- MySQL的启动与连接
- 【每日一题】LeetCode——链表的中间结点
- lua学习笔记20(lua中一些自带库的学习)
- 大数据技术原理及应用课实验4: NoSQL和关系数据库的操作比较
- 云计算——虚拟化VMware ESXI 7.0安装(一)
- Jenkins 命令无法后台运行,使用BUILD
- SpringBoot 整合Swagger2
- 2023 最新版IntelliJ IDEA 2023.1创建Java
- MySQL默认值(DEFAULT)和MySQL非空约束(NOT NUL
- 深度解析 Spring 源码:三级缓存机制探究
- Nginx快速入门:访问日志access.log参数详解 |访问日志记
- 解决mysql:2059 -Authentication plugin
- Go-Zero微服务快速入门和最佳实践(一)
- .NET CORE消息队列RabbitMQ
- java版本使用springboot vue websocket we
- Kubernetes(K8s)与虚拟GPU(vGPU):实现高效管理和
- Spring Boot学习随笔- 集成MyBatis-Plus(二)条
- workstation 用途
- Leetcode-二叉树oj题
- golang面试题大全
- 揭秘智慧礼品背后的故事
- Spring Boot 框架
- Golang入门基础
- docker exec
- SpringBoot集成WebSocket,实现后台向前端推送信息
- SpringBoot-打印请求的入参和出参
- 【自媒体创作利器】AI白日梦+ChatGPT 三分钟生成爆款短视频
- 大数据 DataX-Web 详细安装教程
- Android Studio安装超详细步骤(包括SDK安装不成功,模拟
- 初学者解决 springboot报错Error starting Ap
Spring Boot为开发者提供了多种方式在应用启动时执行自定义代码,这些方式包括注解、接口实现和事件监听器。在本篇博客中,我们将探讨一些常见的方法,以及如何利用它们在应用启动时执行初始化逻辑。
1. @PostConstruct注解
`@PostConstruct`注解可以标注在方法上,该方法将在类被初始化后调用。在Spring Boot应用中,你可以使用这个注解来执行一些初始化的逻辑。
@PostConstruct
public void doSomething(){
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("do something");
}
2. ApplicationListener接口
实现`ApplicationListener`接口并监听`ApplicationStartedEvent`事件,这样你的逻辑将在应用启动后被触发。
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent event) {
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("ApplicationListener executed");
}
}
3. @EventListener注解
使用`@EventListener`注解,可以将方法标记为事件监听器,并在特定事件发生时执行。
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
public class MyEventListener {
@EventListener(ApplicationStartedEvent.class)
public void onApplicationEvent() {
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("@EventListener executed");
}
}
4. ApplicationRunner接口
实现`ApplicationRunner`接口,该接口的`run`方法会在Spring Boot应用启动后执行。
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
public class MyApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("ApplicationRunner executed");
}
}
5. CommandLineRunner接口
与`ApplicationRunner`类似,`CommandLineRunner`接口的`run`方法也在应用启动后执行。
public class MyCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("CommandLineRunner executed");
}
}
Demo代码
完整如下
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartedEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
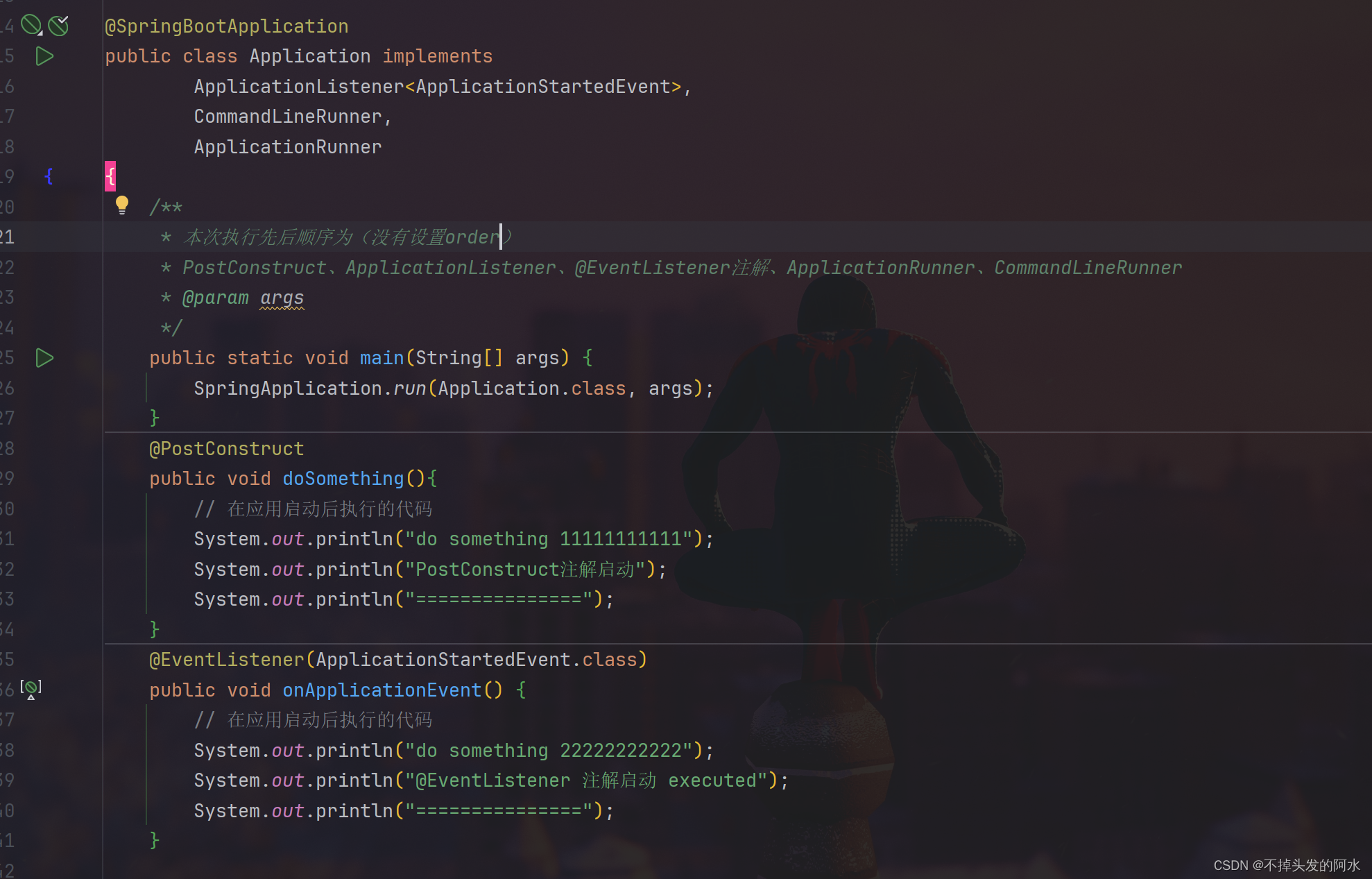
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application implements
ApplicationListener,
CommandLineRunner,
ApplicationRunner
{
/**
* 本次执行先后顺序为(没有设置order)
* PostConstruct、ApplicationListener、@EventListener注解、ApplicationRunner、CommandLineRunner
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@PostConstruct
public void doSomething(){
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("do something 11111111111");
System.out.println("PostConstruct注解启动");
System.out.println("===============");
}
@EventListener(ApplicationStartedEvent.class)
public void onApplicationEvent() {
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("do something 22222222222");
System.out.println("@EventListener 注解启动 executed");
System.out.println("===============");
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent event) {
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("do something 3333333333");
System.out.println("ApplicationListener executed");
System.out.println("===============");
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("do something 44444444");
System.out.println("CommandLineRunner启动");
System.out.println("===============");
}
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
// 在应用启动后执行的代码
System.out.println("do something 55555555");
System.out.println("ApplicationRunner启动");
System.out.println("===============");
}
}
Demo分析
-
@PostConstruct注解方法 (doSomething方法) 在类初始化后被调用,因此会首先输出。
-
ApplicationListener接口方法 (onApplicationEvent方法) 在应用启动后执行,会输出其相关的信息。
-
@EventListener注解方法 (onApplicationEvent方法) 同样在应用启动后执行,会输出其相关的信息。
-
ApplicationRunner接口方法 (run方法) 在ApplicationListener之后执行,它用于在Spring Boot应用启动后执行一些额外的逻辑。
-
CommandLineRunner接口方法 (run方法) 也在ApplicationListener之后执行,用于在Spring Boot应用启动后执行一些额外的逻辑。
总结
通过以上几种方式,你可以根据项目的需求选择合适的初始化方法。无论是使用注解、接口实现,还是事件监听器,Spring Boot提供了灵活的机制来管理应用启动时的自定义逻辑,使得开发者能够更方便地控制应用的初始化过程。在实际项目中,通常根据具体场景选择其中一种或多种方式,以满足不同的需求。
上一篇:详细剖析MySQL临键锁














