您的位置:上海毫米网络优化公司 > 网站优化分享 >
相关推荐recommended
- Mysql 将数据按照年月分组 统计
- SQL Server2022版+SSMS安装(保姆级)
- sql server之导入excel数据
- 查看mysql 或SQL server 的连接数,mysql超时、最大
- SpringBoot异常:类文件具有错误的版本 61.0, 应为 52
- 探索前沿AI技术:什么是LLM框架?什么是Agent应用?什么是Wor
- 30天拿下Rust之深入Cargo
- ERROR 1290 (HY000): The MySQL serve
- OpenHarmony开发-系统烧录
- Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected to
- Windows下Node.js下载安装及环境变量配置教程
- 【k8s】:部署、使用 metrics-server
- 04 Python进阶:MySQL-PyMySQL
- 云计算——虚拟化VMware ESXI 7.0安装(一)
- 5.118 BCC工具之xfsslower.py解读
- 大数据技术原理及应用课实验4: NoSQL和关系数据库的操作比较
- Spring Cloud - 手写 Gateway 源码,实现自定义局
- SSL数字证书
- 一个开源跨平台嵌入式USB设备协议:TinyUSB
- 实验一 关系数据库标准语言SQL 课后习题头歌
- 【每日一题】LeetCode——链表的中间结点
- 爬虫解析——Xpath的安装及使用(五)
- 蓝桥杯(填空题)
- 【Rust】——提取函数消除重复代码和泛型
- go包下载时报proxyconnect tcp: dial tcp 1
- SQLMap的Tamper脚本
- SpringAI初体验之HelloWorld
- SQL IFNULL()函数简介
- visual studio配置node.js开发(完整版)
- Mac清理软件cleanmymac x4.14.4破解版,2024年有
大数据与信息融合——神经网络(实验二)
作者:mmseoamin日期:2024-02-06
一、实验目的
神经网络(Neural Network,NN)是一种由多层神经元组成的模型,通过学习数据的特征和模式来进行分类。本实验利用利用机器学习算法,学习搭建神经网络,实现对数据集的分类任务。
二、实验仪器设备及软件
软件使用Google Cloaboratory的Jupyter笔记,硬件计算单元NAVIDA T4云GPU,编程语言Python。
三、实验原理
通过tensorflow框架搭建一个简单的多层感知机(MLP)神经网络结构。它包括一个输入层、两个隐藏层和一个输出层。其中,每个隐藏层都包含10个神经元,激活函数为ReLU(Rectified Linear Unit),输出层包含3个神经元,激活函数为Softmax。输入层的大小为4,由于这是一个分类问题,输出层使用Softmax函数将输出转换为概率分布,以便进行分类。
四、实验步骤及程序源码
1、实验步骤
- 数据预处理:首先对数据集进行预处理,包括数据的归一化处理、特征提取等操作,以便神经网络模型能够更好地学习数据的特征。
- 构建神经网络模型:选择合适的神经网络结构,包括输入层、隐藏层和输出层的节点数,以及激活函数、损失函数等参数的设置。
- 训练模型:使用数据集的训练集对构建的神经网络模型进行训练,通过反向传播算法不断调整模型的权重和偏置,使模型能够更好地拟合数据。
- 模型评估:使用数据集的测试集对训练好的神经网络模型进行评估,计算模型的准确率、精确率、召回率等指标,以评估模型的性能。
- 模型优化:根据评估结果对模型进行调参和优化,以提高模型的分类性能。
2、实验源程序
(1)iris数据集实验
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')
gpu_info = !nvidia-smi
gpu_info = '\n'.join(gpu_info)
if gpu_info.find('failed') >= 0:
print('Not connected to a GPU')
else:
print(gpu_info)
import xlrd import array import numpy as np from matplotlib import colors from sklearn import svm from sklearn.svm import SVC from sklearn import model_selection import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib as mpl import openpyxl import pandas as pd import tensorflow as tf # 绘图 import seaborn as sns # 数值计算 import numpy as np # sklearn中的相关工具 # 划分训练集和测试集 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
data_path = '/content/drive/MyDrive/大数据与信息融合实验/神经网络分类/iris.xlsx' data = pd.read_excel(data_path,header=None) data=data.values print(data) print(data.shape)
#数据分割 x, y = np.split(data,(4,),axis=1) train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y=model_selection.train_test_split(x,y,random_state=1,test_size=0.3) print(train_X.shape,train_y.shape) print(test_X.shape,test_y.shape)
# 进行独热编码
def one_hot_encode_object_array(arr):
# 去重获取全部的类别
uniques, ids = np.unique(arr, return_inverse=True)
# 返回热编码的结果
return tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(ids, len(uniques))
# 训练集热编码
train_y_ohe = one_hot_encode_object_array(train_y)
# 测试集热编码
test_y_ohe = one_hot_encode_object_array(test_y)
# 利用sequential方式构建模型
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
# 隐藏层1,激活函数是relu,输入大小有input_shape指定
tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation="relu", input_shape=(4,)),
# 隐藏层2,激活函数是relu
tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation="relu"),
# 输出层
tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation="softmax")
])
model.summary()
# 设置模型的相关参数:优化器,损失函数和评价指标 model.compile(optimizer='adam',loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
# 模型训练:epochs,训练样本送入到网络中的次数,batch_size:每次训练的送入到网络中的样本个数 history = model.fit(train_X, train_y_ohe, epochs=100, batch_size=1, verbose=1, validation_data=(test_X, test_y_ohe))
# 输出模型评估报告
y_pred = model.predict(test_X)
print('Accuracy score:', accuracy_score(test_y_ohe.argmax(axis=1), y_pred.argmax(axis=1)))
print(classification_report(test_y_ohe.argmax(axis=1), y_pred.argmax(axis=1)))
# 获取模型训练过程的准确率以及损失率的变化
accuracy = history.history['accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
val_accuracy = history.history['val_accuracy']
epochs = range(len(accuracy))
plt.plot(epochs, accuracy, 'b', label='Training accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs, val_accuracy, 'orange', label='Validation accuracy')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'b', label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'orange', label='Validation Loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
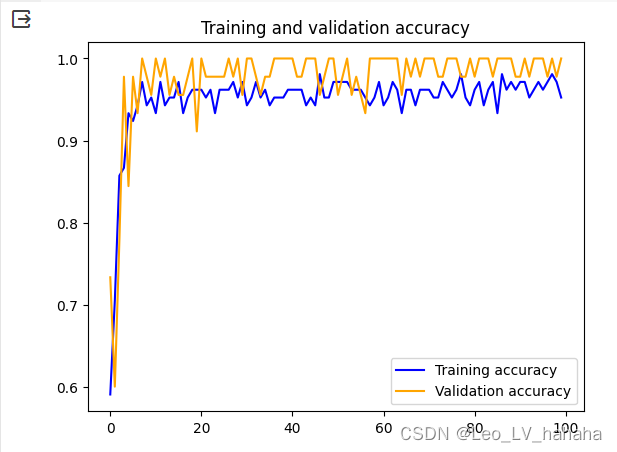
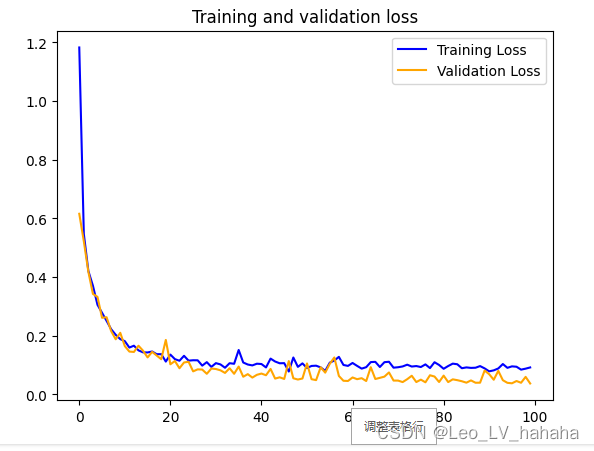
(2)wine数据集实验
对部分代码作出修改:
data_path = '/content/drive/MyDrive/大数据与信息融合实验/神经网络分类/wine.xlsx' data = pd.read_excel(data_path,header=None) data=data.values print(data) print(data.shape)

y,x = np.split(data,(1,),axis=1) train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y=model_selection.train_test_split(x,y,random_state=1,test_size=0.3) print(train_X.shape,train_y.shape) print(test_X.shape,test_y.shape)

# 利用sequential方式构建模型 model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([ # 隐藏层1,激活函数是relu,输入大小有input_shape指定 tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu", input_shape=(13,)), # 隐藏层2,激活函数是relu tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu"), # 输出层 tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation="softmax") ])
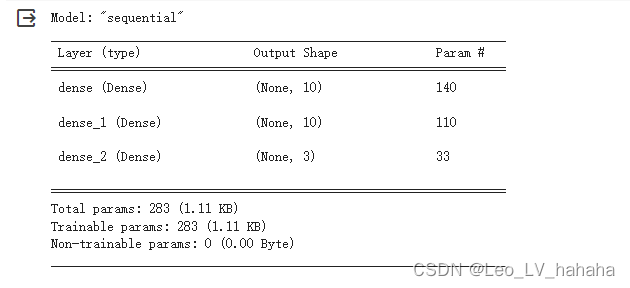
五、实验结果与分析
1、实验结果
(1)iris数据集结果
调整MLP算法的各项参数获得不同的模型:
# 利用sequential方式构建模型 model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([ # 隐藏层1,激活函数是relu,输入大小有input_shape指定 tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation="relu", input_shape=(4,)), # 隐藏层2,激活函数是relu tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation="relu"), # 输出层 tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation="softmax") ])
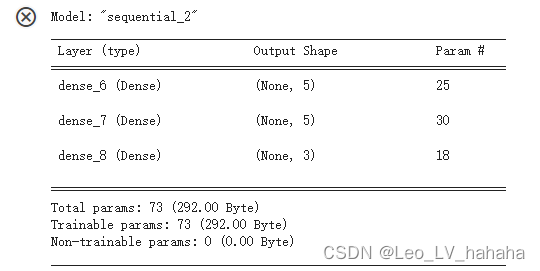
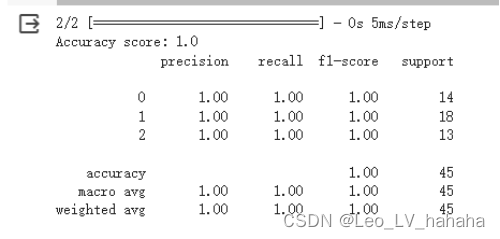
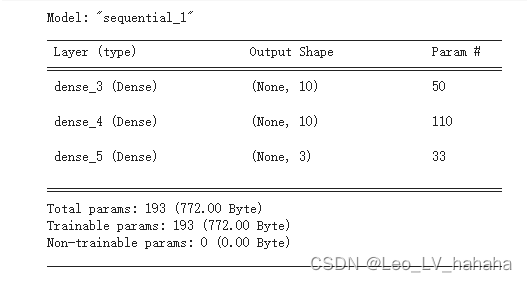
# 利用sequential方式构建模型 model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([ # 隐藏层1,激活函数是relu,输入大小有input_shape指定 tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu", input_shape=(4,)), # 隐藏层2,激活函数是relu tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu"), # 输出层 tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation="softmax") ])
(2)wine数据集结果
调整MLP算法的各项参数获得不同的模型:
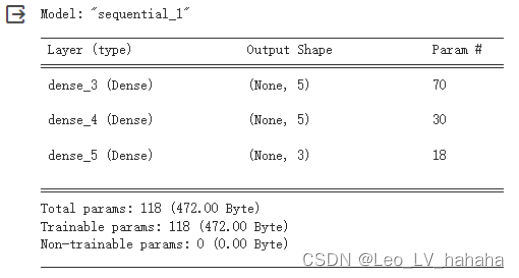
# 利用sequential方式构建模型 model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([ # 隐藏层1,激活函数是relu,输入大小有input_shape指定 tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation="relu", input_shape=(13,)), # 隐藏层2,激活函数是relu tf.keras.layers.Dense(5, activation="relu"), # 输出层 tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation="softmax") ])
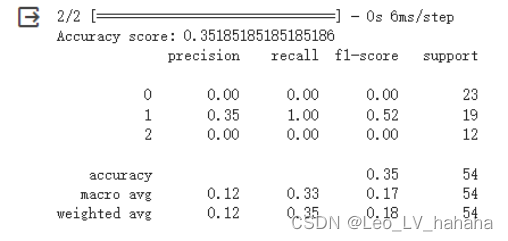
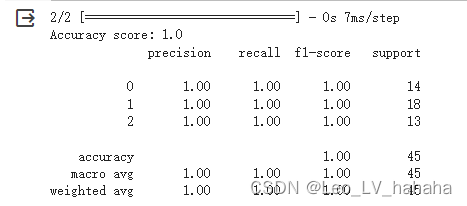
# 利用sequential方式构建模型 model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([ # 隐藏层1,激活函数是relu,输入大小有input_shape指定 tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu", input_shape=(13,)), # 隐藏层2,激活函数是relu tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="relu"), # 输出层 tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation="softmax") ])
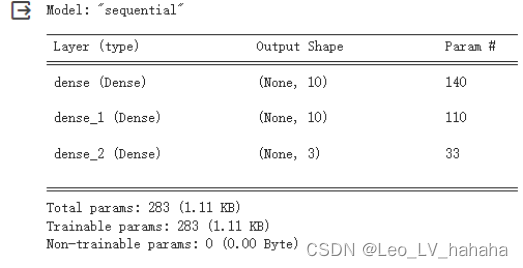
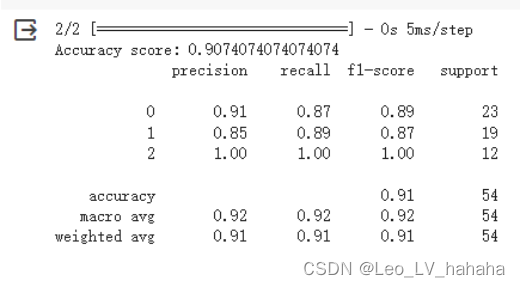
# 利用sequential方式构建模型 model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([ # 隐藏层1,激活函数是relu,输入大小有input_shape指定 tf.keras.layers.Dense(15, activation="relu", input_shape=(13,)), # 隐藏层2,激活函数是relu tf.keras.layers.Dense(15, activation="relu"), # 输出层 tf.keras.layers.Dense(3, activation="softmax") ])
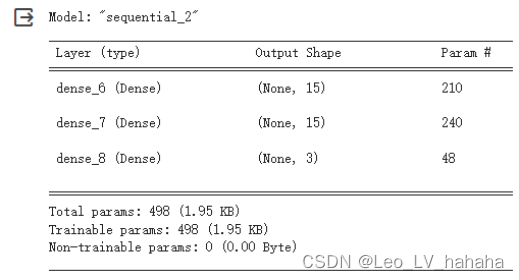
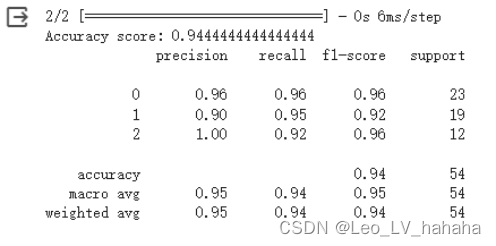
2、实验结果分析
对于iris数据集使用MLP网络,构建两个隐藏层和5个神经元便可以获得较好的模型。但是对于wine数据集,其数据量有明显怎加,在与iris数据集使用相同隐藏层数、激活函数、优化器和损失函数时,即便将神经元增加到十五个也不能得到较为满意的模型,之后可以考虑修改其他参数。














