- RocketMQ与Kafka架构深度对比
- SpringBoot整合参数校验
- The error occurred while executing
- 【vue2】近期bug收集与整理02
- 解锁AI大模型潜力,让文案创作飞跃升级
- 前端(四)——vue.js、vue、vue2、vue3
- 基于时域有限差分法的FDTD的计算电磁学算法-YEE网格下的更新公式推
- 使用SM4国密加密算法对Spring Boot项目数据库连接信息以及y
- 蓝桥杯(填空题)
- C#ORM框架SqlSugar安装及使用(以MySql、sqlite为
- 【python】flask操作数据库工具SQLAlchemy,详细用法
- 数学建模--评价类模型
- Spring AOP的实现方式与原理
- 五种方案图文并茂教你使用DBeaver,SQL文件导入数据库,插入数据
- sql server之导入excel数据
- GOPROXY 代理设置
- RabbitMQ五大常用工作模式
- spring boot自动配置原理,简单易懂
- 【微服务】配置Nacos管理SpringBoot配置文件(附解压包)
- 深度学习超参数调整介绍
- Java实战:Spring Boot生成PDF
- Express框架搭建项目 node.js
- Ubuntu系统使用Docker本地部署Android模拟器并实现公网
- 开源、跨平台安卓摸鱼(投屏)软件 Scrcpy 中文使用指南
- 什么是栈,如何实现?
- Java社区疫情防控系统设计与实现(Idea+Springboot+m
- Mysql为什么只能支持2000w左右的数据量?
- 美团分布式 ID 框架 Leaf 介绍和使用
- 2-1.Hadoop大数据集群搭建之---本地模式
- three.js 基础认识与简单应用
python爬虫框架中,最简单的就是Scrapy框架。执行几个命令就能生成爬虫所需的项目文件,我们只需要在对应文件中调整代码,就能实现整套的爬虫功能。
以下在开发工具PyCharm中用简单的Demo项目来演示爬取小说网站的流程。我们打开小说网首页,将要演示的是如何爬取首页小说推荐列表的小说名称、小说简介、小说作者,这三项元素内容并输出到txt文件中。
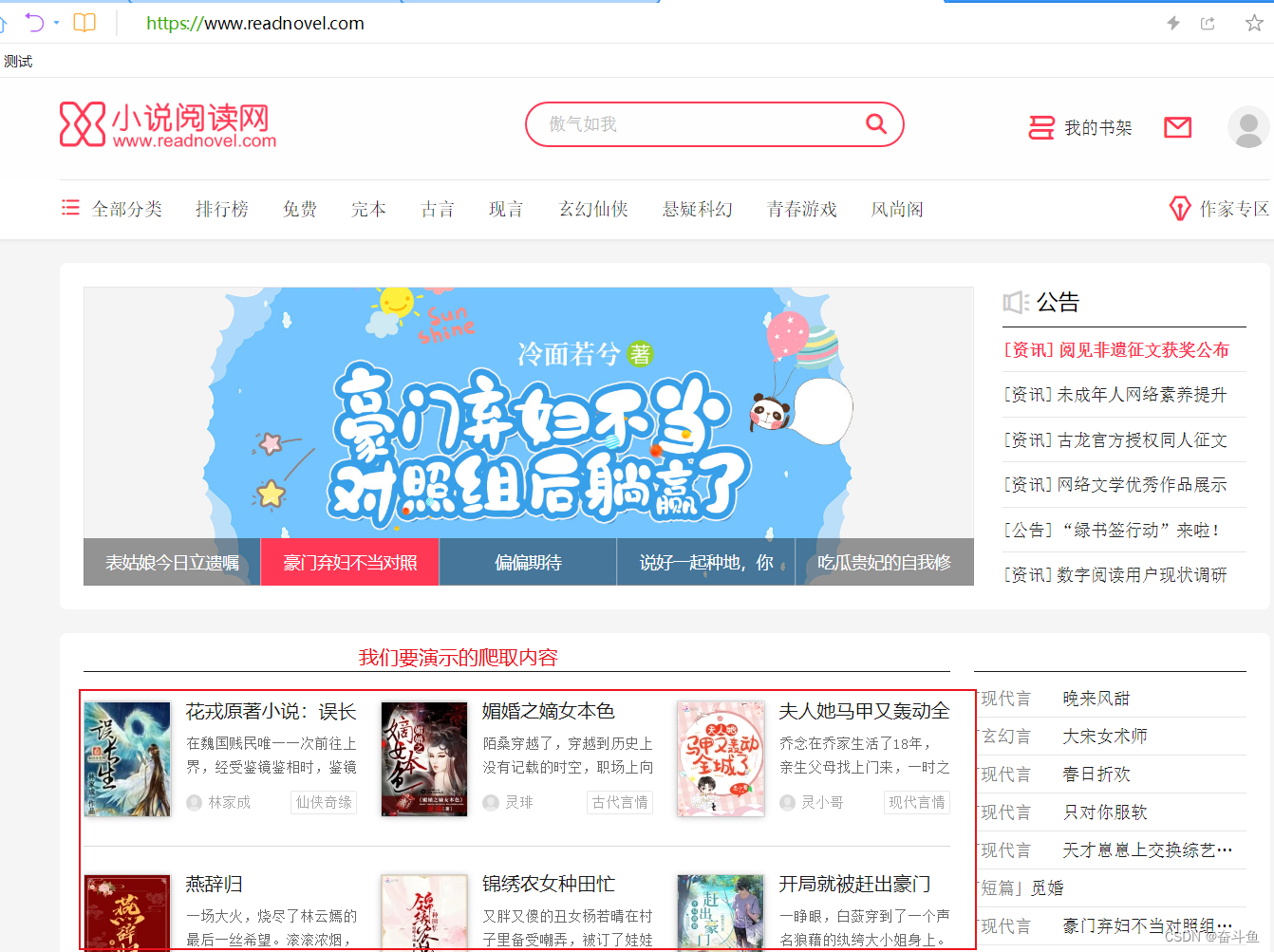
一、安装Scrapy
在PyCharm的终端Terminal中执行pip命令,安装scrapy
pip install scrapy
二、创建Scrapy项目
在项目文件夹执行指令,创建项目名称readNovel
scrapy startproject readNovel

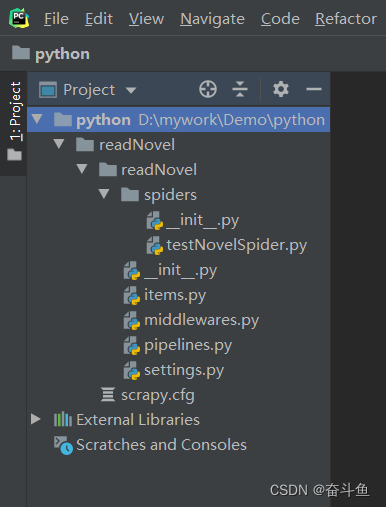
通过cd目录命令进入readNovel/spiders目录下执行scrapy genspider指令,创建一个以基础模板的爬虫脚本文件testNovelSpider,该爬虫搜索的域名为readnovel.com
cd readNovel/readNovel/spiders
scrapy genspider testNovelSpider readnovel.com
执行完文件目录结构如下图
三、Scrapy 文件介绍
上述通过两条简单的命令,就已经创建了Scrapy项目所需的所有文件。现在简单介绍下项目的各文件作用。
1.顶层readNovel:通过startproject 指令创建的项目名称。
2.scrapy.cfg:整个项目的配置文件,定义了项目名称和默认设置文件的位置。
3.次级readNovel:项目代码模块(也可以叫包),包含了所有执行代码内容。
四、代码文件编辑
1.定义字段文件items.py
我们在该文件中定义爬虫将要爬取的三个字段:小说名称、简介、作者。
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class ReadnovelItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
bookTitle = scrapy.Field() #小说名称
bookRemark = scrapy.Field() #小说简介
director = scrapy.Field() #小说作者
2.定义爬虫文件TestNovelspiderSpider.py
需要注意的一点,引入items前,需要使用sys先将items所在目录添加到运行环境,否则在控制台执行爬虫程序时会出现“ ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'items' ”的报错提示。
import scrapy
from scrapy.selector import Selector
import sys
# print(sys.path) #查看当前python解释器搜索目录
import os
prPath = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__))
# print(prPath) #上一级目录 即items所在目录
sys.path.append(prPath) # 将items所在目录添加到运行环境
from items import ReadnovelItem
import re
class TestNovelspiderSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = "testNovelSpider"
# 爬取域名
allowed_domains = ["readnovel.com"]
# 爬取页面
start_urls = ["https://readnovel.com"]
def parse(self, response):
print("开始爬取....")
# 获取要元素的上一级集合
selector = response.xpath('//div[@]/ul/li').extract()
items = []
# 遍历所有对象
for book in selector:
# print(book)
# 用正则表达式匹配从当前book对象中获取到小说名称字符串
bookTitle = re.findall('', book)[0]
# 从获取的小说名称字符串中截取出中文
bookTitle = bookTitle.split("title=")[1].split("\"")[1]
print("小说名:" + bookTitle)
# 用正则表达式匹配从当前book对象中获取到小说名简介
bookRemark = re.findall('.*?
', book)[0]
bookRemark = bookRemark.split("")[1].split("
")[0]
print("小说备注:"+bookRemark)
# 使用Selector选择器,定位到指定并获取text的文本为小说作者
director = Selector(text=book).xpath('//a[@]/text()').extract()[0];
print("小说作者:"+director+"\r\n")
item = ReadnovelItem()
item['bookTitle'] = bookTitle
item['bookRemark'] = bookRemark
item['director'] = director
items.append(item)
# print(items)
return items
以下对上述代码进行说明。
打开并右击页面查看源代码,查找其中一个小说名称可以看到代码段。
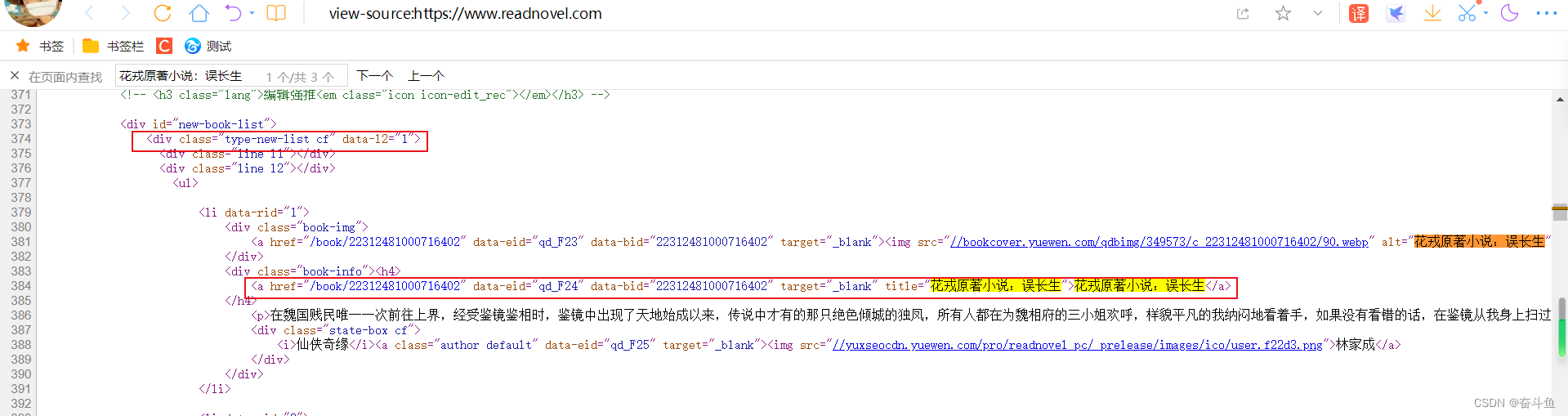
使用xpath获取到上一级的集合成员,然后遍历取出每个成员做处理。
response.xpath('//div[@]/ul/li').extract()
使用re.findall 结合正则表达式抓取模板,“.*?”代表可以匹配所有字符,用于代替名称可变的部分,获取到小说名称。
re.findall('', book)[0]
同理下列取出小说备注、小说作者。
3.定义结果处理文件pipelines.py
将爬取到的各成员内容输出到文本txt中
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# useful for handling different item types with a single interface
from itemadapter import ItemAdapter
import codecs
import time
class ReadnovelPipeline(object):
def process_item(self, item, spider):
today = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d', time.localtime())
fileName = '小说阅读网' + today + '.txt'
print('准备写入内容:')
print(item)
with codecs.open(fileName, 'ab+', 'utf-8') as fp:
fp.write('小说名称:'+item['bookTitle']+'\r\n')
fp.write('小说内容:' + item['bookRemark']+'\r\n')
fp.write('小说作者:' + item['director']+'\r\n\r\n')
# return item
4.调整配置文件settings.py
打开settings.py,添加以下内容,将pipelines的处理文件与爬虫目录下的文件进行关联
BOT_NAME = "readNovel"
SPIDER_MODULES = ["readNovel.spiders"]
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = "readNovel.spiders"
ITEM_PIPELINES = {'readNovel.pipelines.ReadnovelPipeline': 300}
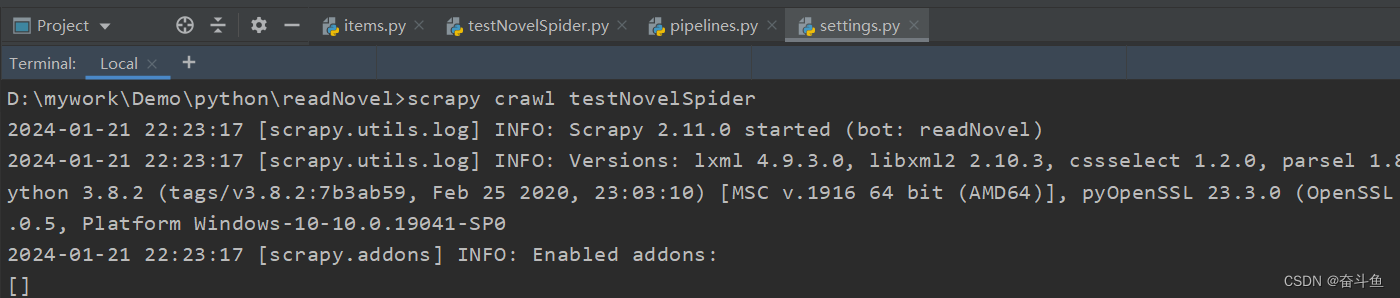
5.运行程序
在终端控制台执行命令
scrapy crawl testNovelSpider
当前目录会生成txt文件,打开查看内容如下。

以上演示程序爬取小说推荐列表并输出到文件成功。
如果文章解决了你的问题,欢迎点赞、收藏或评论。
上一篇:【MySQL】多表关系的基本学习














