- 链表基础知识详解(非常详细简单易懂)
- GmSSL-3.1.1编译
- MySQL 数据库迁移到 Oracle
- 【MyBatis Plus】初识 MyBatis Plus,在 Spr
- 22年国赛tomcat后续(653556547)群
- n皇后问题(DFS)
- Rust面试宝典第6题:快乐数
- 详解爬虫基本知识及入门案列(爬取豆瓣电影《热辣滚烫》的短评 详细讲解代
- 这里有份百度Create大会超长剧透,请查收!
- MYSQL下载及安装完整教程
- 学习使用在mysql中查询指定字段字符串包含多个字符串的方法
- Windows 安装配置 RabbitMQ 详解
- SpringBoot整合Minio的详细步骤
- 漫途水产养殖水质智能监测方案,科技助力养殖业高效生产!
- 【PyJavaC++三种语言OD2023C卷真题】20天拿下华为OD笔
- 个人博客建设必备:精选域名和主机的终极攻略
- 分布式系统架构中的相关概念
- springboot整合支付宝沙箱支付和退款
- 5 万字 124 道MySQL经典面试题总结(2024修订版)
- Lua语法(四)——协程
- 【实战Flask API项目指南】之七 用JWT进行用户认证与授权
- Kettle如何连接SQL Server和问题处理
- 开源浏览器Firefox:使用Docker本地部署并远程访问进行测试
- 【项目实战经验】DataKit迁移MySQL到openGauss(上)
- Linux【OSMCTools 02】OpenStreetMap数据处
- 数据结构:图文详解单链表的各种操作(头插法,尾插法,任意位置插入,删除
- SQL IFNULL()函数简介
- 本地mysql5.7以上版本配置及my.ini
- mysql快速复习(题目进阶1)
- Springboot JPA打印SQL语句及参数(2024最新版)
文章目录
- 声明式事务是什么?
- 一、Spring事务管理器
- 二、基于注解的声明式事务
- 1.1 准备工作
- 1.2 基本事务控制
- 1.3 事务属性:只读
- 1.4 事务属性:超时时间
- 1.5 事务属性:事务异常
- 1.6 事务属性:事务隔离级别
- 1.7 事务属性:事务传播行为
- 三、Spring核心掌握总结
- 总结
声明式事务是什么?
spring-tx : 声明式事务的框架
声明式事务是指使用注解或 XML 配置的方式来控制事务的提交和回滚
开发者只需要添加配置即可, 具体事务的实现由第三方框架实现
程序员:
配置文件即可(注解、xml)
指定哪些方法需要添加事务
以及事务的属性
编程式事务与声明式事事务 区别:
- 编程式事务需要手动编写代码来管理事务
- 而声明式事务可以通过配置文件或注解来控制事务。
使用声明式事务可以将事务的控制和业务逻辑分离开来
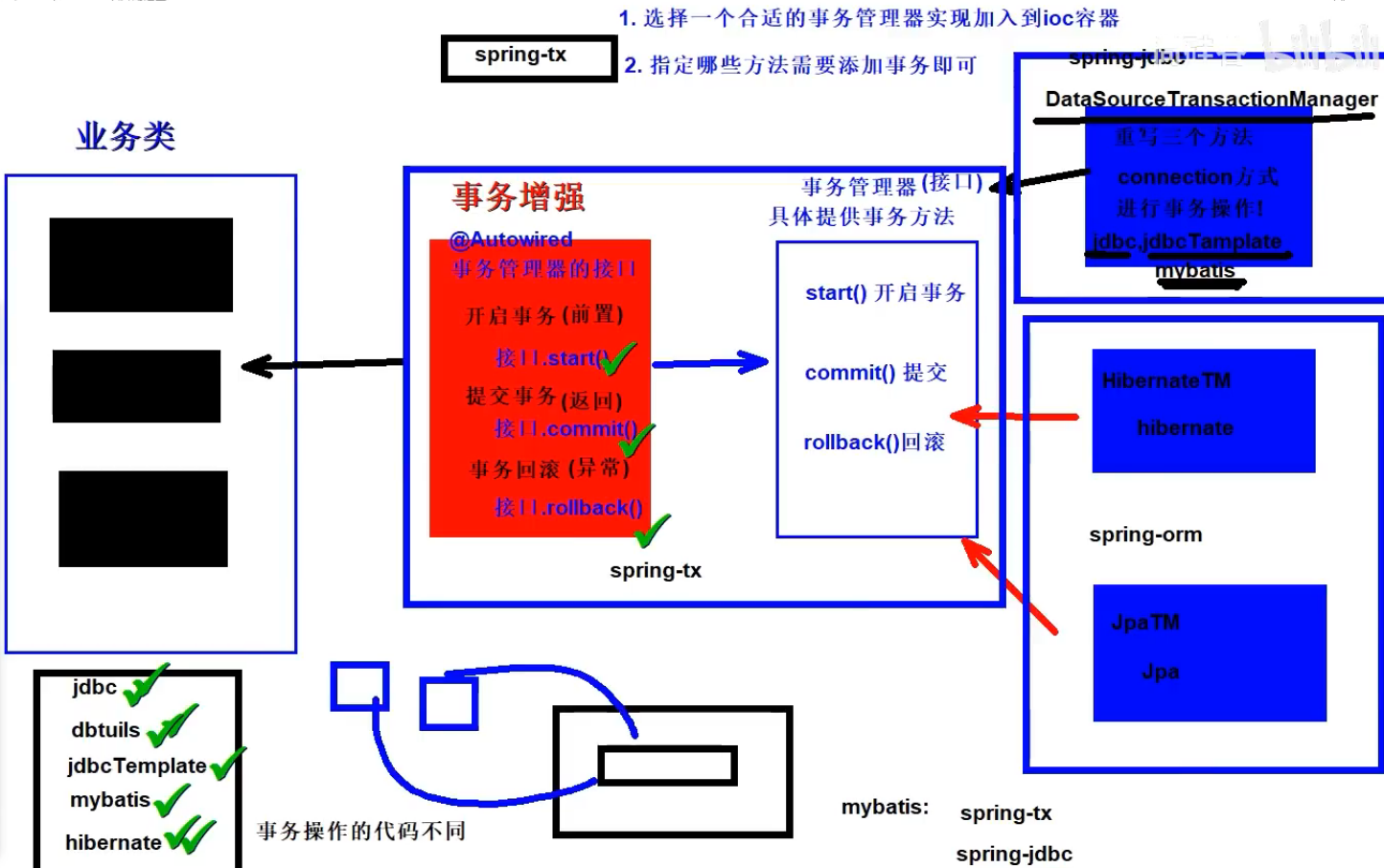
一、Spring事务管理器
Spring声明式事务对应依赖
- spring-tx: 包含声明式事务实现的基本规范(事务管理器规范接口和事务增强等等)
- spring-jdbc: 包含DataSource方式事务管理器实现类DataSourceTransactionManager
- spring-orm: 包含其他持久层框架的事务管理器实现类例如:Hibernate/Jpa等
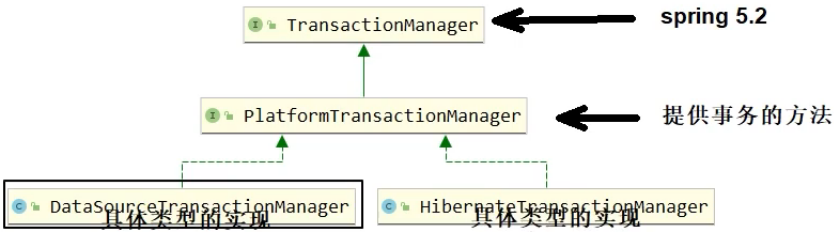
现在要使用的事务管理器是org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager,将来整合 JDBC方式、JdbcTemplate方式、Mybatis方式的事务实现!
DataSourceTransactionManager类中的主要方法:
- doBegin():开启事务
- doSuspend():挂起事务
- doResume():恢复挂起的事务
- doCommit():提交事务
- doRollback():回滚事务
二、基于注解的声明式事务
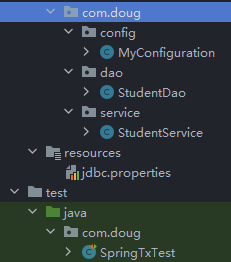
1.1 准备工作
- 导入依赖
org.springframework spring-tx 6.0.6 org.springframework spring-jdbc 6.0.6 - 配置文件
- 外部配置文件
doug.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/studb doug.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver doug.username=root doug.password=root
spring配置文件
package com.doug.config; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import javax.sql.DataSource; @Configuration @PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") @ComponentScan("com.doug") public class MyConfiguration { @Value("${doug.url}") private String url; @Value("${doug.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${doug.username}") private String username; @Value("${doug.password}") private String password; @Bean public DataSource dataSource(){ DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource(); dataSource.setUrl(url); dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver); dataSource.setUsername(username); dataSource.setPassword(password); return dataSource; } @Bean public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){ JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(); jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource); return jdbcTemplate; } }- 准备 dao/service
- dao
@Repository public class StudentDao { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; public void updateNameById(String name,Integer id){ String sql = "update students set name = ? where id = ? ;"; int rows = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, name, id); } public void updateAgeById(Integer age,Integer id){ String sql = "update students set age = ? where id = ? ;"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql,age,id); } }service
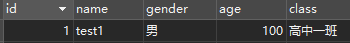
@Service public class StudentService { @Autowired private StudentDao studentDao; public void changeInfo(){ studentDao.updateAgeById(100,1); System.out.println("-----------"); studentDao.updateNameById("test1",1); } }- 测试
@SpringJUnitConfig(MyConfiguration.class) public class SpringTxTest { @Autowired private StudentService studentService; @Test public void TxTest(){ studentService.changeInfo(); } }- 结果
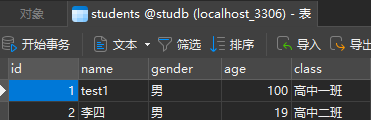
1.2 基本事务控制
- 配置类设置
@Configuration @PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties") @ComponentScan("com.doug") @EnableTransactionManagement // 开启声明式事物管理 public class MyConfiguration { @Value("${doug.url}") private String url; @Value("${doug.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${doug.username}") private String username; @Value("${doug.password}") private String password; @Bean public DataSource dataSource(){ DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource(); dataSource.setUrl(url); dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver); dataSource.setUsername(username); dataSource.setPassword(password); return dataSource; } @Bean public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){ JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(); jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource); return jdbcTemplate; } /** * 装配事务管理实现对象 * @param dataSource * @return */ @Bean public TransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource){ DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource); return transactionManager; } }- 需要事务的方法 添加事务注解
service 层 类方法 添加事务
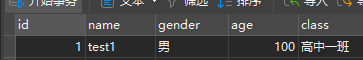
/** * 添加事务 * @Transactional * 位置: 方法 | 类上 * 方法: 当前方法有事务 * 类上: 类下的所有方法都有事务 */ @Transactional public void changeInfo(){ studentDao.updateAgeById(88,1); // 开启事务后 , 这里报错 会进行回滚,前后功能都不会执行 int i = 88/0; // 搞一个报错 System.out.println("-----------"); studentDao.updateNameById("test2",1); }报错 且 数据库无变化,说明已经开启了事务
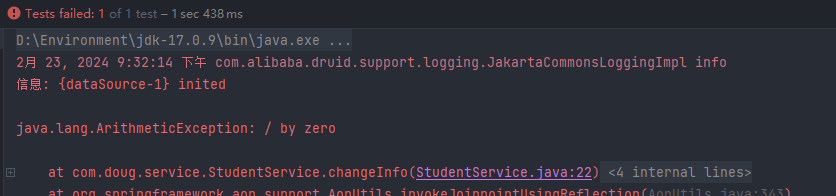
1.3 事务属性:只读
只读模式:
- 只读模式可以提高查询事务的效率!
- 事务只涉及查询代码时,可以使用只读!
- 默认:为FALSE
- 解释:一般情况下,直接在类上添加注解事务
- 类下的所有方法都有实物
- 那么,查询方法可以单独再设置为TRUE,开启只读模式! 提高效率!

@Transactional public class StudentService { @Transactional(readOnly = true) public void getStudentInfo(){ } }1.4 事务属性:超时时间
- 事务在执行过程中,有可能因为遇到某些问题,导致程序卡住,从而长时间占用数据库资源。
- 而长时间占用资源,大概率是因为程序运行出现了问题(可能是Java程序或MySQL数据库或网络连接等等)。
- 此时这个很可能出问题的 程序应该被回滚,撤销它已做的操作,事务结束,把资源让出来,让其他正常程序可以执行。
概括来说就是一句话:超时回滚,释放资源。
/** * 超时时间: * 默认:永远不超时 -1 * 设置timeout = 时间 秒数 超过时间,就会回滚事务和释放异常! org.springframework.transaction.TransactionTimedOutException: Transaction timed out: deadline * 如果类上设置事务属性,方法也设置了事务注解! * 不会生效!,方法上有默认的设置属性会覆盖类上的属性设置! */ @Transactional(timeout = 3) public void changeInfo(){ studentDao.updateAgeById(88,1); try { Thread.sleep(4000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } System.out.println("-----------"); studentDao.updateNameById("test2",1); }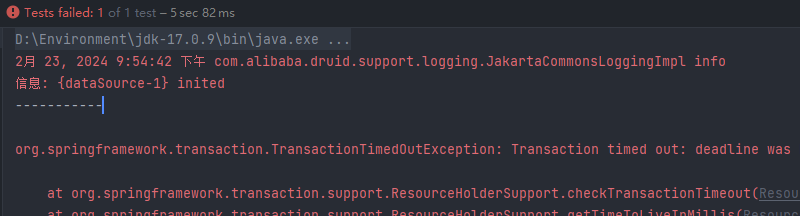
超时,后回滚 数据库无变化
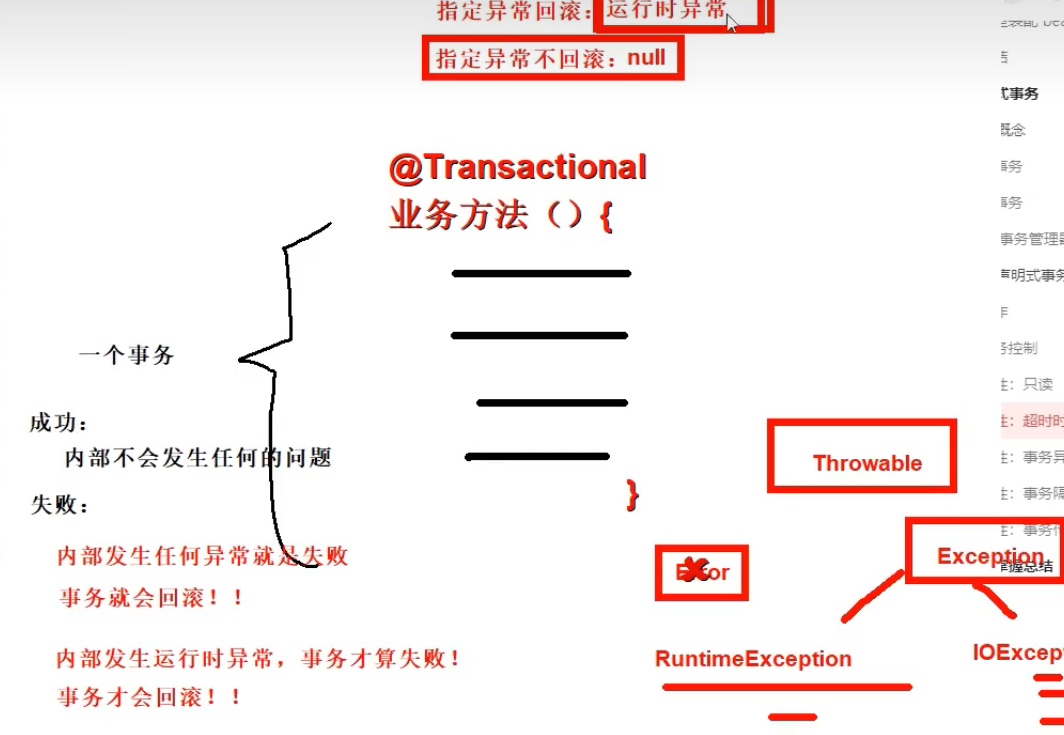
1.5 事务属性:事务异常
指定异常回滚 和 指定异常不回滚

- 默认情况 发生 运行时异常 事务才会回滚!
- RuntimeException and Error
- 我们可以指定发生所有异常都回滚
- rollbackFor = Exception.class
1.6 事务属性:事务隔离级别
数据库事务的隔离级别是指在多个事务并发执行时,数据库系统为了保证数据一致性所遵循的规定。常见的隔离级别包括:
- 读未提交(Read Uncommitted):事务可以读取未被提交的数据,容易产生脏读、不可重复读和幻读等问题。实现简单但不太安全,一般不用。
- 脏读:一个事务读取了另外一个事务未提交的数据
- 不可重复读:一个事务读取另外一个事务提交的修改数据
- 幻读:一个事务读取了另外一个事务插入的数据
- 读已提交(Read Committed):事务只能读取已经提交的数据,可以避免脏读问题,但可能引发不可重复读和幻读。
- 可重复读(Repeatable Read):在一个事务中,相同的查询将返回相同的结果集,不管其他事务对数据做了什么修改。可以避免脏读和不可重复读,但仍有幻读的问题。
- 串行化(Serializable):最高的隔离级别,完全禁止了并发,只允许一个事务执行完毕之后才能执行另一个事务。可以避免以上所有问题,但效率较低,不适用于高并发场景。
- 不同的隔离级别适用于不同的场景,需要根据实际业务需求进行选择和调整。
isolation = 设置事务的隔离级别,mysql默认是repeatable read!
建议可以设置为:第二种级别 Read Committed
1.7 事务属性:事务传播行为
在被调用的子方法中设置传播行为,代表如何处理调用的事务! 是加入,还是新事务等!
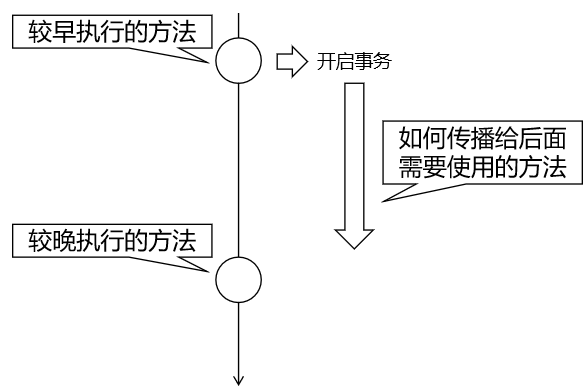

名称 含义 REQUIRED 默认值 如果父方法有事务,就加入,如果没有就新建自己独立! REQUIRES_NEW 不管父方法是否有事务,我都新建事务,都是独立的! 声明两个独立修改数据库的事务业务方法:
- propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED
- 当父方法有事务,就加入其中,合体!(它滚我也滚!)
- 最终就是同一个事物,默认是这样!
- propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED_NEW
- 不管父方法是否有事务,与我无关!
- 独立存在!
注意:
在同一个类中,对于@Transactional注解的方法调用,事务传播行为不会生效。
这是因为Spring框架中使用代理模式实现了事务机制,在同一个类中的方法调用并不经过代理,而是通过对象的方法调用,因此@Transactional注解的设置不会被代理捕获,也就不会产生任何事务传播行为的效果。
三、Spring核心掌握总结
核心点 掌握目标 spring框架理解 spring家族和spring framework框架 spring核心功能 ioc/di , aop , tx spring ioc / di 组件管理、ioc容器、ioc/di , 三种配置方式 spring aop aop和aop框架和代理技术、基于注解的aop配置 spring tx 声明式和编程式事务、动态事务管理器、事务注解、属性
总结
- propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED
- 读未提交(Read Uncommitted):事务可以读取未被提交的数据,容易产生脏读、不可重复读和幻读等问题。实现简单但不太安全,一般不用。
- rollbackFor = Exception.class
- 默认情况 发生 运行时异常 事务才会回滚!
- 需要事务的方法 添加事务注解
- 配置类设置
- 结果
- 测试
- dao
- 准备 dao/service
- 外部配置文件
- 配置文件
- 导入依赖














