- docker搭建部署mysql并挂载指定目录
- 【大数据实时数据同步】超级详细的生产环境OGG(GoldenGate)
- Nginx安装(最全教程)
- Mysql 将数据按照年月分组 统计
- Node.js教程(想入门就来点进来看看)
- 深入理解深度学习:LabML AI注解实现库
- 「SpringBrick快速入门指南」:一款基于Spring Boot
- 探索Headless组件与Tailwind CSS的魔力——前端开发的
- 【mysql】mysql命令使用大全,你想要的都在这里
- idea2023专业版安装破解+maven配置教程
- SpringBoot整合Druid数据库连接池&多数据源&am
- 数字乡村创新实践探索农业现代化与乡村振兴新路径:科技赋能农村全面振兴与
- Docker部署nginx,挂载,并配置nginx.conf
- 若依(前后端分离版)部署全流程 | 宝塔部署SpringBoot项目踩
- MySQL中的any
- Go-Zero微服务快速入门和最佳实践(一)
- 基于在线学习的分布式流量实时分析系统设计与实现
- Linux系统部署SQL Server结合内网穿透实现公网访问本地数据
- 【MySQL】使用C语言连接数据
- 已解决org.springframework.dao.DataAcce
- Golang流程控制语句
- 5 万字 124 道MySQL经典面试题总结(2024修订版)
- 已解决org.springframework.amqp.AmqpIOE
- OpenAI 推出新网络爬虫GPTBot,为GPT-5做准备
- 【每日一题】LeetCode——链表的中间结点
- 刷题之Leetcode24题(超级详细)
- 如何利用SpringSecurity进行认证与授权
- mysql数据库连接报错:is not allowed to conn
- 【Sql】sql server还原数据库的时候,提示:因为数据库正在使
- 超简单的正则表达式从入门到精通

- 🎥 个人主页:Dikz12
- 📕格言:吾愚多不敏,而愿加学
- 欢迎大家👍点赞✍评论⭐收藏
目录
Spring 是什么?
什么是 IoC容器?
传统开发模式
loC开发模式
IoC的优势
IoC 的使用
Bean的存储
方法注解
DI
属性注入
构造⽅法注⼊
Setter 注⼊
@Autowired存在的问题
解决方案:
@Autowired和@Resource的区别
Spring 是什么?
Spring是一个开发应用框架,其目的是用于简化企业级应用程序开发. Springd的原生框架指的是Spring Core、Spring FrameWork; 这个概念是比较抽象的,可以用一句更具体的话来概述:Spring是包含众多工具的 IoC容器.
什么是 IoC容器?
“容器”通常指的是一种可以用来盛放物品的器皿;⽣活中的⽔杯,垃圾桶,冰箱等等这些都是容器,像 List/ Map就是数据存储的容器、Tomcat 就是Web容器;
IoC:Inversion of Control (控制反转),也是Spring两大核心思想之一. 也就是说: Spring是⼀个"控制反转"的容器.
什么是控制反转?
也就是控制权反转,获取依赖对象的过程被反转了,当需要 某个对象时,传统开发模式中需要自己通过new创建对象,现在不需要在进行创建,而是把这个创建对象的任务交给了容器. 程序只需要依赖注入(DI)就可以. 这个容器就是IoC容器.
IoC是一种思想,在生活中也有体现:
比如:传统的驾驶方式,车辆的控制权需要由驾驶员来控制,而现在就可以把驾驶权交给自动化系统来控制。
IoC是一种思想,DI是一种实现方式!
传统开发模式
设计轮⼦(Tire),然后根据轮⼦的⼤⼩设计底盘(Bottom),接着根据底盘设计⻋⾝(Framework),最后根据⻋⾝设计好整个汽⻋(Car)。这⾥就出现了⼀个"依赖"关系:汽⻋依赖⻋⾝,⻋⾝依赖底盘,底盘依赖轮⼦.
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Car car = new Car(17); car.run(); } } static class FrameWork { private Bottom bottom; public FrameWork(int size) { bottom = new Bottom(size); } } static class Bottom { private Tire tire; public Bottom(int size) { tire = new Tire(size); System.out.println("Bottom...init.."); } } static class Tire { public int size; private String color; public Tire(int size) { this.size = size; System.out.println("tire....init...size:"+size); } }从以上代码可以看出,以上程序的问题是:当最底层代码改动之后,整个调⽤链上的所有代码都需要修改.程序的耦合度⾮常⾼(修改⼀处代码,影响其他处的代码修改)
loC开发模式
把调⽤汽⻋的程序⽰例改造⼀下,把创建⼦类的⽅式,改为注⼊传递的⽅式.
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Tire tire= new Tire(17,"red"); Bottom bottom = new Bottom(tire); Framework framework = new Framework(bottom); Car car = new Car(framework); car.run(); } }代码经过以上调整,⽆论底层类如何变化,整个调⽤链是不⽤做任何改变的,这样就完成了代码之间的解耦,从⽽实现了更加灵活、通⽤的程序设计了.
IoC的优势
- 资源集中管理,实现资源的可配置和易管理。
- 降低了使⽤资源双⽅的依赖程度,也就是我们说的耦合度(解耦)。
IoC 的使用
Bean的存储
共有两类注解类型可以实现:
- 1. 类注解:@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component、@Configuration.
- 2. ⽅法注解:@Bean.
@Controller //把这个对象交给Spring进行管理 public class UserController { public void hello() { System.out.println("Hello,Controller"); } }获取对象:
public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(IocDemoApplication.class, args); //从Spring上下⽂中获取对象 UserController userController = context.getBean(UserController.class); userController.hello(); }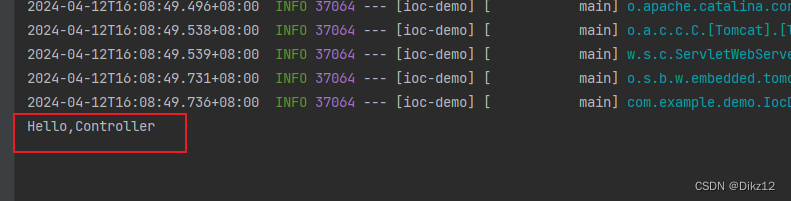
- @Controller:控制层,接收请求,对请求进⾏处理,并进⾏响应.
- @Servie:业务逻辑层,处理具体的业务逻辑.
- @Repository:数据访问层,也称为持久层.负责数据访问操作
- @Component :组件存储.
- @Configuration:配置层.处理项⽬中的⼀些配置信息
方法注解
类注解是添加到某个类上的,但是存在两个问题:
- 1. 使⽤外部包⾥的类,没办法添加类注解
- 2. ⼀个类,需要多个对象,⽐如多个数据源
这种场景,我们就需要使⽤⽅法注解@Bean.
@Configuration public class BeanConfig { @Bean("u1") public User user1() { User user = new User(); user.setName("zhangsan"); user.setAge(18); return user; } }@Bean 方法注解要搭配类注解一起使用,否则就是报错!! 可以对Bean对象进行重命名操作.
DI
依赖注⼊是⼀个过程,是指IoC容器在创建Bean时,去提供运⾏时所依赖的资源,⽽资源指的就是对象.
关于依赖注⼊,Spring也给我们提供了三种⽅式:
- 1. 属性注⼊
- 2. 构造⽅法注⼊
- 3. Setter注⼊
属性注入
属性注⼊是使⽤@Autowired注解实现的. 比如:将Service 类注⼊到 Controller类中.
@Controller //把这个对象交给Spring进行管理 public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; public void hello() { System.out.println("Hello,Controller"); userService.hello(); } }@Service public class UserService { public void hello() { System.out.println("Hello,UserService..."); } }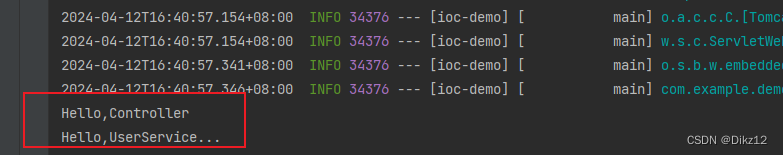
构造⽅法注⼊
@Controller public class UserController2 { //注⼊⽅法2: 构造⽅法 private UserService userService; public UserController2() { } @Autowired public UserController2(UserService userService) { this.userService = userService; } public void hi(){ System.out.println("hi,UserController2..."); userService.hello(); } }去掉@Autowired,就会报异常,如下:
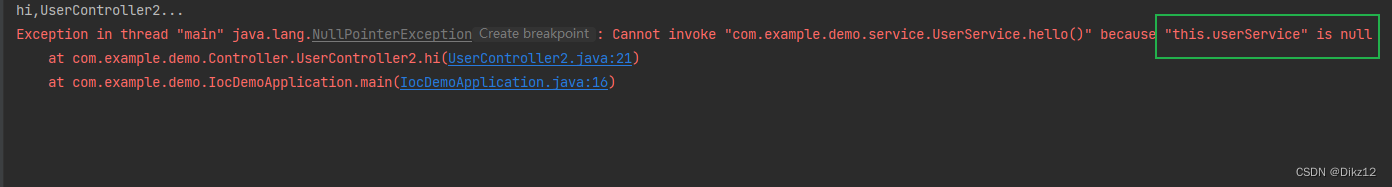
如果类只有⼀个构造⽅法,那么,@Autowired注解可以省略;如果类中有多个构造⽅法,那么需要添加上@Autowired来明确指定到底使⽤哪个构造⽅法。
Setter 注⼊
@Controller public class UserController3 { //注⼊⽅法3: Setter⽅法注⼊ private UserService userService; @Autowired public void setUserService(UserService userService) { this.userService = userService; } public void hello() { System.out.println("hello,UserController3..."); userService.hello(); } }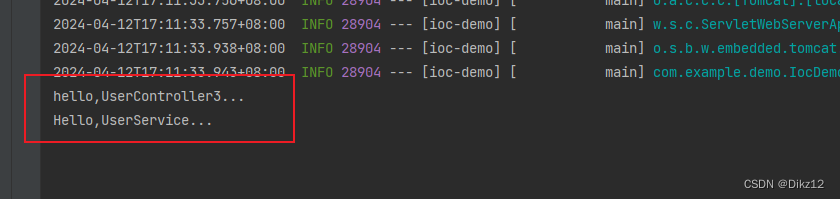
如果去掉@Autowired的话,就会报空指针异常!
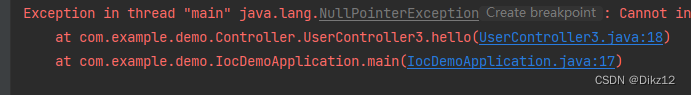
@Autowired存在的问题
当同⼀类型存在多个bean时,使⽤@Autowired会存在问题.
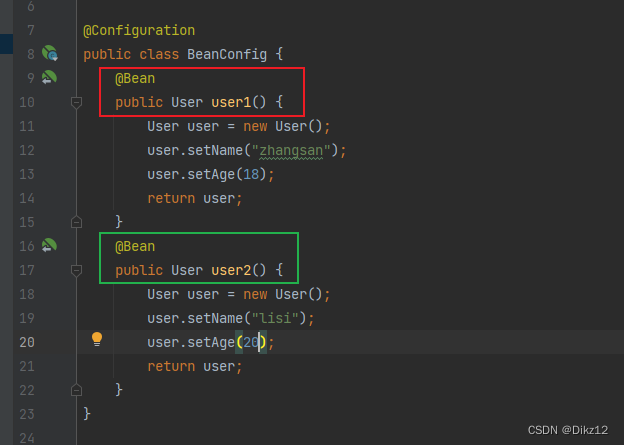
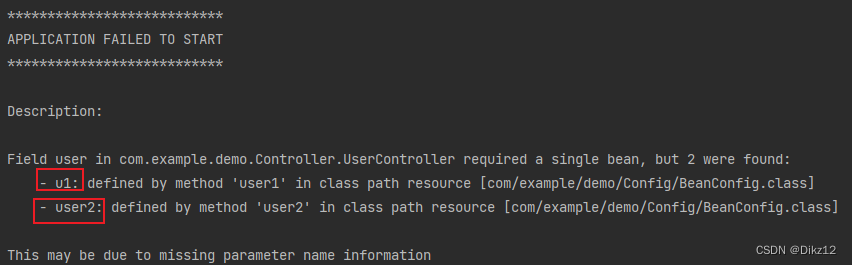
会出两个bean对象,非唯一的bean对象,Spring就不知道要用那个了,直接就启动失败!
解决方案:
1.修改@Autowired的属性名跟Bean的名称一致.
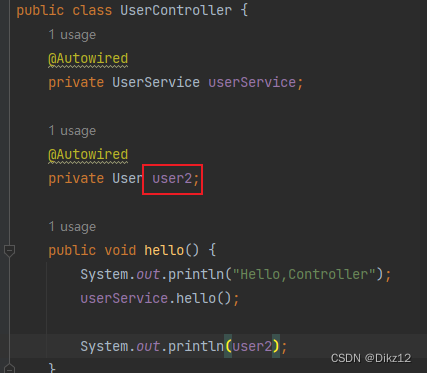
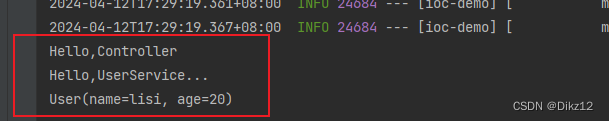
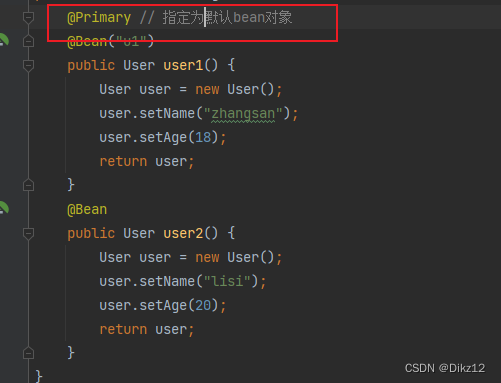
2.使⽤@Primary注解:当存在多个相同类型的Bean注⼊时,加上@Primary注解,来确定默认的实现.
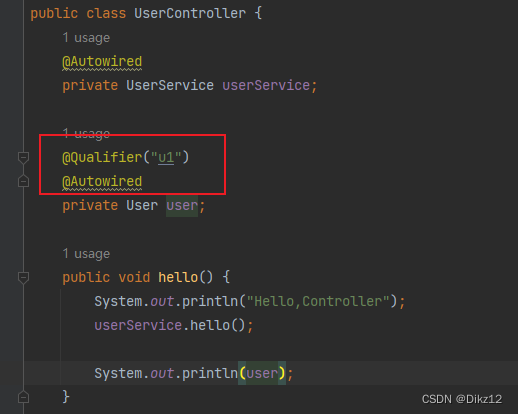
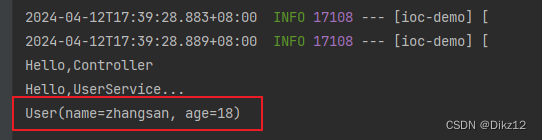
3. 使⽤@Qualifier注解:指定当前要注⼊的bean对象。在@Qualifier的value属性中,指定注⼊的bean的名称。 @Qualifier注解不能单独使⽤,必须配合@Autowired使⽤.
4.使⽤@Resource注解:是按照bean的名称进⾏注⼊。通过name属性指定要注⼊的bean的名称。
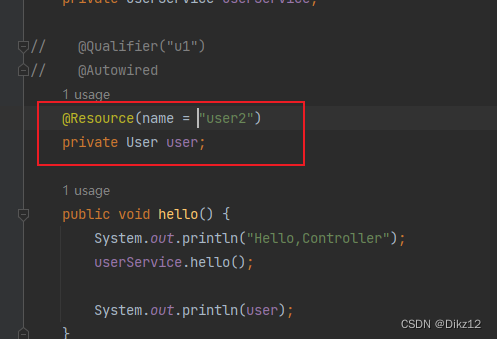
@Autowired和@Resource的区别
- @Autowired默认是以类型注入的,当同一个类型有多个对象,也会按名称进行匹配,如果名称匹配不到,就会报错;@Resource 是按照名称注入的,使用name指定注入。
- @Autowired是由Spring提供的注解;@Resource是JDK提供的注解。














