- 实现SpringMVC底层机制(二)
- 【PyJavaC++三种语言OD2023C卷真题】20天拿下华为OD笔
- 如何使用Flask搭建web程序框架并实现无公网IP远程访问本地程序
- Django学习(1):Django项目的初步创建与简单配置
- SQL拆分字段内容(含分隔符)
- Uncaught SyntaxError: Unexpected to
- Mysql中的Optimize table命令
- 数据库-MySQL 实战项目——学生选课系统数据库设计与实现(附源码)
- SpringBoot 使用【AOP 切面+注解】实现在请求调用 Con
- Spring Boot国际化i18n配置指南
- Rust入门:C++和Rust动态库(dll)的相互调用
- LLM-AI大模型介绍
- 探索设计模式的魅力:开启智慧之旅,AI与机器学习驱动的微服务设计模式探
- SQL中 JOIN 的两种连接类型:内连接(自然连接、自连接、交叉连接
- 【SQL Server】超详细SQLServer日期转换、字符串、数学
- 2024年04月09日 Go生态洞察:2024年上半年Go开发者调查报
- 基于Django美食菜谱网站和点评系统设计与实现(Pycharm+Py
- MySQL用户与权限管理
- 神州云服务平台(型号:DCC-CRL1000)基本配置教学视频
- Go-Zero微服务快速入门和最佳实践(一)
- 云计算时代的运维: 职业发展方向与岗位选择
- 92款超级漂亮的css按钮样式 复制即用
- vanna:基于RAG的text2sql框架
- 深入理解 SQL UNION 运算符及其应用场景
- Navicat、Microsoft SQL Server Manage
- SpringBoot整合参数校验
- golang面试题大全
- 【postgresql 基础入门】表的约束(二) 唯一unique、非
- 【已解决】.nginx: error while loading sh
- 说一下Spring Security中@PermitAll和@PreA
1.什么是BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor是bean的后置处理器,会影响bean的一些行为甚至是替换原有的bean。了解BeanPostProcessor之前最好有对BeanFactoryPostProcessor有一些了解,不了解的小伙伴可以查看我的上篇博文Spring之BeanFactoryPostProcessor
2.BeanPostProcessor是在什么时机注入到Spring中的
BeanPostProcessor从本质上讲也是一个bean,它早于其他普通bean之前实例化,然后作用于其他普通bean,我们看一下Spring源码中实例化时机
具体源码在AbstractApplicationContext#refresh方法中
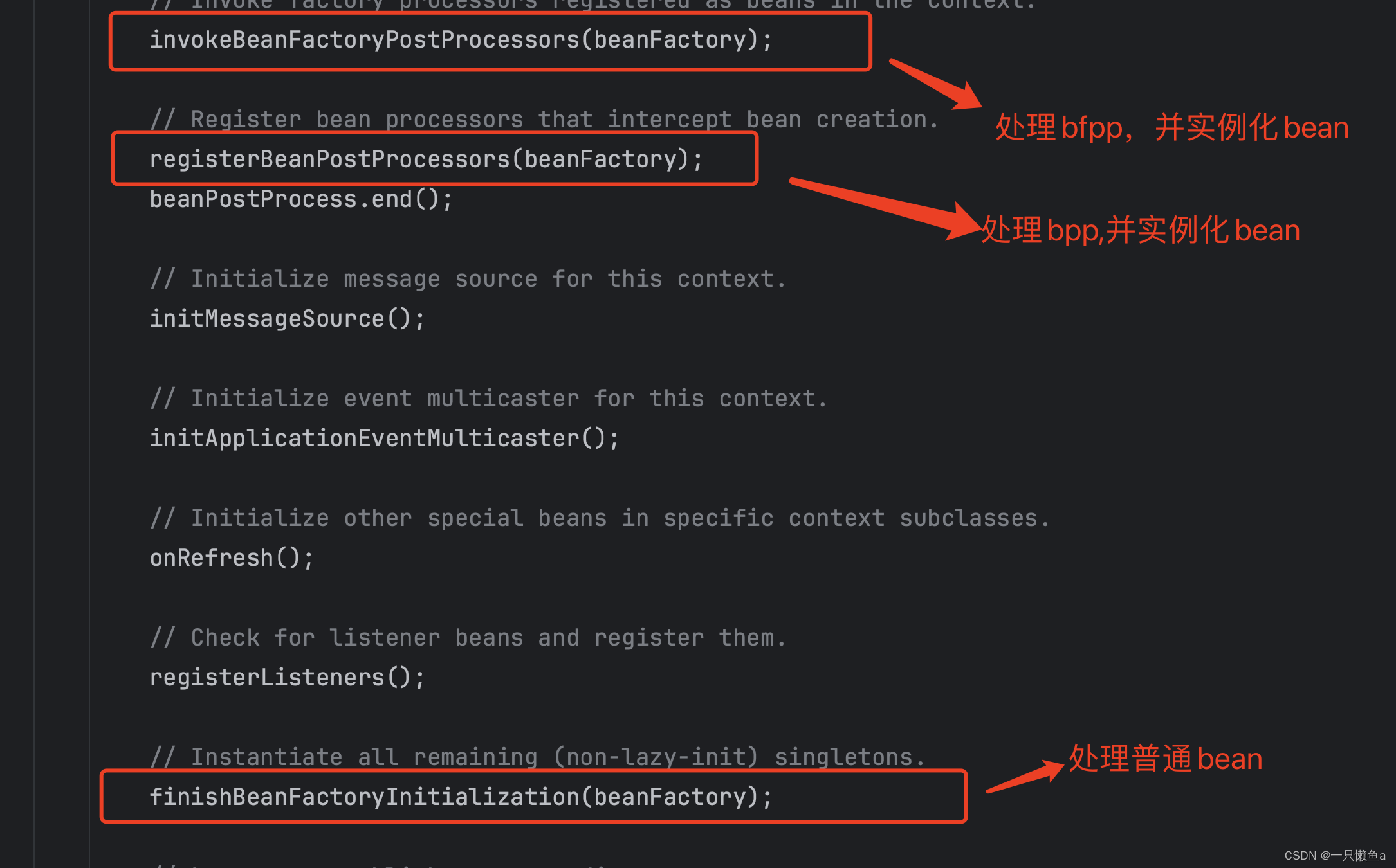
我们可以看到BeanPostProcessor早于普通bean的实例化时机,所以可以对普通bean进行处理,后文我将BeanPostProcessor简称为bpp
这个registerBeanPostProcessors对bpp的处理,和Spring对bfpp的处理很像,我在这里贴一下之前整理的处理顺序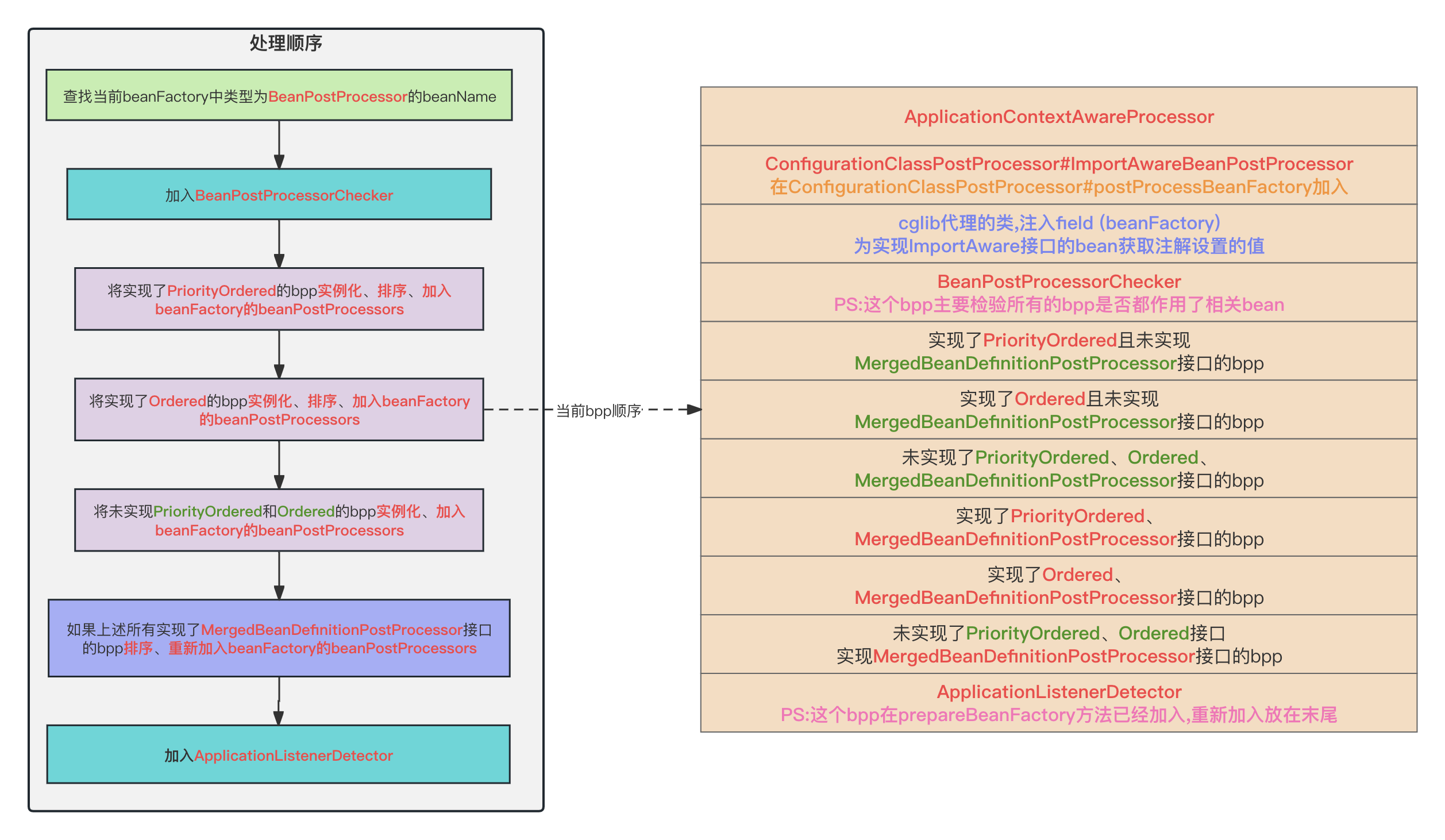
3.BeanPostProcessor一些方法对bean的影响
1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
我们看一下AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean方法
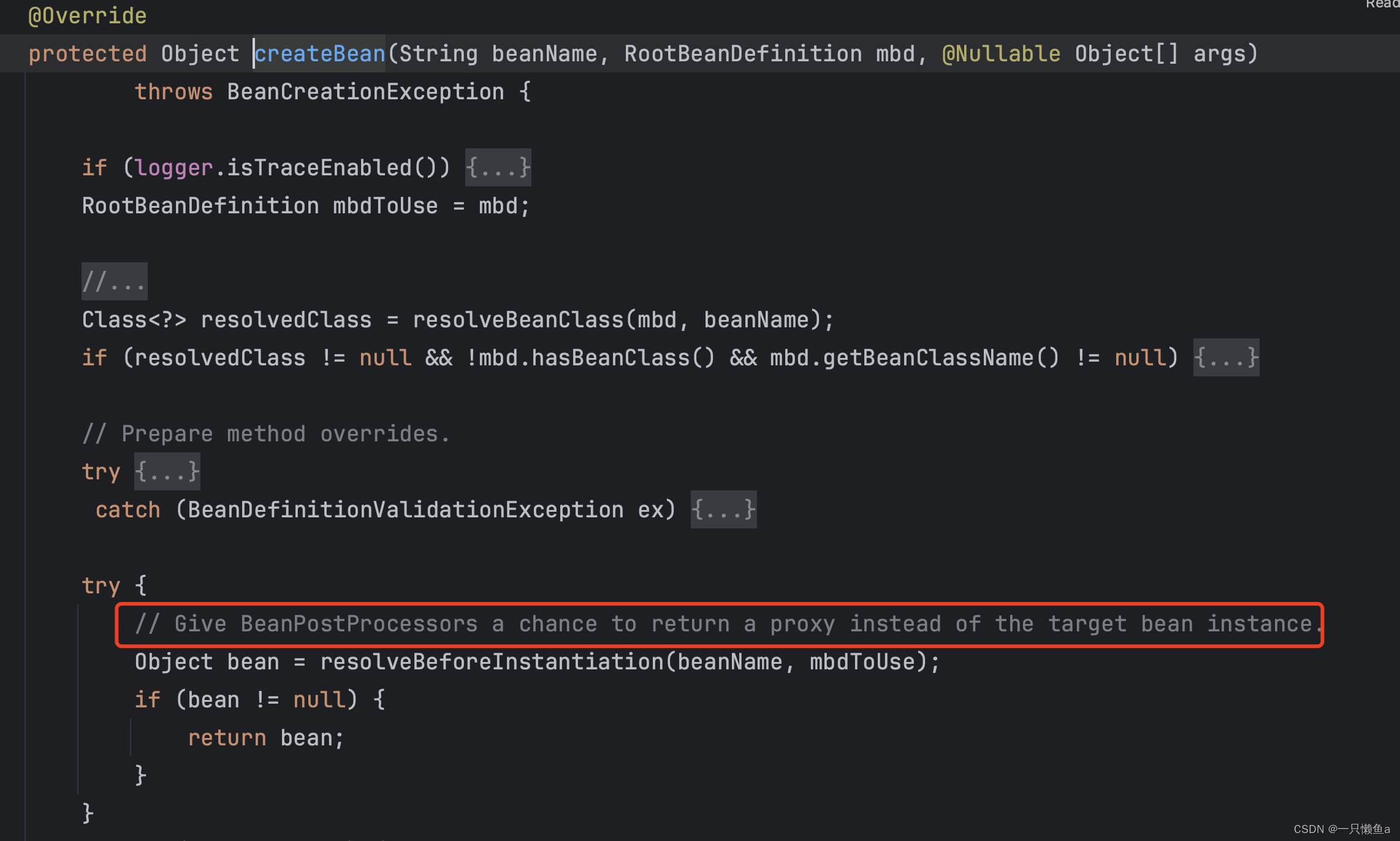
我们看一下注释:给bpp一个机会返回一个代理的对象,这很显然是一个扩展点,我们点进去看看究竟
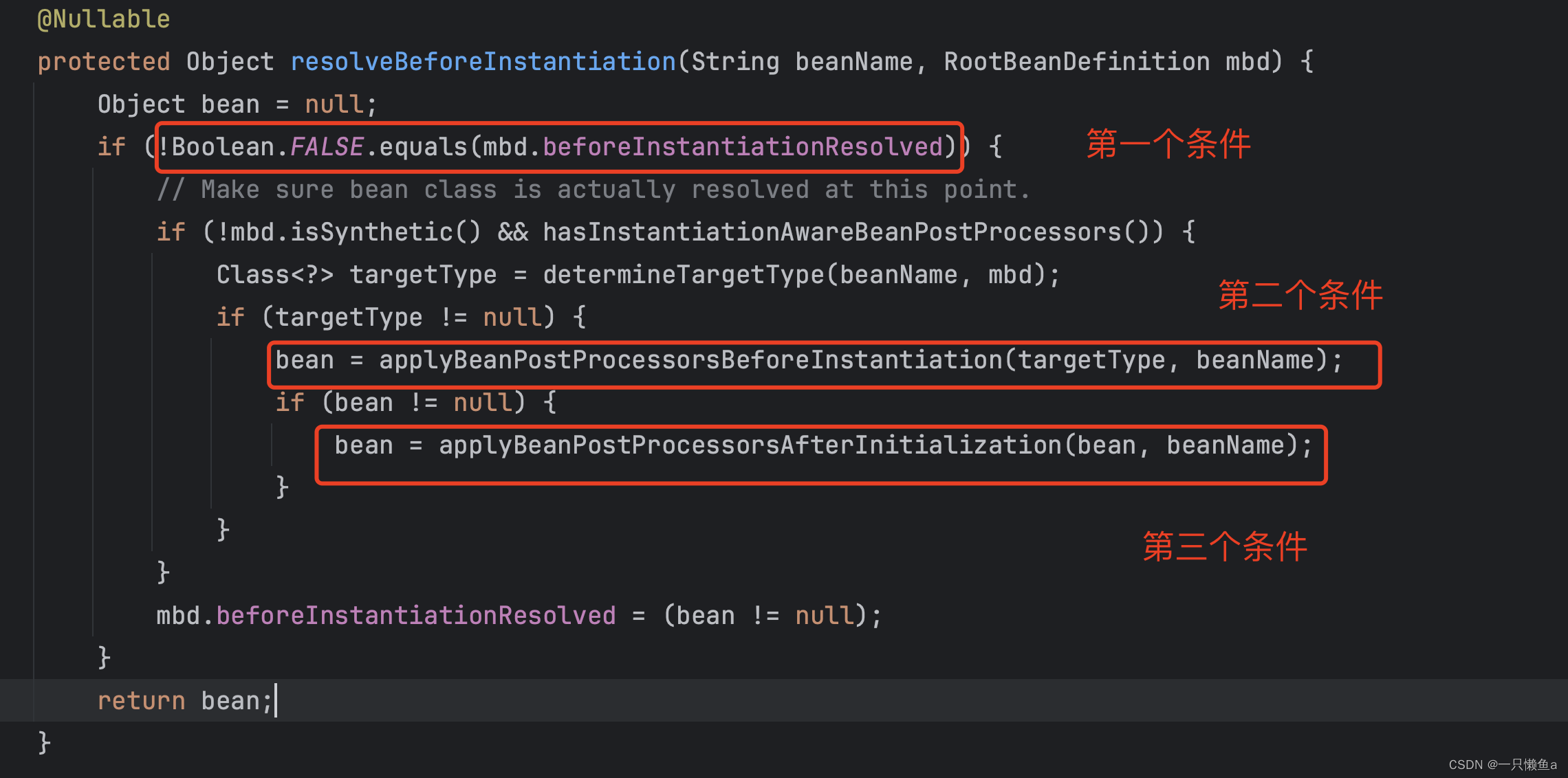
我们看到只要我们完成这三个条件,就不用执行后面的实例化流程了,比如说填充属性的方法(populateBean),各种回调方法,比如ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean
我们来自定义一个bpp,来满足上述条件,看看结果是否符合预期
创建一个普通的类,标记上@Component注解,会被扫描生成bd对象
package com.test.spring.model;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class ModelJ {
}
创建一个实现ApplicationContextAware接口和使用@Autowired注入属性的类
package com.test.spring.model;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class ModelI implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Autowired
private ModelJ modelJ;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
创建一个配置类
package com.test.spring.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
/**
* 这里可以不用加@Configuration
* AnnotationConfigApplicationContext会将构造方法注入的类,解析成bd
*/
@ComponentScan("com.test.spring")
public class AppConfig {
}
创建一个bfpp,修改其beforeInstantiationResolved属性(满足第一条件)
@Component
public class SeventhBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition("modelI")) {
// 这里是ScannedGenericBeanDefinition 还不能强转成RootBeanDefinition
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition scannedGenericBeanDefinition = (ScannedGenericBeanDefinition) registry.getBeanDefinition("modelI");
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClassName(scannedGenericBeanDefinition.getBeanClassName());
try {
// 这个属性是包可见,利用反射强行设置了一下
Field beforeInstantiationResolved = beanDefinition.getClass().getDeclaredField("beforeInstantiationResolved");
beforeInstantiationResolved.setAccessible(true);
beforeInstantiationResolved.set(beanDefinition, true);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
registry.registerBeanDefinition("modelI", beanDefinition);
}
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}
}
创建一个bpp 指定其postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法返回值(满足第二条件),postProcessAfterInitialization就直接使用父类方法,返回原对象(满足第三条件)
package com.test.spring.bpp;
import com.test.spring.model.ModelI;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class FirstBeanPostProcessor implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class beanClass, String beanName) {
if (beanClass == ModelI.class) {
try {
ModelI modelI = (ModelI) beanClass.newInstance();
return modelI;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
return SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
}
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 这个父类方法就是返回原对象,直接使用父类方法
return SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
运行main方法 查看结果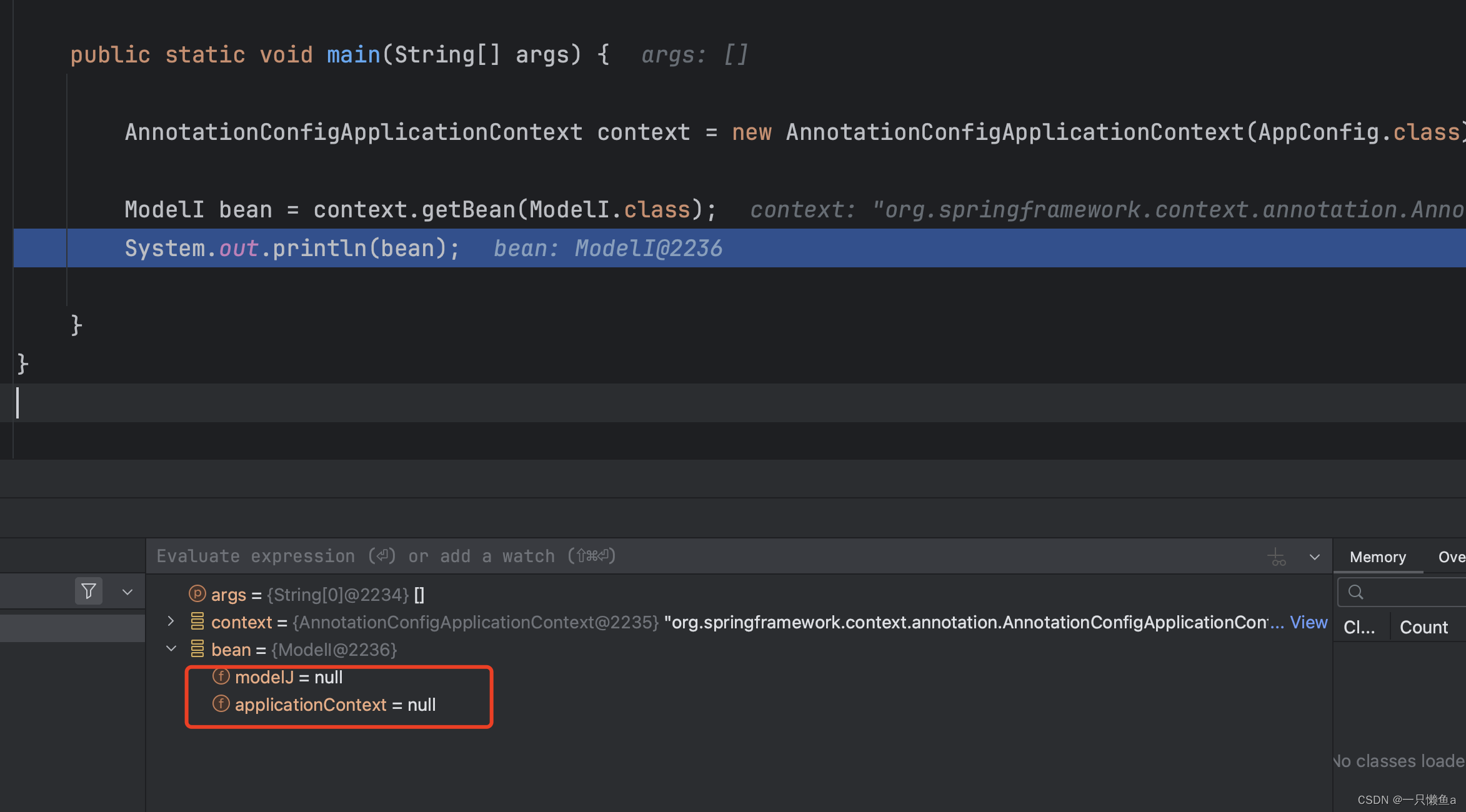 我们可以看到属性注入方法(populateBean)和回调方法(setApplicationContext)都没有执行,Spring处理完bpp的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,就直接返回了
我们可以看到属性注入方法(populateBean)和回调方法(setApplicationContext)都没有执行,Spring处理完bpp的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,就直接返回了
2. MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor#postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
这个类我们拿其子类AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor举例
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor主要是查找所有bean中的注入点,后面在某个时间点将查找的注入点注入到bean中
我们看一下Spring源码怎么定义注入点
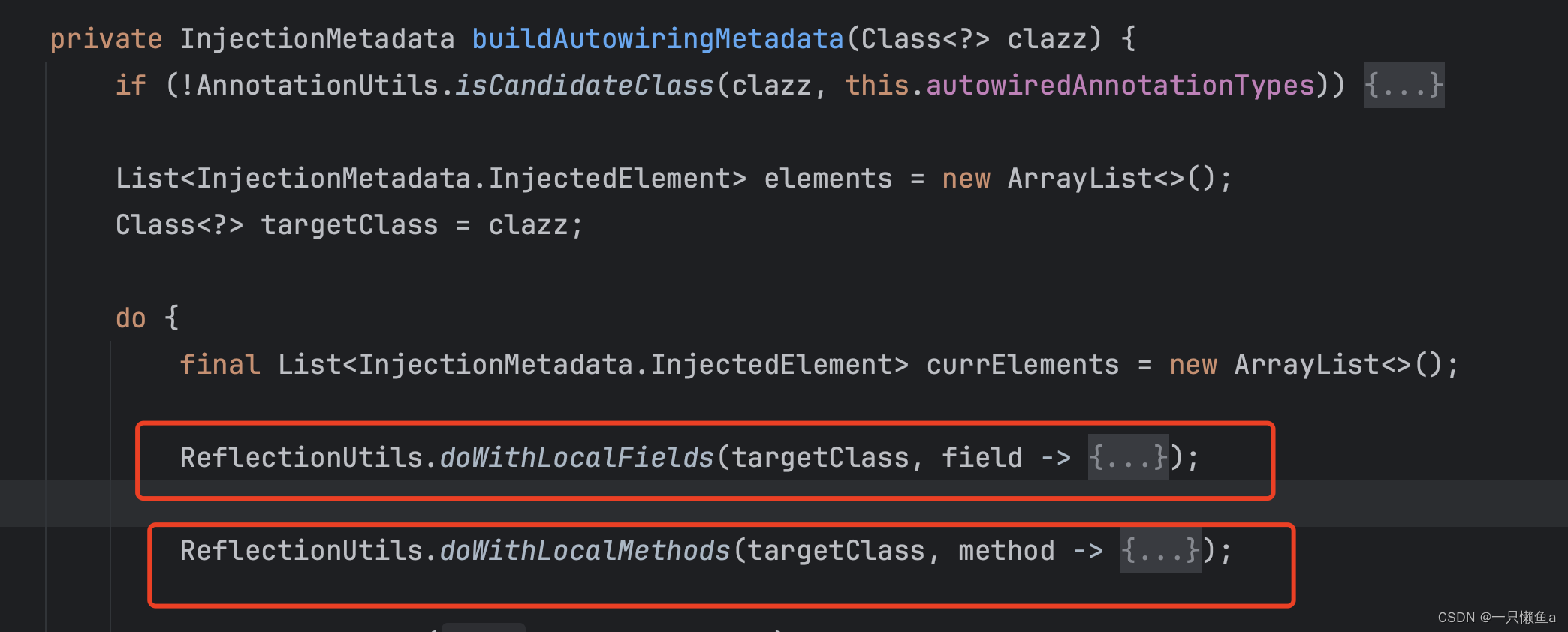
简单来说就是方法或者属性上面加了@Autowired注解就是注入点后期会在某个时间点注入,我们写个简单的例子来看一下
创建一个类ModelK
package com.test.spring.model;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class ModelK {
@Autowired
private ModelI modelI;
private ModelJ modelJ;
@Autowired
public void setModelJ(ModelJ modelJ) {
this.modelJ = modelJ;
}
}
运行main方法 查看结果
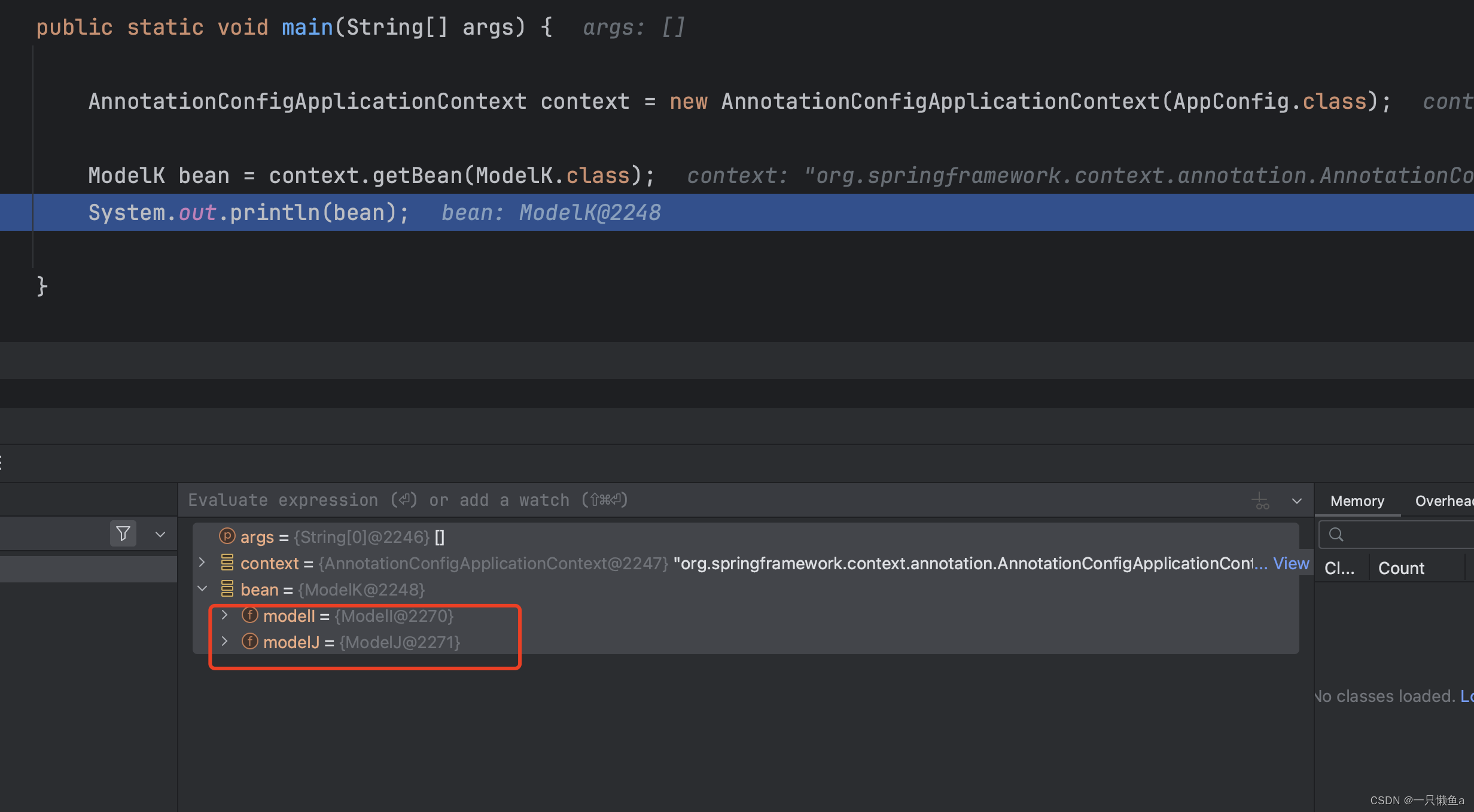 注入点都注入到bean中了
注入点都注入到bean中了
3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation
这个类在populateBean方法中,如果方法返回false就表示这个bean 不填充properties了
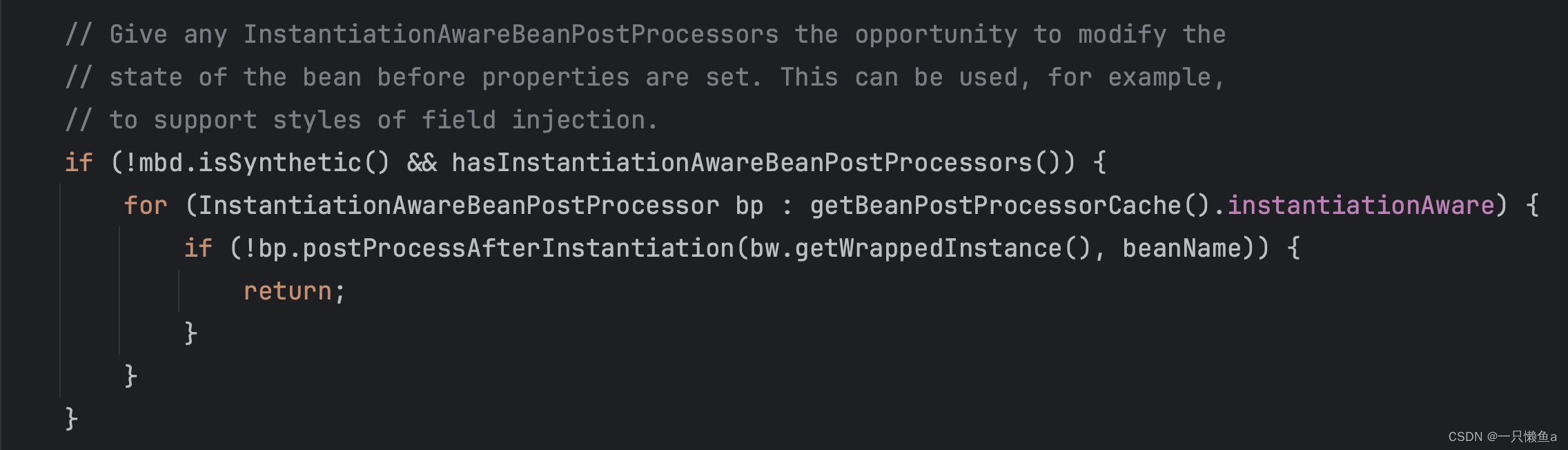
我们写一个简单例子看一下
创建一个类ModelL
package com.test.spring.model;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class ModelL {
@Autowired
private ModelJ modelJ;
}
创建一个bpp
package com.test.spring.bpp;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SecondBeanPostProcessor implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("modelL".equals(beanName)) {
return false;
} else {
return SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
运行main方法 查看结果
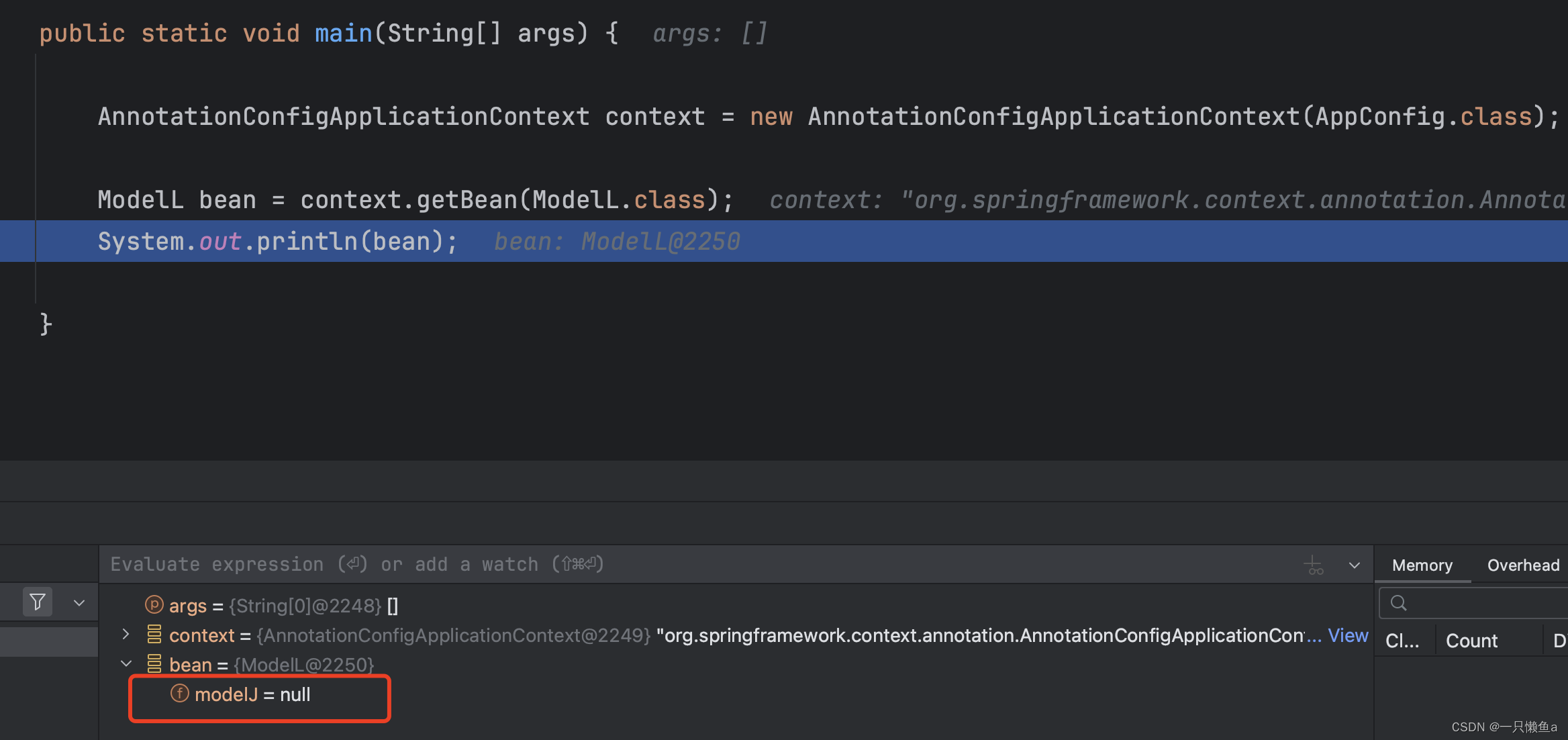
属性modelJ忽略注入了
4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
这个方法前后一般执行了钩子函数 罗列一下
在这个方法之前
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeAwareMethods
- setBeanName
- setBeanClassLoader
- setBeanFactory
相关子类实现
InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$LifecycleElement
- 处理@PostConstruct标注的方法
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
- setEnvironment
- setEmbeddedValueResolver
- setResourceLoader
- setApplicationEventPublisher
- setMessageSource
- setApplicationStartup
- setApplicationContext
在这个方法之后
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeInitMethods
- 处理实现InitializingBean接口的bean
5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization
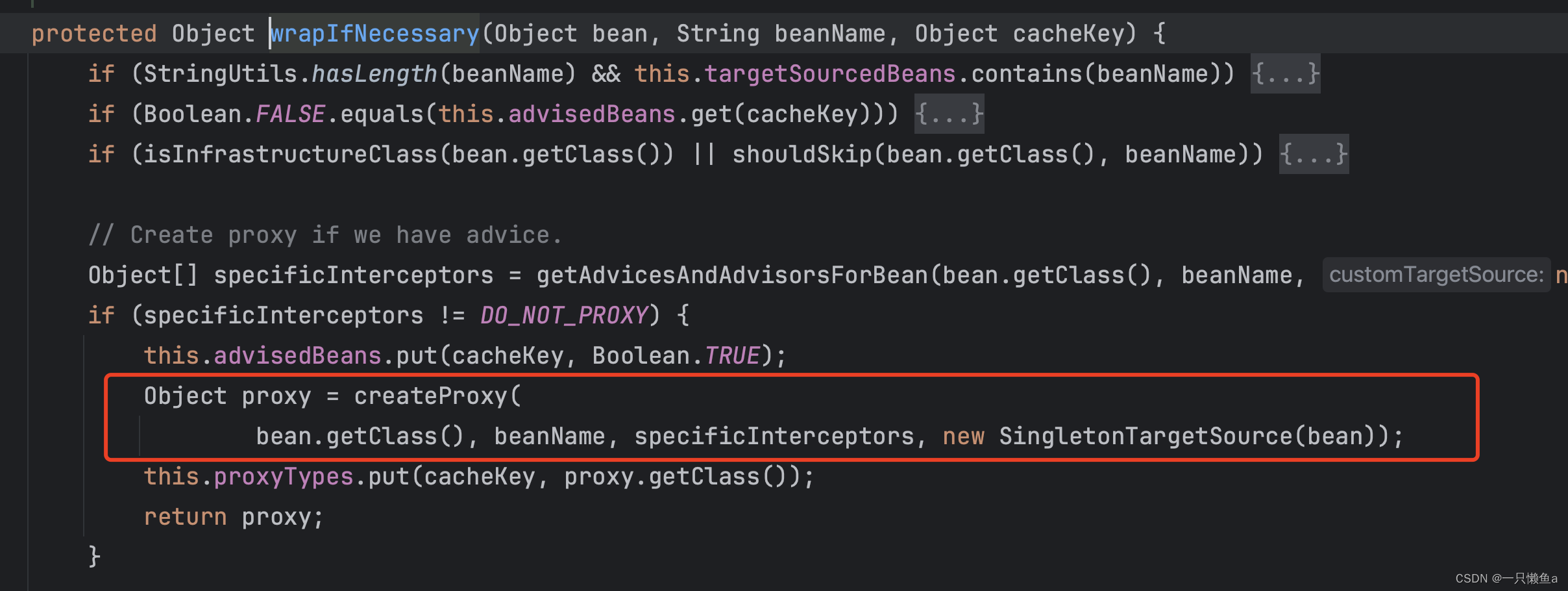
@EnableTransactionManagement注解我们经常使用,应该会很熟悉,其实它的原理就是注入了一个bfpp(AbstractAutoProxyCreator的一个子类,但是子类没有重写postProcessAfterInitialization方法,所以相关逻辑还是在AbstractAutoProxyCreator类中),这个bfpp的重要作用就是动态代理,我们来看相关代码
总结
bpp的作用很强大,但是也很危险,如果不加条件判断要处理的特定bean,所有的bean的都会受影响,所有的bean的都会受影响,所有的bean的都会受影响,重要的事情说三遍。而且这种错误很不容易发现,必须在一个个bpp中debug,所以使用前要做到谨慎再谨慎














