/error/ cd /data/nginx/html/pc/error/ vim 40x.html #错误页面
cd /apps/nginx/conf.d/ vim computer.conf #编辑子配置文件 server { listen 80; server_name www.kgc.com; root /data/nginx/html/pc; error_page 404 =302 /40x.html; #把错误码 404 指定成302 注意此处的 40x.html 需要真实存在建立的页面必须一致 location = /40x.html { root /data/nginx/html/pc/error/; } location / { root /data/nginx/html/pc; } #验证模块可以不写 location /admin{ auth_basic "admin site"; auth_basic_user_file /apps/nginx/conf.d/.httpuser; } }在浏览器中随便输入一个错误连接,观察错误页面

4.11 修改日志的位置
通过修改日志的路径,可以实现日志分离,即不同网站的日志单独存放。
配置实例
mkdir /data/logs #新建存放日志的目录
#编辑子配置文件,指定日志存放位置 vim /apps/nginx/conf.d/mobile.conf server{ listen 80; server_name www.mobile.com; root /data/nginx/m/; error_log /data/logs/m_error.log; access_log /data/logs/m_access.log; } vim /apps/nginx/conf.d/computer.conf server{ listen 80; server_name www.computer.com; root /data/nginx/pc; error_log /data/logs/pc_error.log; access_log /data/logs/pc_access.log; }
nginx -t nginx -s reload #语法检查无误后重载

4.12 检测文件是否存在-----try_files指令
Nginx 的 try_files 指令用于指定在资源文件不存在时如何处理请求。
默认开启,可用于server和location部分。
4.12.1 原理部分
基本语法 #方式一 try_files file ... uri; file 表示要尝试的文件路径, uri 则表示当文件不存在时转发请求的路径。 #举个例子 location / { try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html /fallback.html; } #释义 尝试找到与请求的 URI 对应的文件。 如果文件不存在,则尝试在 URI 后面加上斜杠 (/) 后再查找一个文件。 如果仍然找不到文件,则尝试访问 /index.html。 如果连 /index.html 也不存在,则将请求转发给 /fallback.html。#方式二 try_files file ... =code; =code 表示文件不存在时 返回的状态码 #只会返回指定的 HTTP 响应码,而不会转发请求到指定的 uri #举个例子 location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } #释义 尝试找到与请求的 URI 对应的文件。 如果文件不存在,则尝试在 URI 后面加上斜杠 (/) 后再查找一个文件。 如果仍然找不到文件,则返回 404 响应码。4.12.2 配置实例
服务端 #新建寻找失败跳转页面 mkdir /data/nginx/html/pc/about echo "default page" >> /data/nginx/html/pc/about/default.html #修改配置文件 vim /apps/nginx/conf.d/computer.conf server{ listen 80; server_name www.byydc.com; root /data/nginx/pc; location / { root /data/nginx/html/pc; try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/index.html /about/default.html; } } #重新加载 nginx -t nginx -s reload、 #建立测试文件 cd /data/nginx/html/pc/;touch test echo "find it" >> test客户端 curl www.byydc.com/test #查找一个存在的文件来测试

curl www.byydc.com/tes#查找一个不存在的文件来测试

4.13 长连接相关-----keepalive指令
4.13.1 原理
HTTP Keep-Alive 功能用于实现长连接,允许客户端和服务器之间的 TCP 连接在发送完一个请求后保持打开状态,以便在同一连接上发送多个请求和响应。
可以加在全局或者 server 。
keepalive 配置指令仅对 HTTP/1.0 和 HTTP/1.1 版本的连接有效。
对于 HTTP/2 连接,keepalive 功能是默认启用的,并且无需额外配置。
4.13.2 keepalive_timeout
keepalive_timeout timeout [header_timeout]; #设定保持连接超时时长
keepalive_timeout 用于定义长连接超时时间。
当一个客户端与服务器之间的连接完成一个请求后的等待时间。
如果在这个时间内没有收到新的请求,服务器会关闭连接。
这个时间是以秒为单位的,默认值是 75 秒。
4.13.3 keepalive_requests
keepalive_requests number; #在一次长连接上所允许请求的资源的最大数量
keepalive_requests 用于设置一个连接上可以处理的最大请求数量。
当达到指定数量后,服务器会关闭该连接并且客户端需要重新建立新连接。
默认情况下,keepalive_requests 的值是 100。
如果将 keepalive_requests 设置为 0,则表示在完成每个请求后立即关闭连接,禁用了 Keep-Alive 功能。
4.14 用户上传资料
client_max_body_size 1m; #设置允许客户端上传单个文件的最大值,默认值为1m,上传文件超过此值会出413错误 client_body_buffer_size size; #用于接收每个客户端请求报文的body部分的缓冲区大小;默认16k;超出此大小时,其将被暂存到磁盘上的由下面client_body_temp_path指令所定义的位置 client_body_temp_path path [level1 [level2 [level3]]]; #设定存储客户端请求报文的body部分的临时存储路径及子目录结构和数量,目录名为16进制的数字,使用hash之后的值从后往前截取1位、2位、2位作为目录名 上传文件大于限制 错误代码413
4.15 其他设置
directio size | off; #操作完全和aio相反,aio是读取文件而directio是写文件到磁盘,启用直接I/O,默认为关闭,当文件大于等于给定大小时,例如:directio 4m;同步(直接)写磁盘,而非写缓存。 直接 写入 磁盘 还是等待一定数据量写入磁盘
open_file_cache off; #是否缓存打开过的文件信息 open_file_cache max=N [inactive=time]; #nginx可以缓存以下三种信息: (1) 文件元数据:文件的描述符、文件大小和最近一次的修改时间 (2) 打开的目录结构 (3) 没有找到的或者没有权限访问的文件的相关信息 max=N:#可缓存的缓存项上限数量;达到上限后会使用LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法实现管理 inactive=time:#缓存项的非活动时长,在此处指定的时长内未被命中的或命中的次数少于 open_file_cache_min_uses #指令所指定的次数的缓存项即为非活动项,将被删除 open_file_cache_valid time; #缓存项有效性的检查验证频率,默认值为60s open_file_cache_errors on | off; #是否缓存查找时发生错误的文件一类的信息,默认值为off open_file_cache_min_uses number; #open_file_cache指令的inactive参数指定的时长内,至少被命中此处指定的次数方可被归类为活动项,默认值为1 范例: open_file_cache max=10000 inactive=60s; #最大缓存10000个文件,非活动数据超时时长60s open_file_cache_valid 60s; #每间隔60s检查一下缓存数据有效性 open_file_cache_min_uses 5; #60秒内至少被命中访问5次才被标记为活动数据 open_file_cache_errors on; #缓存错误信息 limit_except method ... { ... },仅用于location #限制客户端使用除了指定的请求方法之外的其它方法 method:GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE,MKCOL, COPY, MOVE, OPTIONS, PROPFIND, PROPPATCH, LOCK, UNLOCK, PATCH limit_except GET { allow 192.168.91.101; deny all; } #除了GET和HEAD 之外其它方法仅允许192.168.1.0/24网段主机使用
-














