- Elasticsearch:从 ES|QL 到 PHP 对象
- Python+MySQL爬取船讯网AIS静态数据
- 全网最最最最详细如何卸载centos7中安装的nginx的教程~
- SQL 注入总结(详细)
- SpringBoot项目中各层的关系和作用
- SQL Server2022版+SSMS安装(保姆级)
- 深度学习超参数调整介绍
- nginx502 Bad Gateway错误解决办法
- Docker进阶:容器与镜像的导入和导出
- Spring-Kafka 3.0 消费者消费失败处理方案
- SQLite、MySQL 和 PostgreSQL 数据库速度比较(本
- nginx设置开启自启
- 服务器运行mysql的时候出现:Error response from
- 缓存相关知识总结
- VPN的介绍及自建点对点的OpenVPN和使用方法:保姆级详细教程,(
- Node-sass与Node.js版本对应关系的深入探讨
- 从零开始实现C++ TinyWebServer(九)---- 项目知识
- Spring Security 之方法级的权限管控 @PreAutho
- java.sql.SQLNonTransientConnectionE
- SpringBoot 解决跨域问题的 5 种方案!
- 【数据库】国产达梦数据库与mysql特点、区别、发展前景
- 前端实现调用打印机和小票打印(TSPL )功能
- 019——IIC模块驱动开发(基于EEPROM【AT24C02】和I.
- 【Spring框架】一篇文章带你彻底搞懂Spring解决循环依赖的底层
- 第一个Spring Boot程序
- Java Spring Boot 写 API 接口
- VMware虚拟机桥接、NAT、仅主机三种网络模式的配置详解
- 一篇讲明白 Hadoop 生态的三大部件
- 2024最新!一文看懂Spring Batch批处理(大白话版,干货满
- Springboot利用CompletableFuture异步执行线程
目录
一、RESTful风格支持
1.1 RESTful风格介绍
1.2 postman使用
二、@PathVariable
2.1 实例程序
2.2 测试结果
三、@PostMapping、@GetMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping
四、@HiddenHttpMethodFilter
4.1 在web.xml配置过滤器
4.2 控制器方法
4.3 JSP页面
4.4 测试结果
往期专栏&文章相关导读
1. Maven系列专栏文章
2. Mybatis系列专栏文章
3. Spring系列专栏文章
4. Spring MVC系列专栏文章
一、RESTful风格支持
1.1 RESTful风格介绍
RESTful风格是一种URL路径的设计风格。在RESTful风格的URL路径中,网络上的任意数据都可以看成一个资源,它可以是一段文本、一张图片,也可以是一个Java对象。而每个资源都会占据一个网络路径,无论对该资源进行增删改查,访问的路径是一致的。
传统URL:
- 查找id为1的学生:
- http://localhost:8080/student/findById?id=30
- 删除id为1的学生:
- http://localhost:8080/student/deleteById?id=30
- RESTful风格URL:
- 查找id为30的学生:
- http://localhost:8080/student/30
- 删除id为30的学生:
- http://localhost:8080/student/30
那么如何区分对该资源是哪一种操作?通过请求方式不同,判断进行的是什么操作。
之前我们学过两种请求方式,GET请求和POST请求,而访问RESTful风格的URL一共有四种请求方式:
- GET请求:查询操作
- POST请求:新增操作
- DELETE请求:删除操作
- PUT请求:修改操作
RESTful风格URL:
- 查找id为30的学生:
- http://localhost:8080/student/30 GET方式请求
- 删除id为30的学生:
- http://localhost:8080/student/30 DELETE方式请求
RESTful风格的优点:
结构清晰、符合标准、易于理解、扩展方便。
1.2 postman使用
默认情况下浏览器是无法发送DELETE请求和PUT请求的,我们可以使用Postman工具发送这些请求。这里我已经把该工具上传到我的资源里面去了,有需要的读者可以去下载:
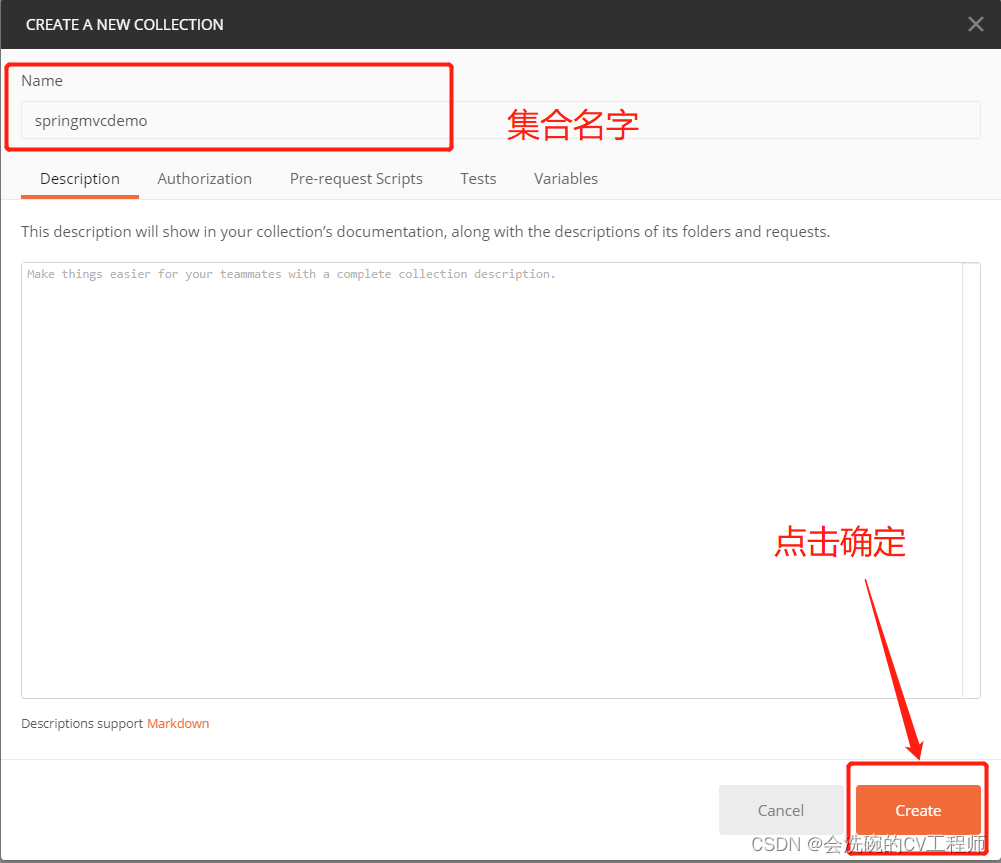
点击new-collection创建请求集合
添加请求 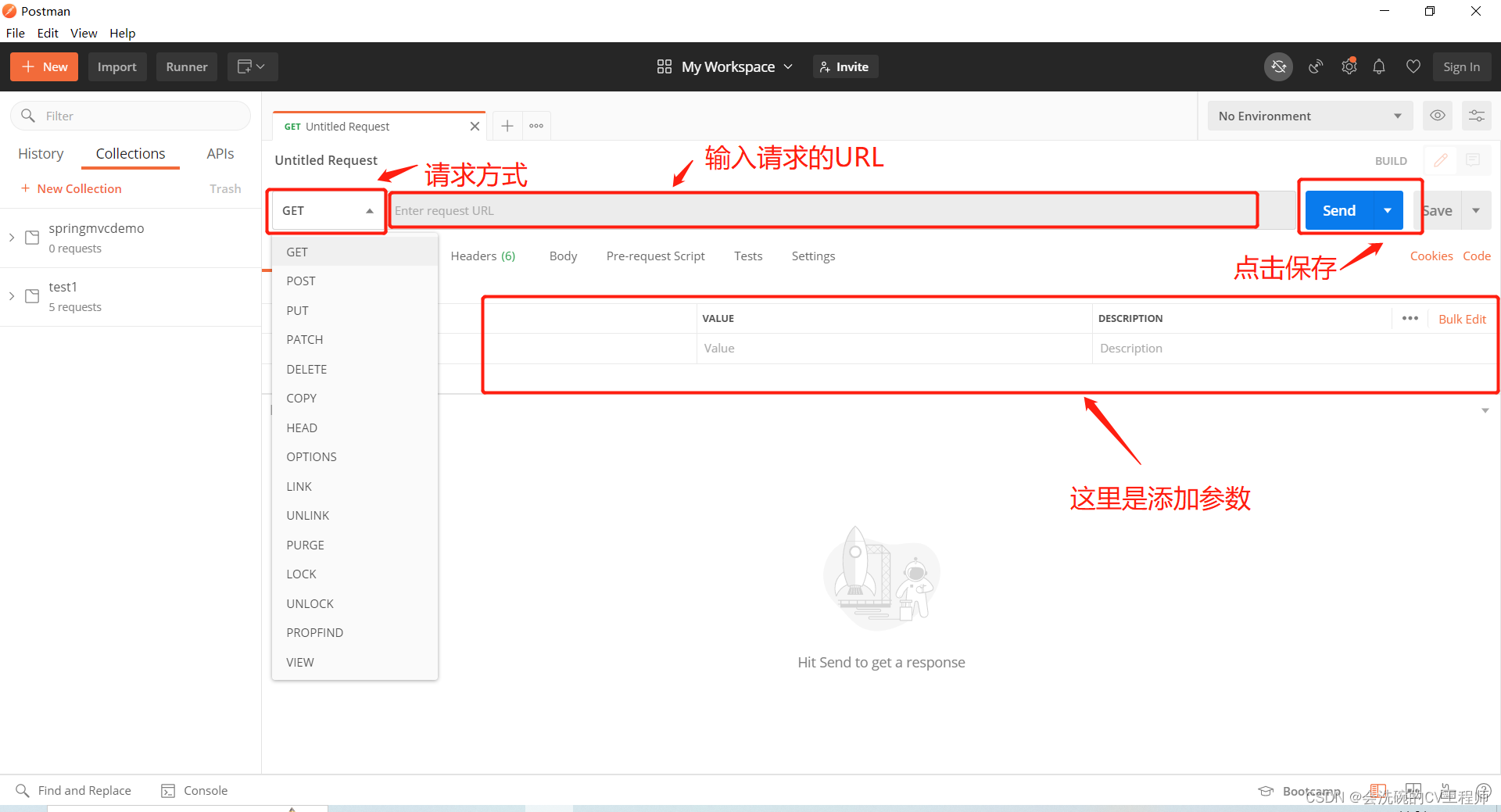
注:那里是点击发送,右边的才是点击保存
保存请求到集合,以后可以随时发送该请求
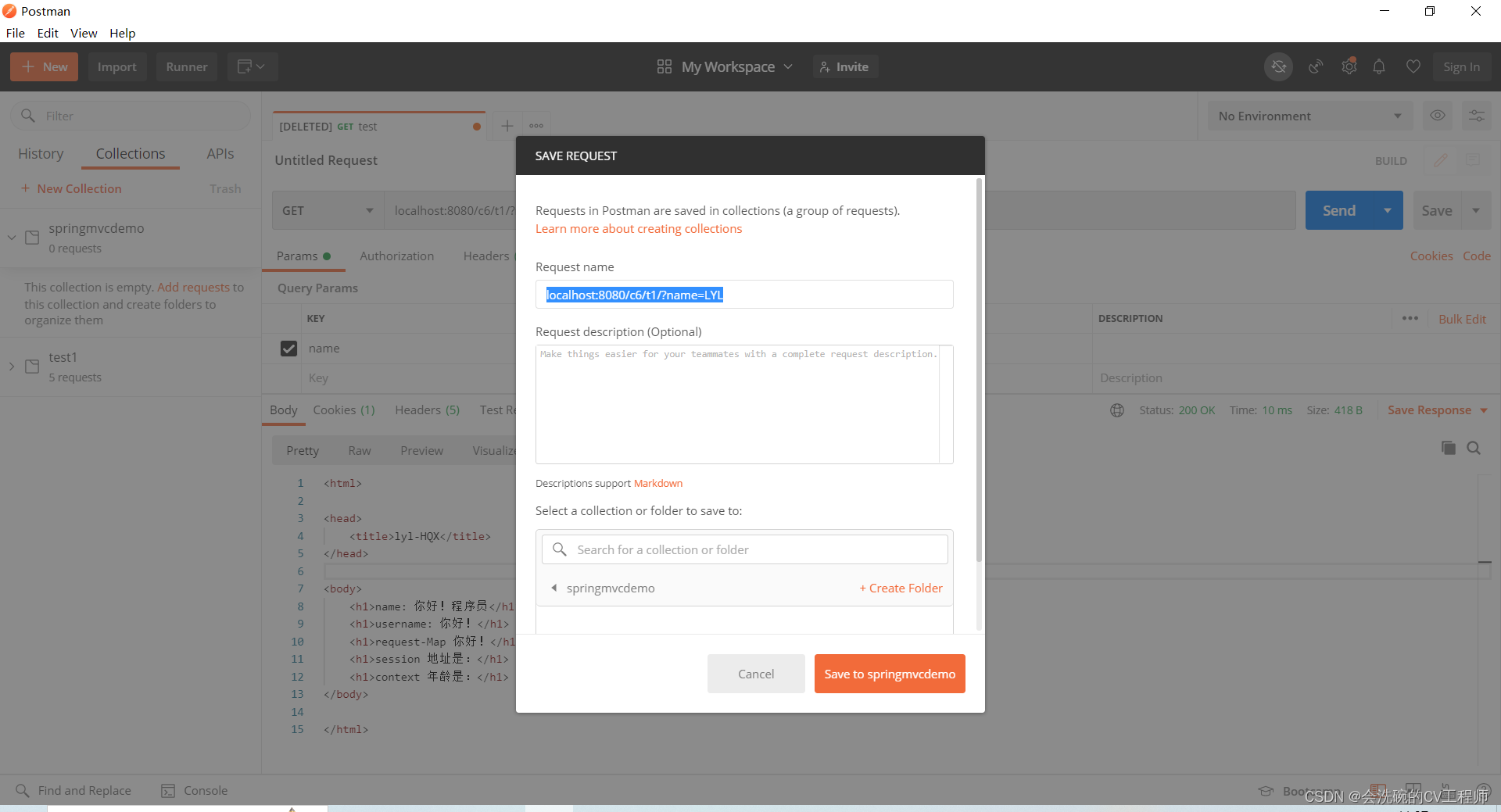 测试:
测试:

OK,这里的name加了@ModelAttribute注解,因此是从model中获取的 ,并不是从请求路径上面获取的。
二、@PathVariable
作用:在RESTful风格的URL中获取占位符的值
位置:方法参数前
属性:
value:获取哪个占位符的值作为参数值,如果占位符和参数名相同,可以省略该属性。
2.1 实例程序
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.domain.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/student")
// 模拟学生的增删改查控制器
public class StudentController {
// 路径的{id}表示占位符,最后会封装到方法的参数中使用
// 删除学生
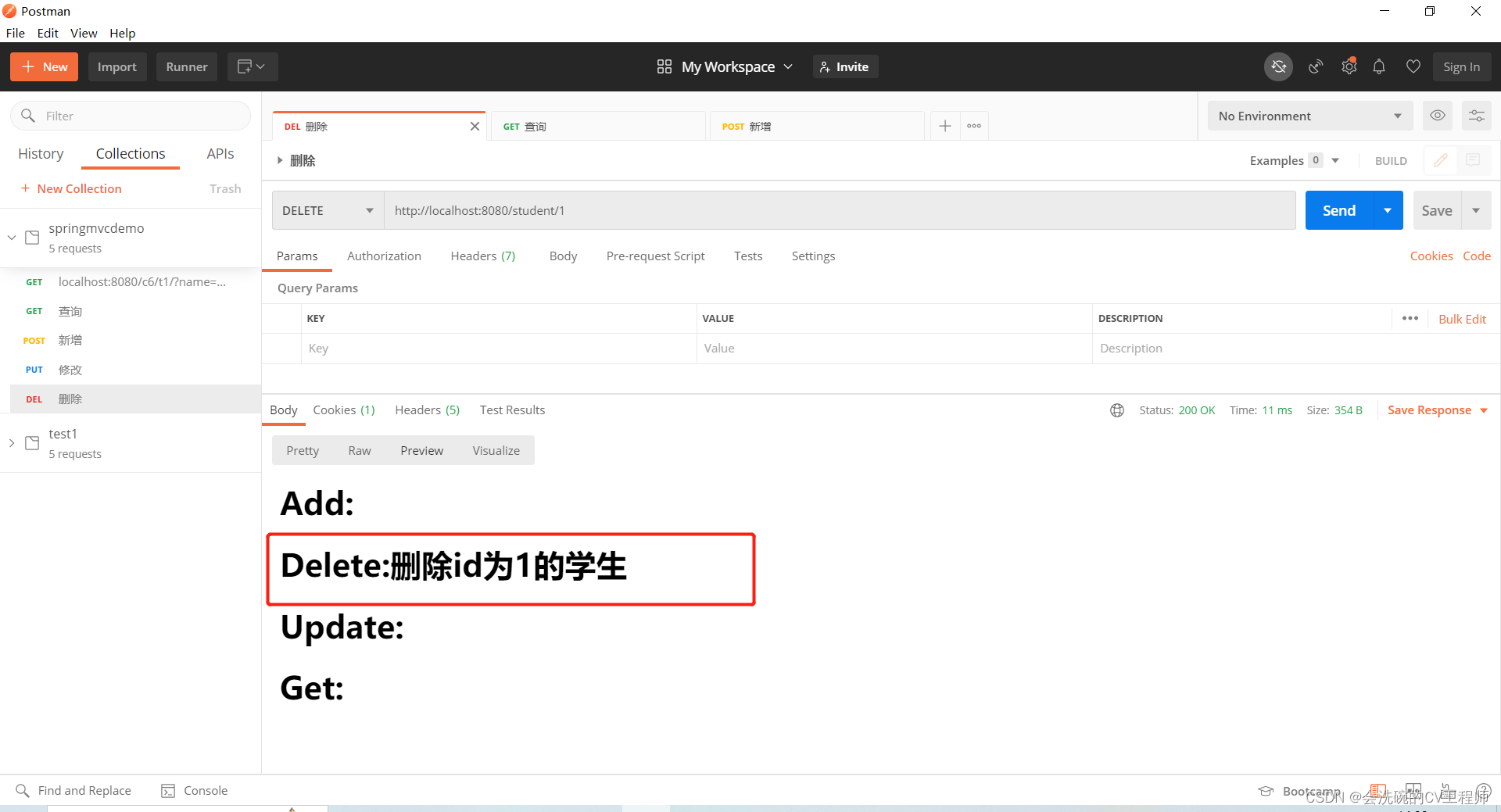
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteStudent(@PathVariable("id") int id, HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("删除id为"+id+"的学生");
String str = "删除id为"+id+"的学生";
request.setAttribute("delete",str);
return "student";
}
// 如果占位符和参数名相同,可以省略@PathVariable的value属性
// 根据id查询学生
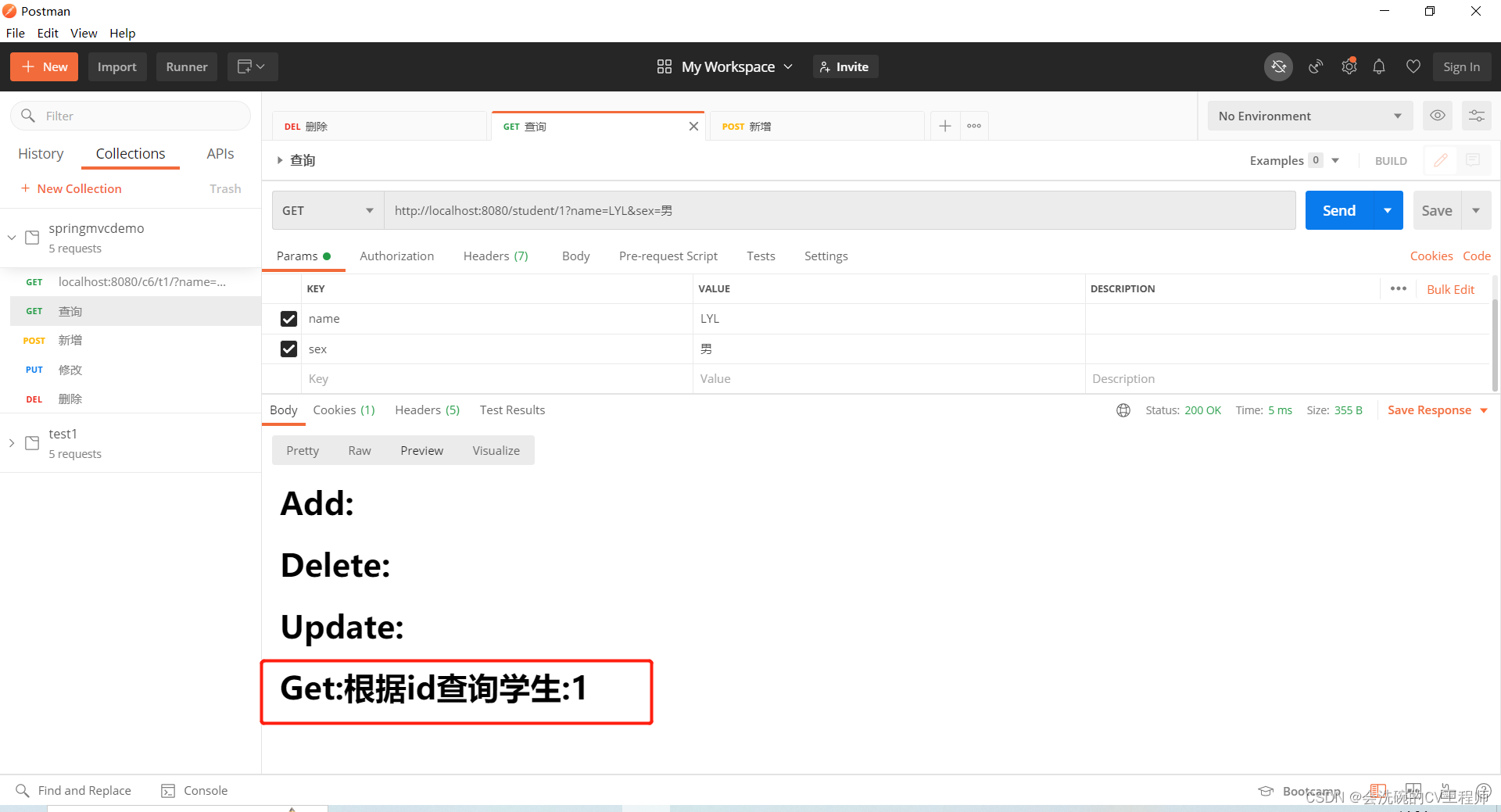
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String findStudentById(@PathVariable int id,HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("get","根据id查询学生:"+id);
System.out.println("根据id查询学生\t"+id);
return "student";
}
// 新增学生
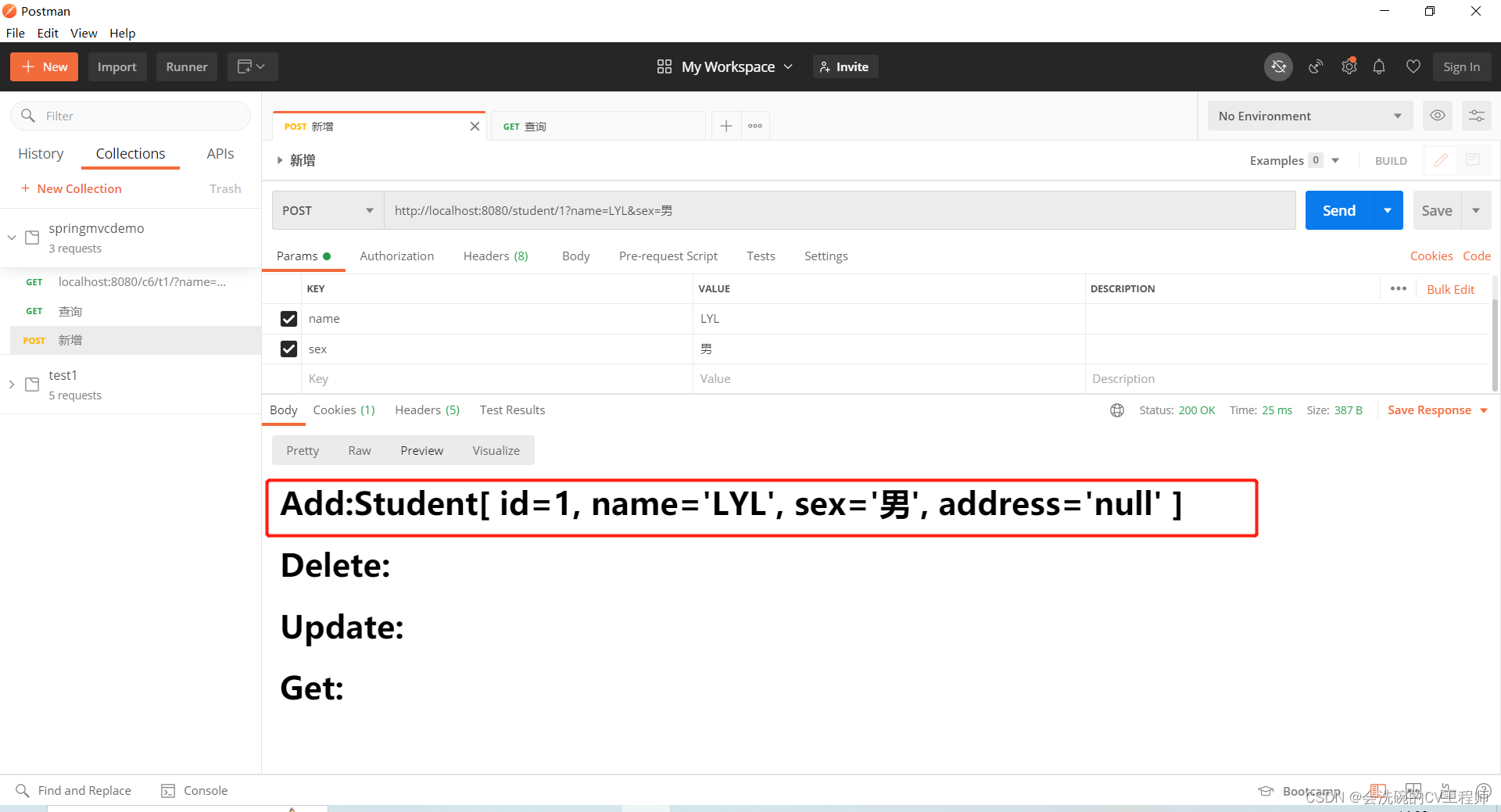
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addStudent(@PathVariable int id, Student student, HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("add",student.toString());
System.out.println("新增学生:"+student+"\t"+id);
return "student";
}
// 修改学生
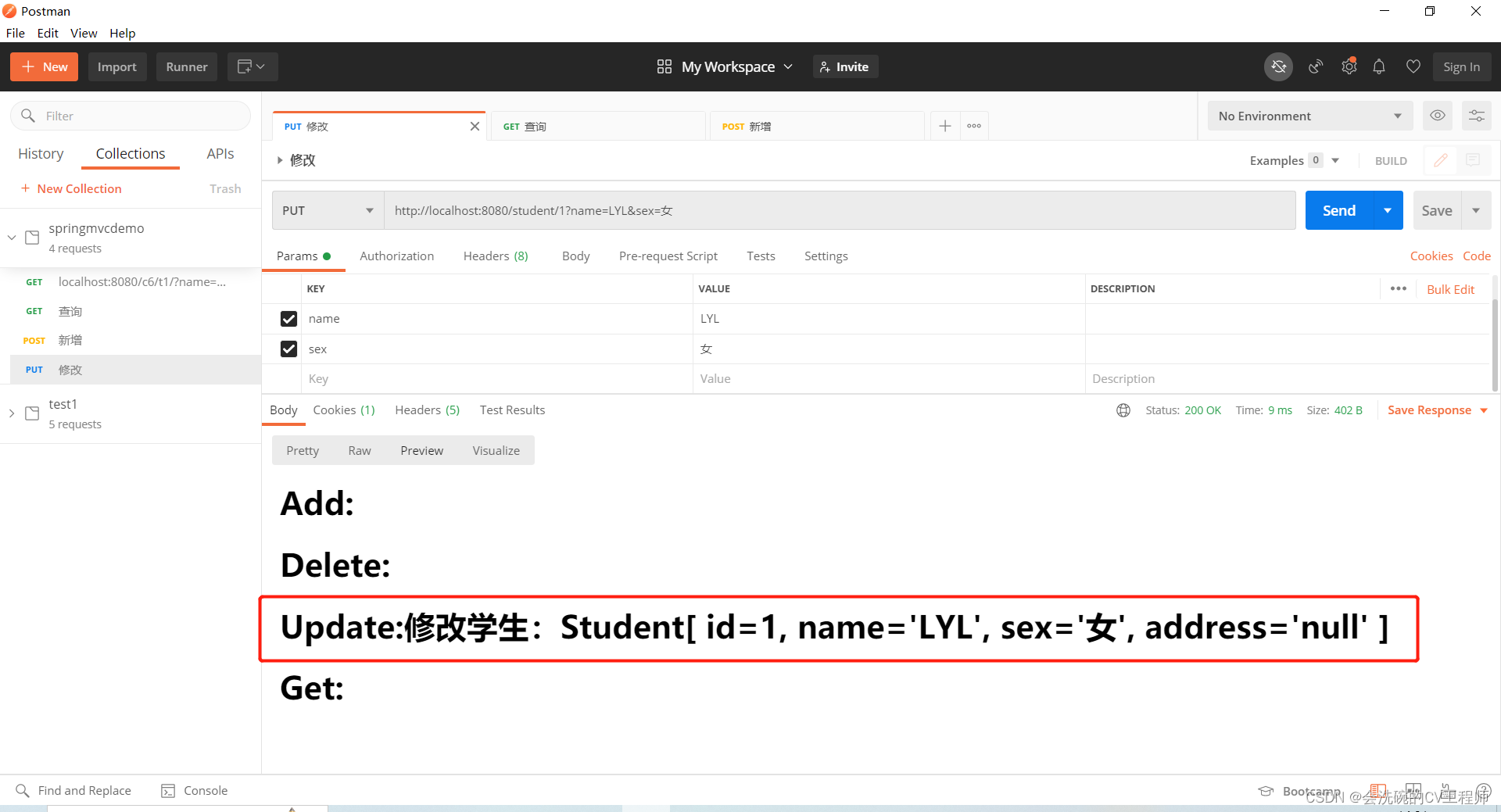
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String updateStudent(@PathVariable int id,Student student,HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("修改学生\t"+id+"\t"+student);
request.setAttribute("update","修改学生:"+student);
return "student";
}
}
JSP页面:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
student
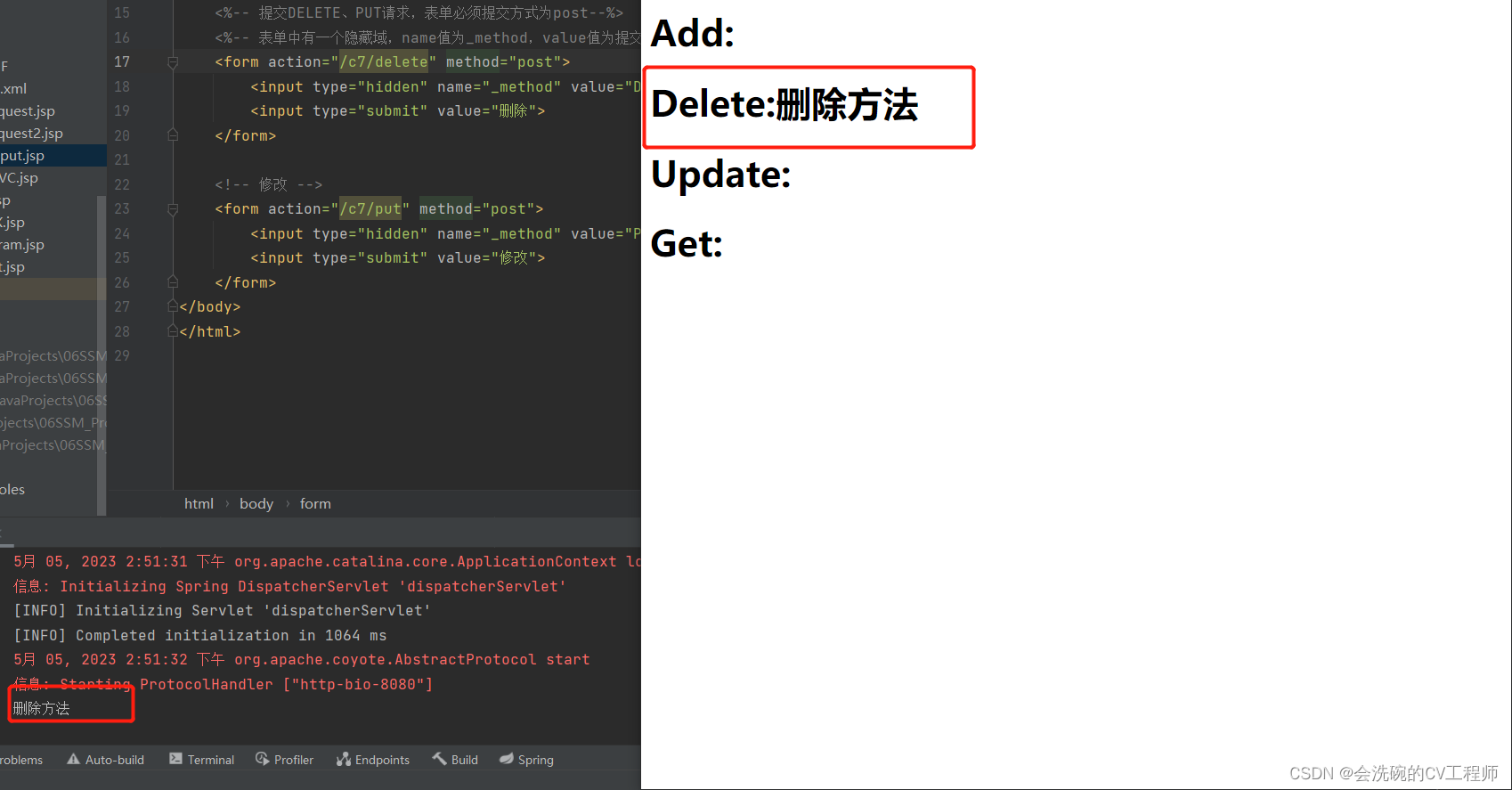
Add:${requestScope.add}
Delete:${requestScope.delete}
Update:${requestScope.update}
Get:${requestScope.get}
2.2 测试结果
访问方式:
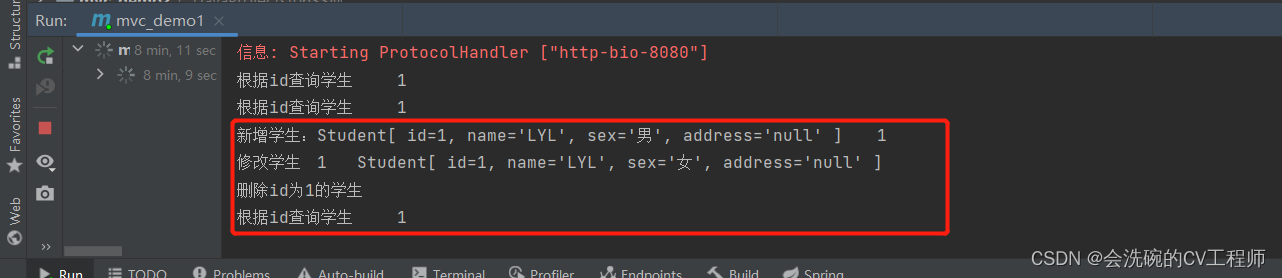
新增学生:POST http://localhost:8080/student/1?name=LYL&sex=男
修改学生:PUT http://localhost:8080/student/1?name=LYL&sex=女
删除学生:DELETE http://localhost:8080/student/1
查询学生:GET http://localhost:8080/student/1
OK,可以看到都是页面都是随着不同的请求方式,出来也页面也不一样。
看一下控制台是否打印对应的日志:
OK,也都是成功显示的了。
三、@PostMapping、@GetMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping
为了简化请求方式@RequestMapping的写法,就产生了了这四个注解。写法如下:
@Controller @RequestMapping("/student") // 模拟学生的增删改查控制器 public class StudentController { // 路径的{id}表示占位符,最后会封装到方法的参数中使用 // 删除学生 //@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE) @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public String deleteStudent(@PathVariable("id") int id, HttpServletRequest request){ System.out.println("删除id为"+id+"的学生"); String str = "删除id为"+id+"的学生"; request.setAttribute("delete",str); return "student"; } // 如果占位符和参数名相同,可以省略@PathVariable的value属性 // 根据id查询学生 //@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET) @GetMapping("/{id}") public String findStudentById(@PathVariable int id,HttpServletRequest request){ request.setAttribute("get","根据id查询学生:"+id); System.out.println("根据id查询学生\t"+id); return "student"; } // 新增学生 //@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.POST) @PostMapping("/{id}") public String addStudent(@PathVariable int id, Student student, HttpServletRequest request){ request.setAttribute("add",student.toString()); System.out.println("新增学生:"+student+"\t"+id); return "student"; } // 修改学生 //@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT) @PutMapping("/{id}") public String updateStudent(@PathVariable int id,Student student,HttpServletRequest request){ System.out.println("修改学生\t"+id+"\t"+student); request.setAttribute("update","修改学生:"+student); return "student"; } }
四、@HiddenHttpMethodFilter
由于浏览器form表单只支持GET与POST请求,而DELETE、PUT请求并不支持。SpringMVC有一个过滤器,可以将浏览器的POST请求改为指定的请求方式,发送给的控制器方法。用法如下:
4.1 在web.xml配置过滤器
httpMethodFilter org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter httpMethodFilter /*
4.2 控制器方法
package com.example.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/c7")
public class MyController7 {
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public String testDelete(HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("删除方法");
request.setAttribute("delete","删除方法");
return "student";
}
@PutMapping("/put")
public String testPut(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("update","修改方法");
System.out.println("修改方法");
return "student";
}
}
4.3 JSP页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
DELETE、PUT提交
<%-- 提交DELETE、PUT请求,表单必须提交方式为post--%>
<%-- 表单中有一个隐藏域,name值为_method,value值为提交方式--%>
4.4 测试结果
OK,我们去访问上面那个jsp:http://localhost:8080/delete-put.jsp
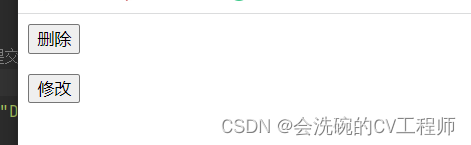
OK,我们点击删除时:
点击修改时:
可以看得到都是成功请求的了。
往期专栏&文章相关导读
大家如果对于本期内容有什么不了解的话也可以去看看往期的内容,下面列出了博主往期精心制作的Maven,Mybatis等专栏系列文章,走过路过不要错过哎!如果对您有所帮助的话就点点赞,收藏一下啪。其中Spring专栏有些正在更,所以无法查看,但是当博主全部更完之后就可以看啦。
1. Maven系列专栏文章
| Maven系列专栏 | Maven工程开发 |
| Maven聚合开发【实例详解---5555字】 |
2. Mybatis系列专栏文章
| Mybatis系列专栏 | MyBatis入门配置 |
| Mybatis入门案例【超详细】 | |
| MyBatis配置文件 —— 相关标签详解 | |
| Mybatis模糊查询——三种定义参数方法和聚合查询、主键回填 | |
| Mybatis动态SQL查询 --(附实战案例--8888个字--88质量分) | |
| Mybatis分页查询——四种传参方式 | |
| Mybatis一级缓存和二级缓存(带测试方法) | |
| Mybatis分解式查询 | |
| Mybatis关联查询【附实战案例】 | |
| MyBatis注解开发---实现增删查改和动态SQL | |
| MyBatis注解开发---实现自定义映射关系和关联查询 |
3. Spring系列专栏文章
| Spring系列专栏 | Spring IOC 入门简介【自定义容器实例】 |
| IOC使用Spring实现附实例详解 | |
| Spring IOC之对象的创建方式、策略及销毁时机和生命周期且获取方式 | |
| Spring DI简介及依赖注入方式和依赖注入类型 | |
| Spring IOC相关注解运用——上篇 | |
| Spring IOC相关注解运用——下篇 | |
| Spring AOP简介及相关案例 | |
| 注解、原生Spring、SchemaBased三种方式实现AOP【附详细案例】 | |
| Spring事务简介及相关案例 | |
| Spring 事务管理方案和事务管理器及事务控制的API | |
| Spring 事务的相关配置、传播行为、隔离级别及注解配置声明式事务 |
4. Spring MVC系列专栏文章
| SpringMVC系列专栏 | Spring MVC简介附入门案例 |
| Spring MVC各种参数获取及获取方式自定义类型转换器和编码过滤器 | |
| Spring MVC获取参数和自定义参数类型转换器及编码过滤器 | |
| Spring MVC处理响应附案例详解 | |
| Spring MVC相关注解运用 —— 上篇 | |
| Spring MVC相关注解运用 —— 中篇 | |
| Spring MVC相关注解运用 —— 下篇 | |
| Spring MVC多种情况下的文件上传 | |
| Spring MVC异步上传、跨服务器上传和文件下载 | |
| Spring MVC异常处理【单个控制异常处理器、全局异常处理器、自定义异常处理器】 | |
| Spring MVC拦截器和跨域请求 | |
| SSM整合案例【C站讲解最详细流程的案例】 |