- 【云原生系列】云计算概念与架构设计介绍
- VSCode 正则表达式 匹配多行
- java.sql.SQLIntegrityConstraintViol
- 二刷大数据(一)- Hadoop
- Android Studio安装超详细步骤(包括SDK安装不成功,模拟
- 前端 Vue启动本地(.exe)文件
- Spring Cloud - 手写 Gateway 源码,实现自定义局
- Lua语法(四)——协程
- 【k8s】:部署、使用 metrics-server
- SpringBoot前端传递数组后端怎么接收
- docker exec
- Leetcode-二叉树oj题
- Python江苏南京二手房源爬虫数据可视化系统设计与实现
- SQL拆分字段内容(含分隔符)
- 「PHP系列」PHP表单及表单验证详解
- Node.js教程(想入门就来点进来看看)
- SQL Server数据库日志查看若已满需要清理的三种解决方案
- 剑指offer刷题笔记-链表
- 【Linux】环境下部署Nginx服务 - 二进制部署方式
- SpringBoot 整合Swagger2
- 已解决com.rabbitmq.client.ShutdownSign
- 滑动窗口最大值(力扣239)
- Matlab方程组拟合【案例源码+视频教程】
- 使用 Docker 部署 Nacos 并配置 MySQL 数据源
- com.mysql.cj.exceptions.CJCommunica
- SQL中 JOIN 的两种连接类型:内连接(自然连接、自连接、交叉连接
- 大数据技术原理及应用课实验4: NoSQL和关系数据库的操作比较
- 「PHP系列」PHP 函数详解
- 篮球竞赛|基于Springboot的篮球竞赛预约平台系统设计与实现(源
- 如何学习正则表达式
目录
前言
Exchange(交换机)的类型与应用
- 交换机的属性
1. 直连交换机:Direct Exchange
2. 主题交换机:Topic Exchange
3. 扇形交换机:Fanout Exchange
4. 默认交换机(直连)
前言
在讲交换机之前我们需要了解一些概念,在RabbitMQ工作流程有一项叫Exchange(交换机:消息的分发中心),它的作用是将生产者发送的消息转发到具体的队列,队列再将消息以推送或者拉取方式给消费者进行消费。
原:在RabbitMQ中生产者发送的信息不会直接投递到队列中,而是先将消息投递到交换机中,在由交换机路由到一个或多个队列中。
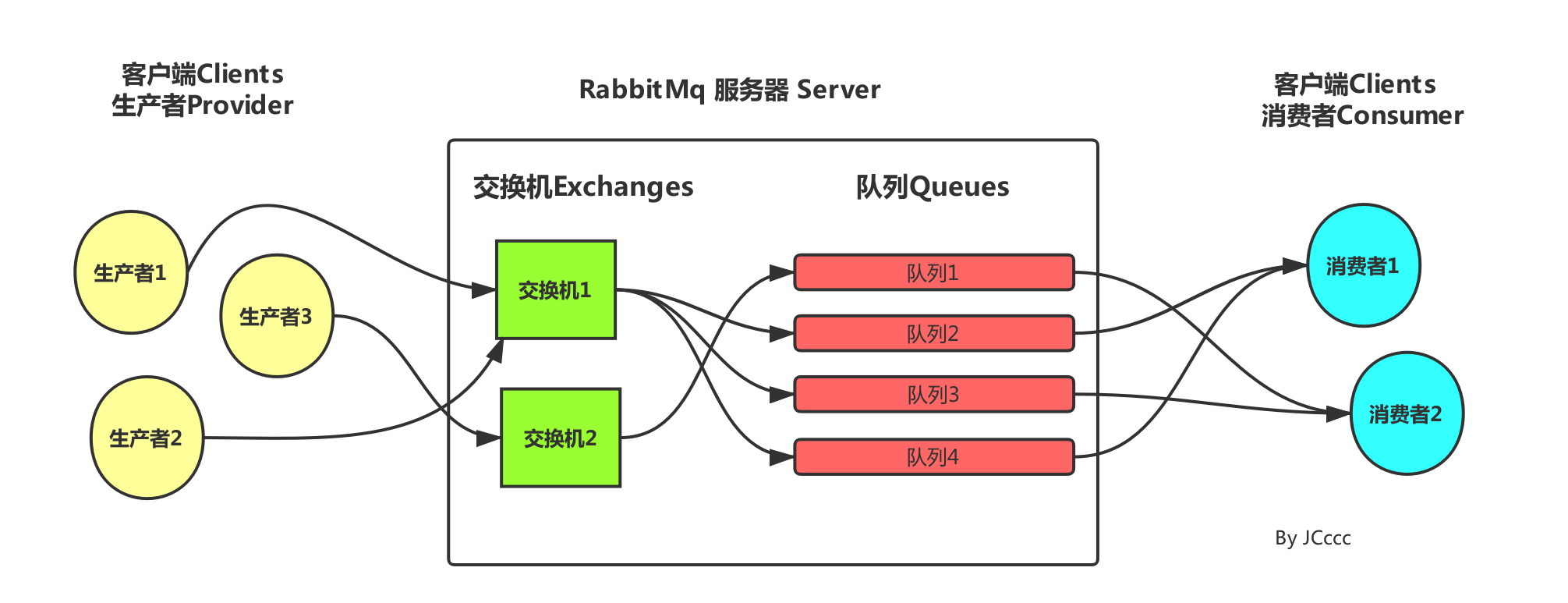
流程:生产者 --(路由键)---> 交换机 --(绑定键)---> 队列 --(pull,push)--->消费者
这里就需要了解这两个东西:
- 路由键(RoutingKey):每个消息都有一个称为路由键(routing key)的属性,它其实就是一个简单的字符串(或者可以说是一种规则的字符串)
- 绑定键(BindingKey):就是指定将队列跟接收路由键的交换机进行绑定
生产者将信息发送给哪个Exchange是由RoutingKey决定的,而Exchange与哪个队列绑定是由BindingKey决定的。
Exchange(交换机)的类型与应用
- 交换机的属性
除交换机类型外,在声明交换机时还可以附带许多其他的属性,其中最重要的几个分别是:
- Type:交换机名称
- Durability:是否持久化。如果持久性,则RabbitMQ重启后,交换机还存在
- Auto-delete:当所有与之绑定的消息队列都完成了对此交换机的使用后,是否删掉它
- Internal:当前Exchange是否用于RabbitMQ内部使用,默认fasle
- Arguments:扩展参数
这里就直接开始操作,配置在一篇就已做了讲解,非常简单!接下来的代码也之上在原基础上做了添加。
项目结构:
所需依赖:
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-amqporg.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-weborg.projectlombok lomboktrue 1. 直连交换机:Direct Exchange
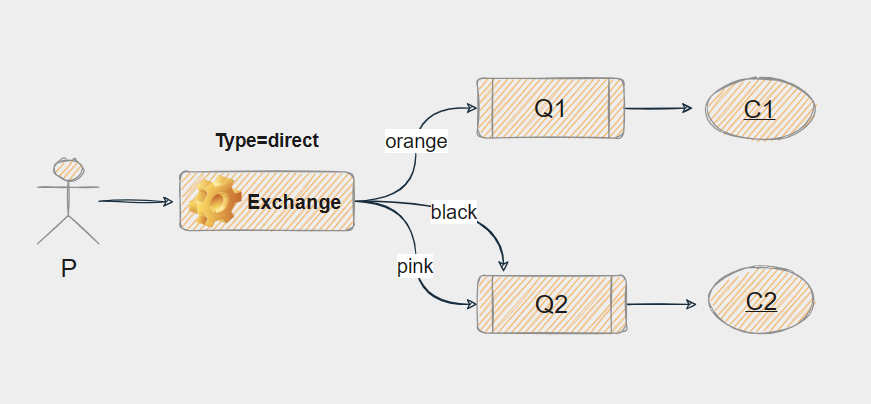
- 这是最简单的一种交换机类型。
- 当一个队列与交换机绑定时,需要指定一个路由键(RoutingKey),只有当消息的路由键与该队列绑定时指定的绑定键(BindingKey)完全匹配时,消息才会被路由到该队列。
如下图:
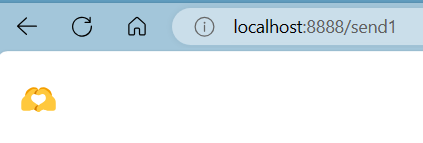
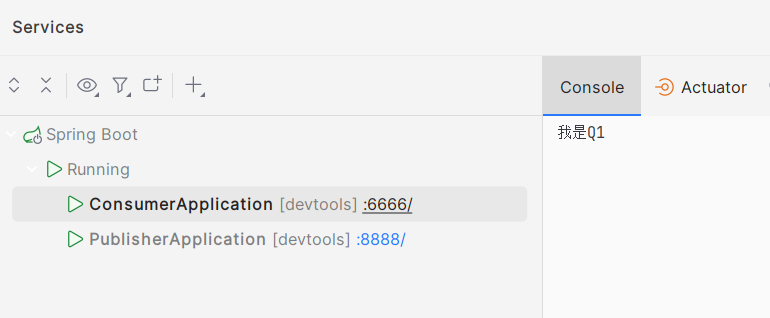
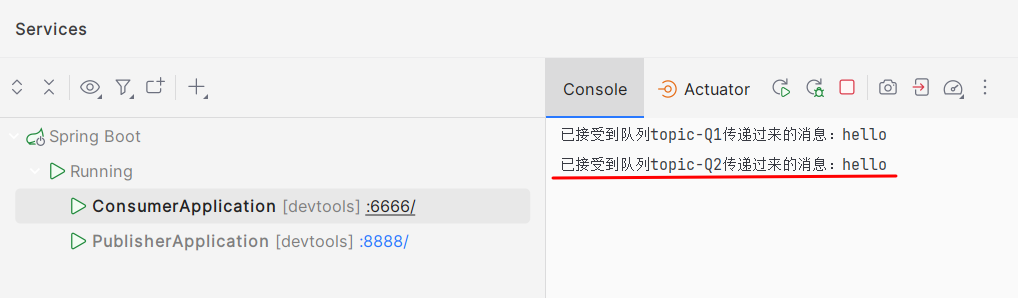
一、p发送消息时带了一个叫black的routing_key,交换机接受后会送到与black绑定的binding_key的队列中,也就是Q2。以此类推...
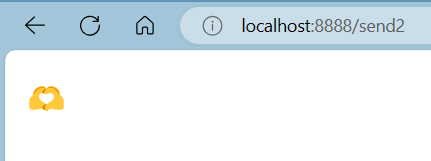
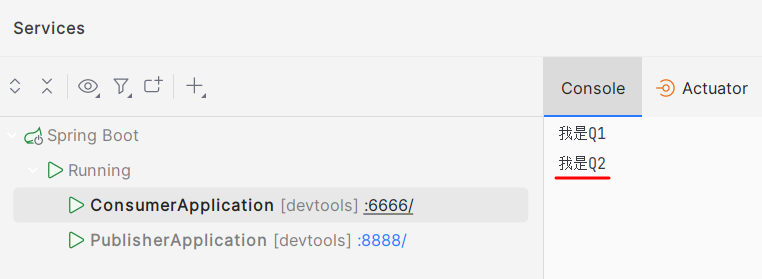
二、还有一种情况,当Q2也与交换机绑定了black,这时p发送的信息会同时推送到Q1和Q2两个队列中。
- 生产者
package com.ycxw.publisher.demos; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding; import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder; import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; //定义队列 @Configuration @SuppressWarnings("all") public class RabbitConfig { /** * 定义队列 Q1 * @return */ @Bean public Queue directQ1() { return new Queue("direct-Q1"); } /** * 定义队列 Q2 * @return */ @Bean public Queue directQ2() { return new Queue("direct-Q2"); } /** * 自定义直连交换机 * @return */ @Bean public DirectExchange directExchange() { return new DirectExchange("direct-exchange", true, false); } /** * 将队列 Q1与交换机进行绑定,并设置路由键 * @return */ @Bean public Binding bindingQ1() { return BindingBuilder.bind(directQ1()) .to(directExchange()) .with("direct_orange"); } /** * 将队列 Q2与交换机进行绑定,并设置路由键 * @return */ @Bean public Binding bindingQ2() { return BindingBuilder.bind(directQ2()) .to(directExchange()) .with("direct_black"); } }package com.ycxw.publisher.demos; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * 模拟发送请求 */ @RestController public class Sender { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate; @RequestMapping("/send1") public String sendFirst() { /*向消息队列发送消息 converAndSend(交换机,路由键,发送的信息)*/ rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("direct-exchange", "direct_orange", "我是Q1"); return "🫶"; } @RequestMapping("/send2") public String sendSecond() throws JsonProcessingException { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("direct-exchange", "direct_black", "我是Q2"); return "🫶"; } }- 消费者接受信息
package com.ycxw.consumer.demos; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @RabbitListener(queues = {"direct-Q1"}) public class DirectReceiver { @RabbitHandler public void handler(String msg) { System.out.println(msg); } }package com.ycxw.consumer.demos; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @RabbitListener(queues = {"direct-Q2"}) public class DirectReceiver2 { @RabbitHandler public void handler(String msg) { System.out.println(msg); } }
- 测试
Q1队列:
Q2队列:
直连交换机适用场景:
有优先级的任务,根据任务的优先级把消息发送到对应的队列,这样可以指派更多的资源去处理高优先级的队列。
2. 主题交换机:Topic Exchange
直连交换机的缺点!
直连交换机的routing_key方案非常简单,如果我们希望一条消息发送给多个队列,那么这个交换机需要绑定上非常多的routing_key。假设每个交换机上都绑定一堆的routing_key连接到各个队列上,那么消息的管理就会异常地困难。所以RabbitMQ提供了一种主题交换机,发送到主题交换机上的消息需要携带指定规则的routing_key。
主题交换机的routing_key需要有一定的规则,交换机和队列的binding_key需要采用*.#.*.....的格式,每个部分用 . 分开,其中
- * 表示一个单词
- # 表示任意数量(零个或多个)单词。
主题交换机会根据这个规则将数据发送到对应的(多个)队列上。
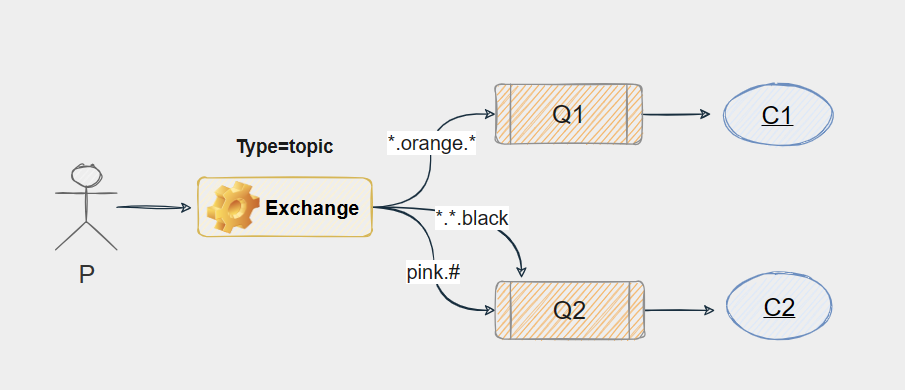
示例:
- 队列Q1绑定键为 *.orange.*
- 队列Q2绑定键为 *.*.black 与 pink.#
- 如果一条消息携带的路由键为 a.orange.b,那么队列Q1将会收到
- 如果一条消息携带的路由键为 a.b.black 或 pink.a(pink.a.b、pink.abc.sb.as....),那么队列Q2将会收到
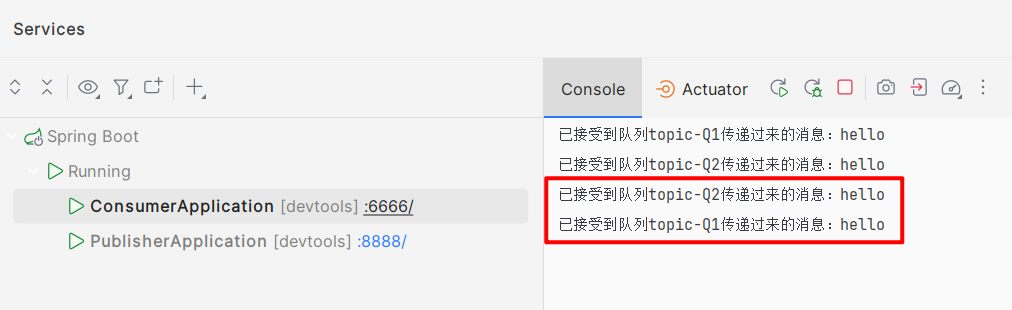
- 如果想让Q1和Q2都接收到P发出的信息,那么路由键为 xx.orange.black 或 pink.orange.xx
- 生产者
/** * 定义路由键规则 */ public static String A_KEY ="*.orange.*"; public static String B_KEY ="*.*.black"; public static String C_KEY ="pink.#"; /** * 定义队列 Q1 * @return */ @Bean public Queue topicQ1() { return new Queue("topic-Q1"); } /** * 定义队列 Q2 * @return */ @Bean public Queue topicQ2() { return new Queue("topic-Q2"); } /** * 自定义主题交换机 * @return */ @Bean public TopicExchange topicExchange() { return new TopicExchange("topic-exchange", true, false); } @Bean public Binding topic_q1(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQ1()) .to(topicExchange()) .with(A_KEY); } @Bean public Binding topic_q2(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQ2()) .to(topicExchange()) .with(B_KEY); } @Bean public Binding topicq2(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQ2()) .to(topicExchange()) .with(C_KEY); } /** * 同时绑定Q1、Q2 */ @Bean public Binding topicq1(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQ1()) .to(topicExchange()) .with(C_KEY); }模拟发送请求:通过路劲传参(指定路由)
@RequestMapping("/send3") public String sendThree(@RequestParam String rex) throws JsonProcessingException { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topic-exchange", rex, "hello"); return "🫶"; }- 消费者接受信息
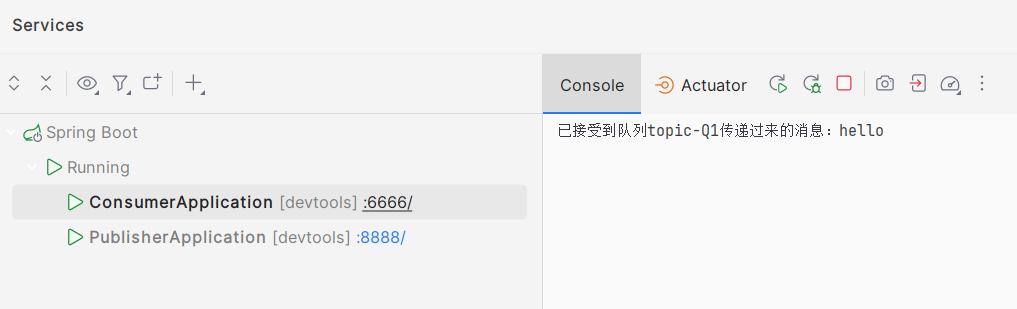
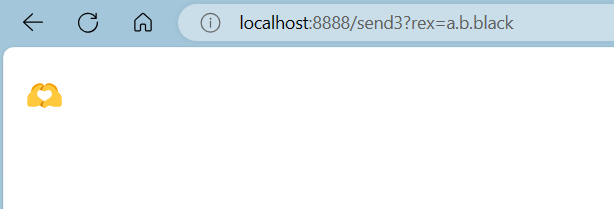
package com.ycxw.consumer.demos; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Map; @Component public class TopicReceiver { @RabbitListener(queues = {"topic-Q1"}) @RabbitHandler public void handler(String msg){ System.out.println("已接受到队列topic-Q1传递过来的消息:"+msg); } @RabbitListener(queues = {"topic-Q2"}) @RabbitHandler public void handlerB(String msg) { System.out.println("已接受到队列topic-Q2传递过来的消息:" + msg); } }- 测试
Q1队列:
Q2队列:
同时调用两个队列:
3. 扇形交换机:Fanout Exchange
扇形交换机是最基本的交换机类型,它所能做的事情非常简单———广播消息。
扇形交换机会把能接收到的消息全部发送给绑定在自己身上的队列。因为广播不需要“思考”,所以扇形交换机处理消息的速度也是所有的交换机类型里面最快的。
这个交换机没有路由键概念,就算你绑了路由键也是无视的。
注意!!!:扇形交换机没有路由键,所以发送请求会被所有绑定的交换机队列接收
- 生产者
/** * 定义队列 Q1 * @return */ @Bean public Queue fanoutQ1() { return new Queue("fanout-Q1"); } /** * 定义队列 Q2 * @return */ @Bean public Queue fanoutQ2() { return new Queue("fanout-Q2"); } /** * 定义扇形交换机 * @return */ @Bean public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){ return new FanoutExchange("fanout-exchange",true,false); } /** * 绑定队列 (没有路由键) * @return */ @Bean public Binding fanout_q1(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQ1()) .to(fanoutExchange()); } @Bean public Binding fanout_q2(){ return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQ2()) .to(fanoutExchange()); }- 模拟发送信息
@RequestMapping("/send4") public String sendFour() throws JsonProcessingException { //必须填写路由键这项,否则接收不到信息。 //由于扇形交换机没有路由键,所以这向需要填空,不然会将发送的信息(hello)解析为路由键 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanout-exchange","","hello"); return "🫶"; }- 消费者
package com.ycxw.consumer.demos; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class FanoutReceiver { @RabbitListener(queues = {"fanout-Q1"}) @RabbitHandler public void handler(String msg) { System.out.println("已接受到队列fanout-Q1传递过来的消息:" + msg); } @RabbitListener(queues = {"fanout-Q2"}) @RabbitHandler public void handlerB(String msg) { System.out.println("已接受到队列fanout-Q2传递过来的消息:" + msg); } }- 测试
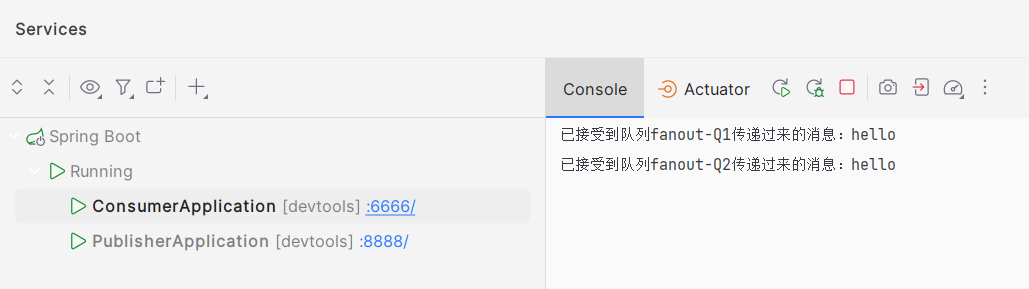
4. 默认交换机(直连)
实际上是一个由RabbitMQ预先声明好的名字为空字符串的直连交换机(direct exchange)。它有一个特殊的属性使得它对于简单应用特别有用处:那就是每个新建队列(queue)都会自动绑定到默认交换机上,绑定的路由键(routing key)名称与队列名称相同。
如:当你声明了一个名为”hello”的队列,RabbitMQ会自动将其绑定到默认交换机上,绑定(binding_key)的路由键名称也是为”hello”。
因此,当携带着名为”hello”的路由键的消息被发送到默认交换机的时候,此消息会被默认交换机路由至名为”hello”的队列中
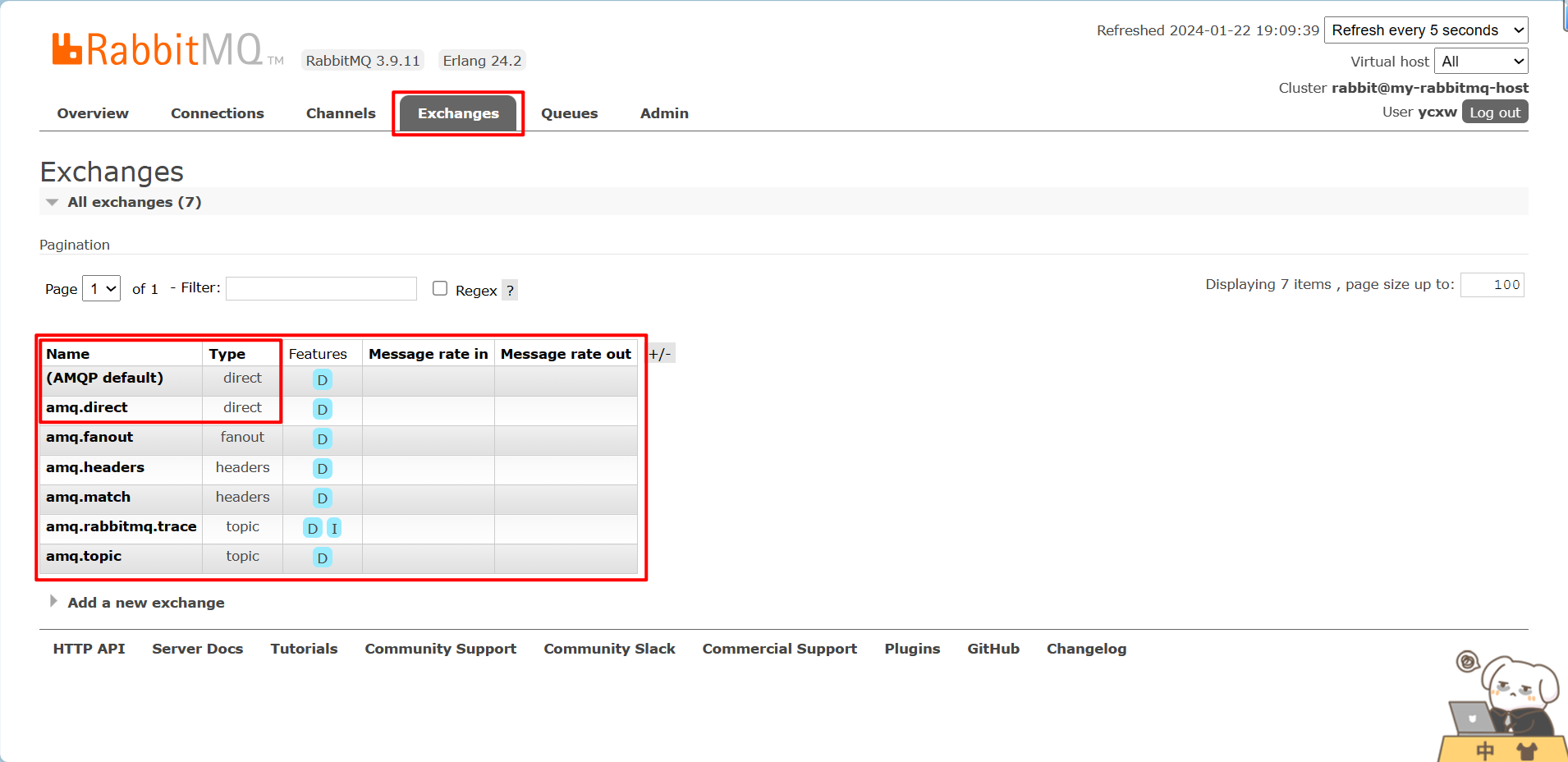
类似amq.*的名称的交换机:
这些是RabbitMQ默认创建的交换机。这些队列名称被预留做RabbitMQ内部使用,不能被应用使用,否则抛出403 (ACCESS_REFUSED)错误
- 测试
- 消费者
- 模拟发送信息
- 生产者
- 测试
- 消费者接受信息
- 测试
- 消费者接受信息
- 生产者














