- 华为ensp中链路聚合两种(lacp-static)模式配置方法
- CC++之(五)洛谷刷题基础题 --- 新年好
- 【Mysql-12】一文解读【事务】-【基本操作四大特性并发事务问题事
- java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org
- 【数据库】国产达梦数据库与mysql特点、区别、发展前景
- MyBatis和MyBatis Plus并存及问题解决
- The artifact mysql:mysql-connector-
- MySQL知识点总结(五)——锁
- 【Docker系列】在 Linux 上安装 Docker Compos
- mysql快速复习(题目进阶1)
- 个人博客建设必备:精选域名和主机的终极攻略
- Nginx快速入门:访问日志access.log参数详解 |访问日志记
- 【Ambari】Ansible自动化部署大数据集群
- Docker 安装 Nginx 部署前端项目
- 【手写数据库toadb】虚拟文件描述符,连接表对象与物理文件的纽带,通
- 数据结构——链表
- springboot 实现登录注册
- IntelliJ IDEA 编辑器的全局搜索中使用正则表达式
- SpringCloud最新最全面试题
- Nginx系列:windows10系统下安装nginx的安装并配置!
- MySQL中如何将字符串替换
- PostgreSQL误删数据的救命稻草
- org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupl
- 【Node.js小知识】npm install出现:npm ERR!
- 宝塔面板安装Python和Flask(新版Python项目)
- 2-1.Hadoop大数据集群搭建之---本地模式
- 事务及SpringBoot中的事务开启
- 【算法专题】FloodFill 算法
- MySQL 之 安装与配置环境变量
- SpringBoot异常:类文件具有错误的版本 61.0, 应为 52
Spring 事务(Transactional)失效的七种原因及解决方案(含项目代码)
简介
“Spring框架提供了强大的事务管理功能,能够确保数据库操作的一致性和可靠性。然而,有时候我们可能会遇到Spring事务失效的情况,导致数据不一致或操作失败。本文将探讨Spring事务失效的原因,以及如何避免和解决这些问题。通过深入了解失效原因,我们可以更好地利用Spring事务管理功能,确保系统的稳定性和可靠性。”
项目搭建
代码仓库URL:https://gitee.com/itwenke/spring-boot-demo/tree/master/transactional
项目截图:
pom配置
mysql mysql-connector-java com.baomidou mybatis-plus-boot-starter 3.5.3.1
数据库配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring-boot-demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&rewriteBatchedStatements=true&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
数据表结构
CREATE TABLE `bank_account` ( `id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `account` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8mb4_bin NOT NULL COMMENT '账户', `balance` bigint NOT NULL COMMENT '余额', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_bin COMMENT='银行账户';
失效原因
私有方法private
Spring的事务代理通常是通过Java动态代理或CGLIB动态代理生成的,这些代理要求目标方法是公开可访问的(public)。私有方法无法被代理,因此事务将无效。
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
private void addBankAccount(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
throw new Exception("测试事务回滚");
}
直接使用时,这种场景也不太容易出现,因为IDEA会有提醒。
解决方法是将目标方法改为public或protected。
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void addBankAccount(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
throw new Exception("测试事务回滚");
}
目标类没有配置为Bean
Spring的事务管理需要在Spring容器中配置的Bean上才能生效。如果目标类没有被配置为Spring Bean,那么事务将无法被应用。
public class NonBeanDemo {
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void addBankAccount(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
IBankAccountService bankAccountService = SpringBeanUtil.getBean(IBankAccountService.class);
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
throw new Exception("测试事务回滚");
}
}
解决方法是确保目标类被正确配置为Spring Bean。
@Component
public class NonBeanDemo {
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void addBankAccount(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
IBankAccountService bankAccountService = SpringBeanUtil.getBean(IBankAccountService.class);
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
throw new Exception("测试事务回滚");
}
}
异常不匹配
@Transactional注解默认处理运行时异常,即只有抛出运行时异常,才会触发事务回滚。
@Transactional
public void addBankAccount(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
throw new Exception("测试事务回滚");
}
解决方法是@Transactional设置为@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)。
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void addBankAccount(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
throw new Exception("测试事务回滚");
}
跨越多个线程
如果您的应用程序在多个线程之间共享数据库连接和事务上下文,事务可能会失效,除非适当地配置事务传播属性。
- 子线程抛异常,主线程正常:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void addBankAccount1() {
new Thread(() -> {
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
bankAccount.setAccount("11111111");
bankAccount.setBalance(10000L);
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
}).start();
new Thread(() ->{
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
bankAccount.setAccount("22222222");
bankAccount.setBalance(10000L);
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
throw new RuntimeException("测试事务回滚");
}).start();
}
- 主线程抛异常,子线程正常:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void addBankAccount2() {
new Thread(() -> {
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
bankAccount.setAccount("11111111");
bankAccount.setBalance(10000L);
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
}).start();
new Thread(() ->{
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
bankAccount.setAccount("22222222");
bankAccount.setBalance(10000L);
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
}).start();
throw new RuntimeException("测试事务回滚");
}
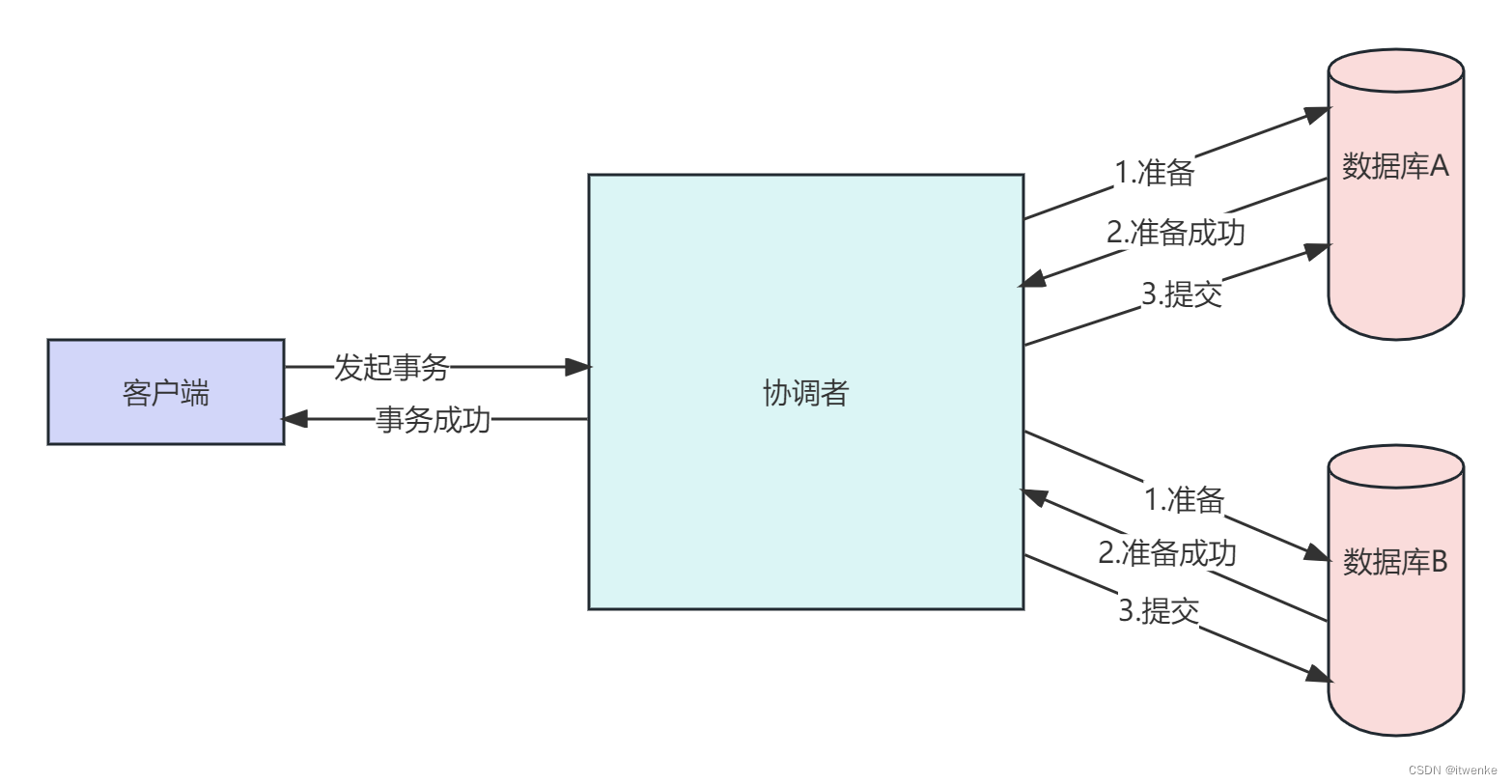
解决方法:参考分布式事务2PC(二阶段提交)方案,2PC是同步阻塞协议,需要等待各个线程执行完成才能进行”提交“还是”回滚”的操作。
public class MultiThreadingTransactionManager {
/**
* 事务管理器
*/
private final PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager;
/**
* 超时时间
*/
private final long timeout;
/**
* 时间单位
*/
private final TimeUnit unit;
/**
* 主线程门闩:当所有的子线程准备完成时,通知主线程判断统一”提交“还是”回滚”
*/
private final CountDownLatch mainStageLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
/**
* 子线程门闩:count 为0时,说明子线程都已准备完成了
*/
private CountDownLatch childStageLatch = null;
/**
* 是否提交事务
*/
private final AtomicBoolean isSubmit = new AtomicBoolean(true);
/**
* 构造方法
*
* @param platformTransactionManager 事务管理器
* @param timeout 超时时间
* @param unit 时间单位
*/
public MultiThreadingTransactionManager(PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
this.platformTransactionManager = platformTransactionManager;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.unit = unit;
}
/**
* 任务执行器
*
* @param tasks 任务列表
* @param executorService 线程池
* @return 是否执行成功
*/
public boolean execute(List tasks, ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executorService) {
// 排查null空值
tasks.removeAll(Collections.singleton(null));
// 属性初始化
init(tasks.size());
for (Runnable task : tasks) {
// 创建线程
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// 判断其它线程是否已经执行任务失败,失败就不执行了
if (!isSubmit.get()) {
childStageLatch.countDown();
}
// 开启事务
DefaultTransactionDefinition defaultTransactionDefinition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
TransactionStatus transactionStatus = platformTransactionManager.getTransaction(defaultTransactionDefinition);
try {
// 执行任务
task.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 任务执行失败,设置回滚
isSubmit.set(false);
}
// 计数器减一
childStageLatch.countDown();
try {
// 等待主线程的指示,判断统一”提交“还是”回滚”
mainStageLatch.await();
if (isSubmit.get()) {
// 提交
platformTransactionManager.commit(transactionStatus);
} else {
// 回滚
platformTransactionManager.rollback(transactionStatus);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 线程池执行任务
executorService.execute(thread);
}
try {
// 主线程等待所有子线程准备完成,避免死锁,设置超时时间
childStageLatch.await(timeout, unit);
long count = childStageLatch.getCount();
// 主线程等待超时,子线程可能发生长时间阻塞,死锁
if (count > 0) {
// 设置回滚
isSubmit.set(false);
}
// 主线程通知子线程”提交“还是”回滚”
mainStageLatch.countDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 返回执行结果是否成功
return isSubmit.get();
}
/**
* 属性初始化
* @param size 任务数量
*/
private void init(int size) {
childStageLatch = new CountDownLatch(size);
}
}
注意事项1: 2PC是同步阻塞协议,各个任务会等待所有的任务完成准备阶段才能进一步执行,所以在使用中一定要给任务列表提供充足的空闲线程,比如任务列表长度为8,线程池最大线程数不能小于8,否则会使其中的几个任务得不到执行,而其他线程会一直进行等待。即使有一阶段超时处理,事务也始终得不到提交。
注意事项2: 如果你的任务是对数据库进行操作,需要考虑数据库连接是否充足,线程等待过程中不会释放数据库连接,如果Connection不够,即使任务被线程池调度执行,也会阻塞在获取数据库连接中,同样会发生“死锁”。
事务传播属性
事务传播属性定义了事务如何传播到嵌套方法或外部方法。如果事务传播属性设置不正确,可能会导致事务失效或不符合预期的行为。
以下是七种事务传播类型:
- REQUIRED: 如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务,如果当前没有事务,则创建一个新的事务。这是最常用的传播行为,也是默认的,适用于大多数情况。(默认事务:有就加入,没有就新建)
- REQUIRES_NEW: 无论当前是否存在事务,都创建一个新的事务。如果当前存在事务,则将当前事务挂起。适用于需要独立事务执行的场景,不受外部事务的影响。(独立事务:有没有,都新建)
- SUPPORTS: 如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务,如果当前没有事务,则以非事务方式执行。适用于不需要强制事务的场景,可以与其他事务方法共享事务。(不强制事务:有就加入,没有就没有)
- NOT_SUPPORTED: 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则将当前事务挂起。适用于不需要事务支持的场景,可以在方法执行期间暂时禁用事务。(非事务:有不加入,没有也不新建)
- MANDATORY: 如果当前存在事务,则加入该事务,如果当前没有事务,则抛出异常。适用于必须在事务中执行的场景,如果没有事务则会抛出异常。(强制事务:有就加入,没有就抛异常)
- NESTED: 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务中执行,如果当前没有事务,则创建一个新的事务。嵌套事务是外部事务的一部分,可以独立提交或回滚。适用于需要在嵌套事务中执行的场景。(嵌套事务:有就嵌套,没有就新建)
- NEVER: 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。适用于不允许在事务中执行的场景,如果存在事务则会抛出异常。(强制非事务:没有就没有,有就抛异常)
使用CGLIB动态代理
默认情况下,Spring的事务代理使用基于接口的JDK动态代理。如果您将@Transactional注解声明在接口上,而目标类是使用CGLIB代理的,事务将不会生效。
解决方法是将@Transactional注解移到目标类的方法上,或者配置Spring以使用CGLIB代理接口。
内部类访问
类内部非直接访问带注解标记的方法addBankAccount,而是通过类普通方法 testInnerClass,然后由 testInnerClass 调用 addBankAccount。
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void addBankAccount(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
throw new Exception("测试事务回滚");
}
public void testInnerClass(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
addBankAccount(bankAccount);
}
解决方法是使用SpringBeanUtil.getBean()获取代理对象。
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void addBankAccount(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
bankAccountService.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
throw new Exception("测试事务回滚");
}
public void testInnerClass(BankAccount bankAccount) throws Exception {
InnerClassDemo innerClassDemo = SpringBeanUtil.getBean(InnerClassDemo.class);
innerClassDemo.addBankAccount(bankAccount);
}














