- 全国主要城市建筑轮廓(含层高)矢量数据分享及最新AI提取建筑分布方法介
- 自动化机器学习流水线:基于Spring Boot与AI机器学习技术的融
- Python赋能AI数据分析开启人工智能新时代
- 算法D11 | 栈和队列练习 | 20. 有效的括号 1047. 删除
- 【c++】:STL模板中string的使用
- 运维:mysql常用的服务器状态命令
- mysql 中OPTIMIZE TABLE语句用法详解
- re:Invent 构建未来:云计算&生成式 AI 诞生科技新
- 每日五道java面试题之spring篇(六)
- 实现:mysql-5.7.42 到 mysql-8.2.0 的升级(二
- VPN的介绍及自建点对点的OpenVPN和使用方法:保姆级详细教程,(
- 【爬虫】实战1-爬取Boss直聘信息数据
- 机器学习在安全领域的应用:从大数据中识别潜在安全威胁
- Nginx快速入门:访问日志access.log参数详解 |访问日志记
- Spring Cloud Nacos集成Seata2.0 AT模式
- ELFK日志分析系统之搭建ELF+Filebeaat+Zookeepe
- 【微服务】接口幂等性常用解决方案
- 【精·超简单】SpringBoot 配置多个数据源(连接多个数据库)
- 升级php版本(简单明了,轻松升级php任意版本)
- 【Spring】spring中怎么解决循环依赖的问题
- 说一下Spring Security中@PermitAll和@PreA
- 使用Navicat导出导出 MySQL 数据库表结构、表数据到Exce
- 金融支付系统中的云计算与边缘计算
- MySQL日期类型及默认设置
- 【大数据】大数据概论与Hadoop
- IntelliJ IDEA 2023.3 的 AI Assistant
- 蓝桥杯(填空题)
- 搭建nacos集群,并通过nginx实现负载均衡
- “AI 程序员”席卷而来,吴恩达四步设计让 Agent 提前超越 GP
- PHP教程:PHP如何利用post与get方式传值接收数据
堆的应用(一)top K问题
- 一.top k问题的应用本质解析
- 二.top K问题使用案例——从100亿整型的文件中找出前5个最大值
- 1.建堆
- 1.1过程分析
- 1.2过程图模拟
- 1.3向上调整算法代码
- 1.4建堆代码
- 2.处理文件中剩余剩余元素
- 2.1过程分析
- 2.2过程图示例
- 2.3向下调整算法代码
- 2.4处理后续元素代码
- 三.附录源码
一.top k问题的应用本质解析
top k问题解决的是获取前几个最值的问题。
我们知道堆的功能主要是选数,选出最大值或者最小值。那么我们每次获取堆顶元素后,再将剩余元素调整成堆,就可以选出次大的数,如果我们只想要前k个最大值或者最小值,就只需要获取堆顶元素k次,调整k次。比如王者荣耀中的国服榜单,需要的是这个英雄的前十名,我们只需要获取前10名即可。
学习了堆的实现,我们对于比较少的数据可以采用建堆一直push的方式,再取堆顶元素再pop从而找到次大值的方法,循环k次上述操作即可实现。但是如果数据非常多,那么malloc申请空间会失败,此时堆无法建立开辟,此时我们应该如何解决呢?
以找前k个最大值为例:
上面的问题是因为内存不足,为了解决这个问题,这里我们可以从文件中读取k个数据并且建一个小堆,然后再依次处理剩余的元素。
为什么要建小堆?
这里很多人可能第一印象就是建立大堆,从而选出前k个最大值,但是我们想一个问题,如果最大的值在前k个数中,那么最大值就会在堆顶,那么其他k-1个需要找的值就都会比堆顶小,导致无法入堆。
因此我们需要建小堆,如果比堆顶的元素大,那么就和堆顶的元素交换,然后再调整,这样的话最大值就会沉入堆底,直到前k个最大的数都进入堆中。
总结:前k个最小值建大堆,前k个最大值建小堆
我们通过以下的案例来学习解决这一问题。
二.top K问题使用案例——从100亿整型的文件中找出前5个最大值
由一的分析我们可以得知需要建小堆。
我们首先先创建足够多的整形随机数,并保存在文件中。为了验证我们的top k是否正确,我们将随机值取模于一个10000000,保证数据都在这个范围内,然后我们自己手动插入几个“探子”,我们在该txt文件中改变几个值的大小为超过10000000,这样我们就可以通过这几个“探子”是否被找到从而验证是否正确。
在读取前k个元素时顺便建堆,我们采取向上调整建堆的方法。
向上调整建堆:模拟堆的插入的思想,我们使用向上调整算法来建堆(详情请看上篇:堆的实现)
1.建堆
1.1过程分析
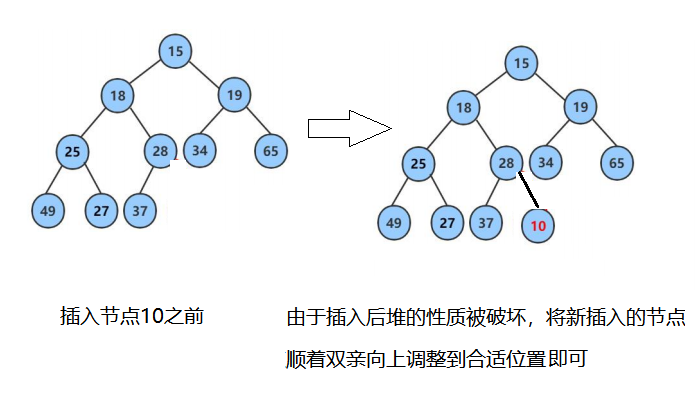
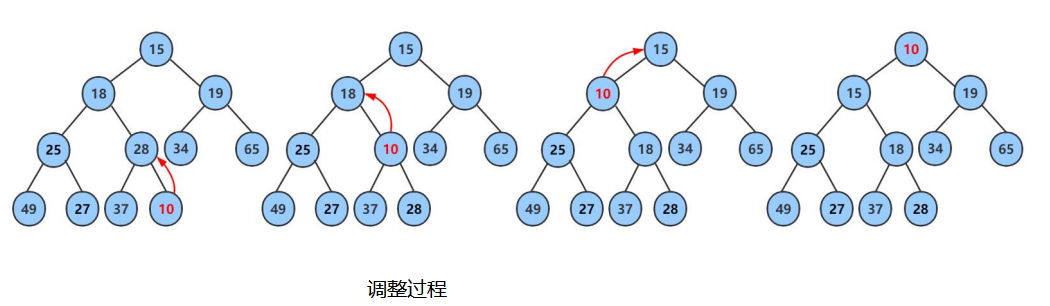
由于向上调整算法和向下调整算法的前提是插入前仍然是堆,插入后改变了堆的性质。因此首先将第一个元素看作堆,然后后面的元素模拟依次入堆的操作,也就是将后面元素的下标依次作为最后一个节点的坐标传入向上调整算法函数之中,这样的话每次向上调整传入下标前面的值为堆,从而满足前提条件。
1.2过程图模拟
1.3向上调整算法代码
void AdjustUp(Hpdatatype* a, int child) { int parent = (child - 1) / 2; while (child > 0) { if (a[child] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); child = parent; parent = (child - 1) / 2; } else { break; } } }1.4建堆代码
int* heap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k); for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { fscanf(fout, "%d", &heap[i]); //从文件中读取数据存储到heap中去 AdjustUp(heap, i); //开始调整 }2.处理文件中剩余剩余元素
2.1过程分析
依次读取文件中的数据,并存储在变量tmp之中,再将其和和堆顶元素比较,比堆顶大,就和堆顶交换(堆顶是最小值,如果它比tmp小,就证明它不是我们需要找的元素),然后再向下调整,如果比堆顶元素小,则不需要入堆,。直到文件读取结束。
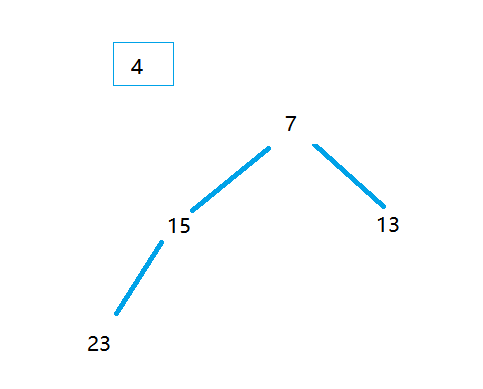
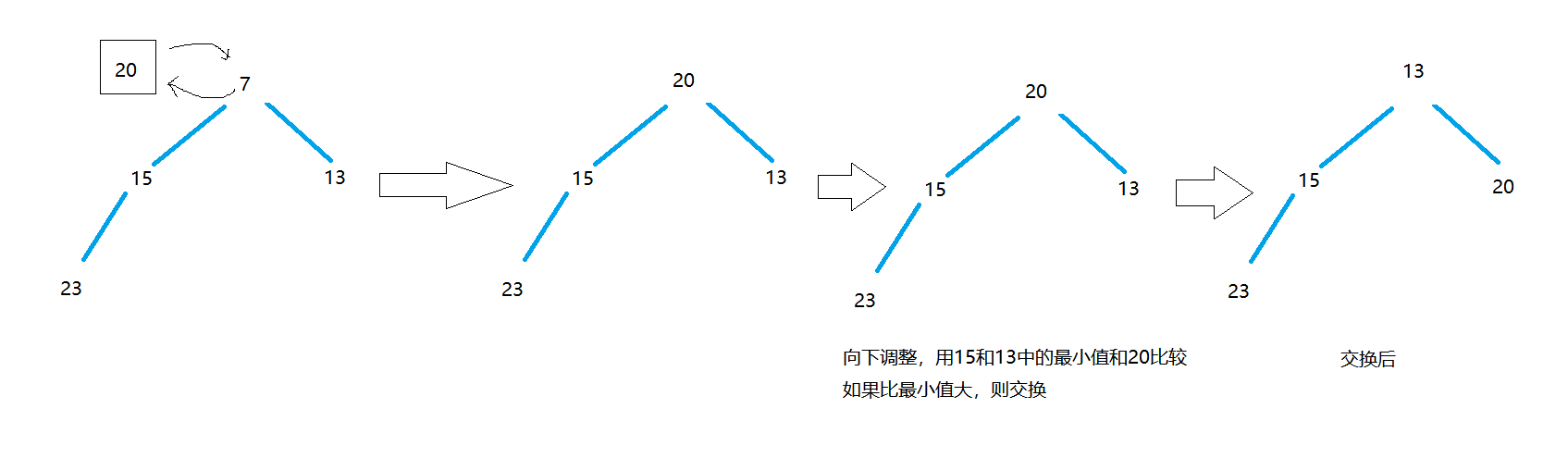
2.2过程图示例
和4比较,不需要入堆,如图:
和20比较,需要入堆,如图:
2.3向下调整算法代码
void AdjustDown(Hpdatatype* a, int size, int parent) { int child = parent * 2 + 1; while (child < size) { if (child + 1 < size && a[child] > a[child + 1]) { child++; } if (a[child] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { break; } } }2.4处理后续元素代码
int tmp = 0;//存储读取的值 while (fscanf(fout, "%d", &tmp) != EOF) { if (tmp > heap[0]) { Swap(&tmp, &heap[0]); AdjustDown(heap, k, 0); } }三.附录源码
向上调整算法代码:
void AdjustUp(Hpdatatype* a, int child) { int parent = (child - 1) / 2; while (child > 0) { if (a[child] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); child = parent; parent = (child - 1) / 2; } else { break; } } }向下调整算法代码:
void AdjustDown(Hpdatatype* a, int size, int parent) { int child = parent * 2 + 1; while (child < size) { if (child + 1 < size && a[child] > a[child + 1]) { child++; } if (a[child] < a[parent]) { Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; } else { break; } } }创建数据代码如下:
void creatInform() { int n = 10000000; srand(time(0)); const char* file = "data.txt"; FILE* fin = fopen(file, "w"); if (fin == NULL) { perror("fopen error"); return; } for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { int x = (rand() + i) % 10000000; fprintf(fin, "%d\n", x); } fclose(fin); }测试代码如下:
void testTopK(const char* file, int k) { FILE* fout = fopen(file, "r"); if (fout == NULL) { perror("fopen error"); return; } int* heap = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k); //建堆 for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { fscanf(fout, "%d", &heap[i]); AdjustUp(heap, i); } int tmp = 0; while (fscanf(fout, "%d", &tmp) != EOF) { if (tmp > heap[0]) { Swap(&tmp, &heap[0]); AdjustDown(heap, k, 0); } } fclose(fout); for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { printf("%d ", heap[i]); } }以上是本次所有内容,谢谢观看。
上一篇:【算法专题】动态规划之子序列问题














