- nginx输出日志配置与查看
- 实现SpringMVC底层机制(二)
- Windows 安装配置 RabbitMQ 详解
- uniapp+springboot 实现前后端分离的个人备忘录系统【超
- C# 使用 RabbitMQ 的详细使用方法
- Go语言面试宝典:50道必会题目与精解
- MySQL DDL 通用语法
- SQL INSERT INTO 语句(在表中插入)
- 一文详解SpringBoot 定时任务(cron表达式)
- Windows下Node.js下载安装及环境变量配置教程
- 输了,腾讯golang一面凉了
- SpringMVC运行时出现404错误(解决办法汇总,基本包含所有错误
- Node.js教程(想入门就来点进来看看)
- MysqlOracle的DATE、DATETIME 和 TIMESTA
- AI小说推文工具,一键生成AI视频推文助手
- 逆向爬虫技术的进阶应用与实战技巧
- Spring Boot基础 习题题库【附答案】4
- vue2项目导出操作实现(后端接口导出、前端直接做导出)
- Hbase解决ERROR: KeeperErrorCode = Con
- 【Golang】Golang超级实用的代码流
- 机器学习入门基础(万字总结)(建议收藏!!!)
- 关于MYSQL的XA事务(分布式事务)的了解以及MySQL5.7.7对
- 查看mysql 或SQL server 的连接数,mysql超时、最大
- 【SpringSecurity】五、UserDetails接口和Use
- 运维:mysql常用的服务器状态命令
- xcode c++项目设置运行时参数
- 高校心理教育辅导系统|基于Springboot的高校心理教育辅导系统设
- [运维] 可视化爬虫易采集-EasySpider(笔记)
- 大白话,visual studio code配置PHP+解决PHP缺少
- 【Oracle】oracle、mysql、sql server三者区别
文章目录
- 概序
- 架构图
- TCP的3次握手4次挥手
- 时序图
- 核心参数
- AcceptCount
- MaxConnections
- MinSpareThread/MaxThread
- MaxKeepAliveRequests
- ConnectionTimeout
- KeepAliveTimeout
- 内部线程
- Acceptor
- Poller
- TomcatThreadPoolExecutor
- 测试
- 参考
每个Spring Boot版本和内置容器不同,结果也不同,这里以Spring Boot 2.7.10版本 + 内置Tomcat容器举例。
概序
在SpringBoot2.7.10版本中内置Tomcat版本是9.0.73,SpringBoot内置Tomcat的默认设置如下:
- Tomcat的连接等待队列长度,默认是100
- Tomcat的最大连接数,默认是8192
- Tomcat的最小工作线程数,默认是10
- Tomcat的最大线程数,默认是200
- Tomcat的连接超时时间,默认是20s
相关配置及默认值如下
server: tomcat: # 当所有可能的请求处理线程都在使用中时,传入连接请求的最大队列长度 accept-count: 100 # 服务器在任何给定时间接受和处理的最大连接数。一旦达到限制,操作系统仍然可以接受基于“acceptCount”属性的连接。 max-connections: 8192 threads: # 工作线程的最小数量,初始化时创建的线程数 min-spare: 10 # 工作线程的最大数量 io密集型建议10倍的cpu数,cpu密集型建议cpu数+1,绝大部分应用都是io密集型 max: 200 # 连接器在接受连接后等待显示请求 URI 行的时间。 connection-timeout: 20000 # 在关闭连接之前等待另一个 HTTP 请求的时间。如果未设置,则使用 connectionTimeout。设置为 -1 时不会超时。 keep-alive-timeout: 20000 # 在连接关闭之前可以进行流水线处理的最大HTTP请求数量。当设置为0或1时,禁用keep-alive和流水线处理。当设置为-1时,允许无限数量的流水线处理或keep-alive请求。 max-keep-alive-requests: 100架构图
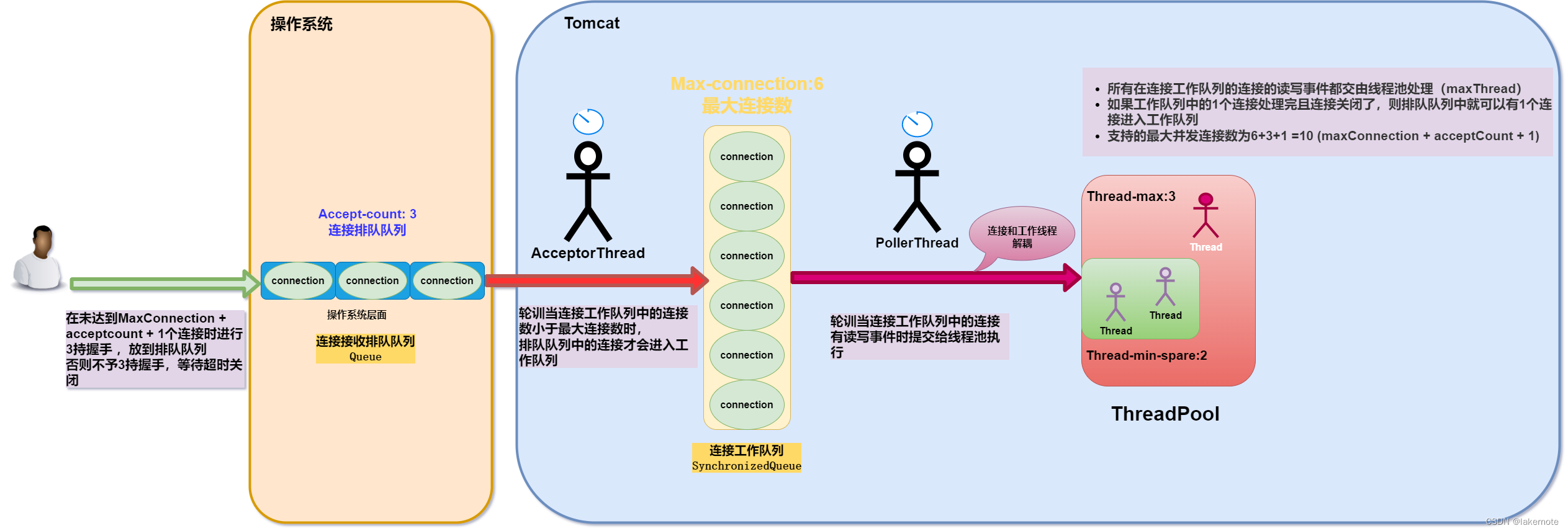
当连接数大于maxConnections+acceptCount + 1时,新来的请求不会收到服务器拒绝连接响应,而是不会和新的请求进行3次握手建立连接,一段时间后(客户端的超时时间或者Tomcat的20s后)会出现请求连接超时。
TCP的3次握手4次挥手
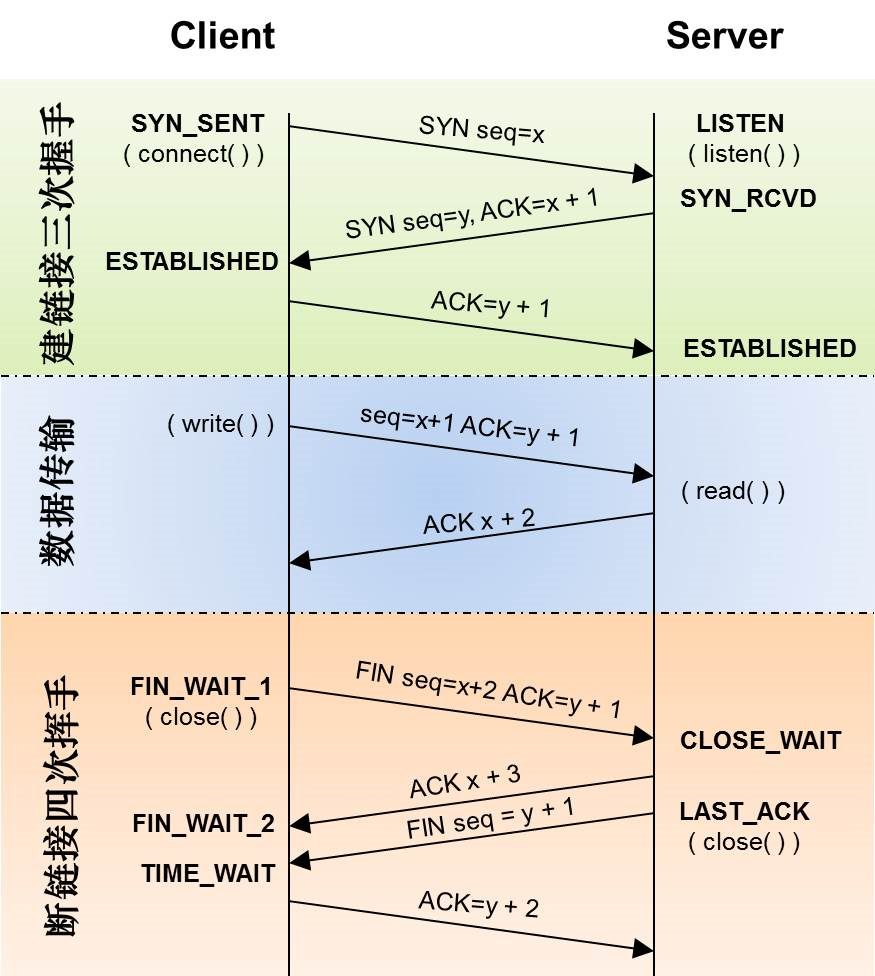
时序图
核心参数
AcceptCount
全连接队列容量,等同于backlog参数,与Linux中的系统参数somaxconn取较小值,Windows中没有系统参数。
NioEndpoint.java
serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open(); socketProperties.setProperties(serverSock.socket()); InetSocketAddress addr = new InetSocketAddress(getAddress(), getPortWithOffset()); // 这里 serverSock.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptCount());
MaxConnections
Acccptor.java
// 线程的run方法。 public void run() { while (!stopCalled) { // 如果我们已达到最大连接数,等待 connectionLimitLatch.countUpOrAwait(); // 接受来自服务器套接字的下一个传入连接 socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept() // socket.close 释放的时候 调用 connectionLimitLatch.countDown();
MinSpareThread/MaxThread
AbstractEndpoint.java
// tomcat 启动时 public void createExecutor() { internalExecutor = true; // 容量为Integer.MAX_VALUE TaskQueue taskqueue = new TaskQueue(); TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(getName() + "-exec-", daemon, getThreadPriority()); // Tomcat扩展的线程池 executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(getMinSpareThreads(), getMaxThreads(), 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,taskqueue, tf); taskqueue.setParent( (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor); }重点重点重点
Tomcat扩展了线程池增强了功能。
- JDK线程池流程:minThreads --> queue --> maxThreads --> Exception
- Tomcat增强后: minThreads --> maxThreads --> queue --> Exception
MaxKeepAliveRequests
长连接,在发送了maxKeepAliveRequests个请求后就会被服务器端主动断开连接。
在连接关闭之前可以进行流水线处理的最大HTTP请求数量。当设置为0或1时,禁用keep-alive和流水线处理。当设置为-1时,允许无限数量的流水线处理或keep-alive请求。
较大的 MaxKeepAliveRequests 值可能会导致服务器上的连接资源被长时间占用。根据您的具体需求,您可以根据服务器的负载和资源配置来调整 MaxKeepAliveRequests 的值,以平衡并发连接和服务器资源的利用率。
NioEndpoint.setSocketOptions socketWrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests()); Http11Processor.service(SocketWrapperBase socketWrapper) keepAlive = true; while(!getErrorState().isError() && keepAlive && !isAsync() && upgradeToken == null && sendfileState == SendfileState.DONE && !protocol.isPaused()) { // 默认100 int maxKeepAliveRequests = protocol.getMaxKeepAliveRequests(); if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) { keepAlive = false; } else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 && // socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) { keepAlive = false; }ConnectionTimeout
连接的生存周期,当已经建立的连接,在connectionTimeout时间内,如果没有请求到来,服务端程序将会主动关闭该连接。
- 在Tomcat 9中,ConnectionTimeout的默认值是20000毫秒,也就是20秒。
- 如果该时间过长,服务器将要等待很长时间才会收到客户端的请求结果,从而导致服务效率低下。如果该时间过短,则可能会出现客户端在请求过程中网络慢等问题,而被服务器取消连接的情况。
- 由于某个交换机或者路由器出现了问题,导致某些post大文件的请求堆积在交换机或者路由器上,tomcat的工作线程一直拿不到完整的文件数据。
NioEndpoint.Poller#run()
// Check for read timeout if ((socketWrapper.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_READ) == SelectionKey.OP_READ) { long delta = now - socketWrapper.getLastRead(); long timeout = socketWrapper.getReadTimeout(); if (timeout > 0 && delta > timeout) { readTimeout = true; } } // Check for write timeout if (!readTimeout && (socketWrapper.interestOps() & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) { long delta = now - socketWrapper.getLastWrite(); long timeout = socketWrapper.getWriteTimeout(); if (timeout > 0 && delta > timeout) { writeTimeout = true; } }KeepAliveTimeout
等待另一个 HTTP 请求的时间,然后关闭连接。当未设置时,将使用 connectionTimeout。当设置为 -1 时,将没有超时。
Http11InputBuffer.parseRequestLine
// Read new bytes if needed if (byteBuffer.position() >= byteBuffer.limit()) { if (keptAlive) { // 还没有读取任何请求数据,所以使用保持活动超时 wrapper.setReadTimeout(keepAliveTimeout); } if (!fill(false)) { // A read is pending, so no longer in initial state parsingRequestLinePhase = 1; return false; } // 至少已收到请求的一个字节 切换到套接字超时。 wrapper.setReadTimeout(connectionTimeout); }内部线程
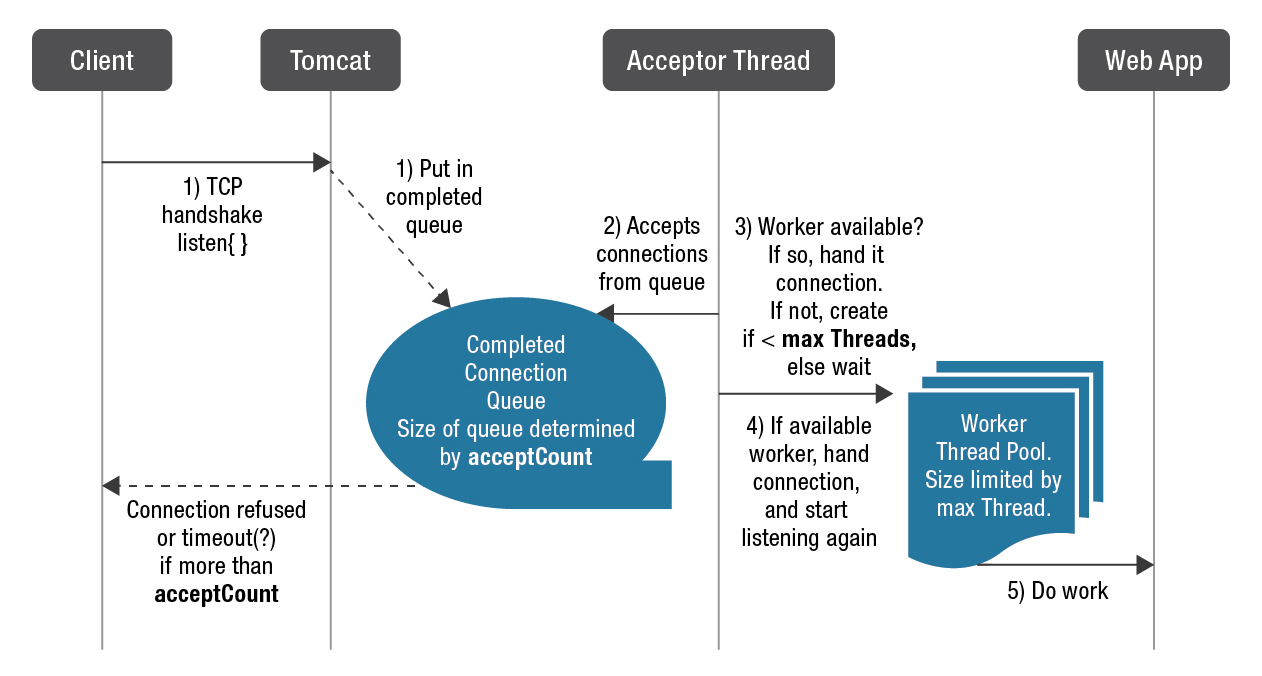
Acceptor
Acceptor: 接收器,作用是接受scoket网络请求,并调用setSocketOptions()封装成为NioSocketWrapper,并注册到Poller的events中。注意查看run方法org.apache.tomcat.util.net.Acceptor#run
public void run() { while (!stopCalled) { // 等待下一个请求进来 socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept(); // 注册socket到Poller,生成PollerEvent事件 endpoint.setSocketOptions(socket); // 向轮询器注册新创建的套接字 - poller.register(socketWrapper); - (SynchronizedQueue(128))events.add(new PollerEvent(socketWrapper))Poller
Poller:轮询器,轮询是否有事件达到,有请求事件到达后,以NIO的处理方式,查询Selector取出所有请求,遍历每个请求的需求,分配给Executor线程池执行。查看org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioEndpoint.Poller#run()
public void run() { while (true) { //查询selector取出所有请求事件 Iteratoriterator = keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null; // 遍历就绪键的集合并调度任何活动事件。 while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey sk = iterator.next(); iterator.remove(); NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) sk.attachment(); // 分配给Executor线程池执行处理请求key if (socketWrapper != null) { processKey(sk, socketWrapper); - processSocket(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ/SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) - executor.execute((Runnable)new SocketProcessor(socketWrapper,SocketEvent)) } } TomcatThreadPoolExecutor
真正执行连接读写操作的线程池,在JDK线程池的基础上进行了扩展优化。
AbstractEndpoint.java
public void createExecutor() { internalExecutor = true; TaskQueue taskqueue = new TaskQueue(); TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(getName() + "-exec-", daemon, getThreadPriority()); // tomcat自定义线程池 executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(getMinSpareThreads(), getMaxThreads(), 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,taskqueue, tf); taskqueue.setParent( (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor); }TomcatThreadPoolExecutor.java
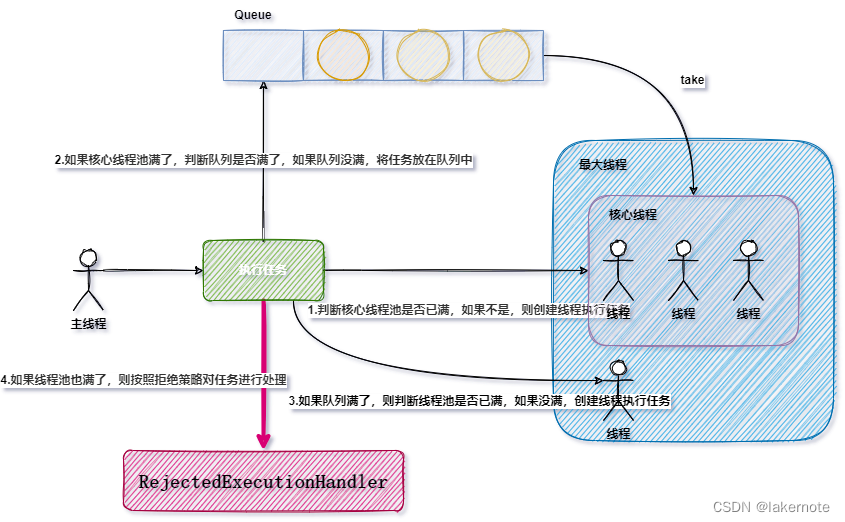
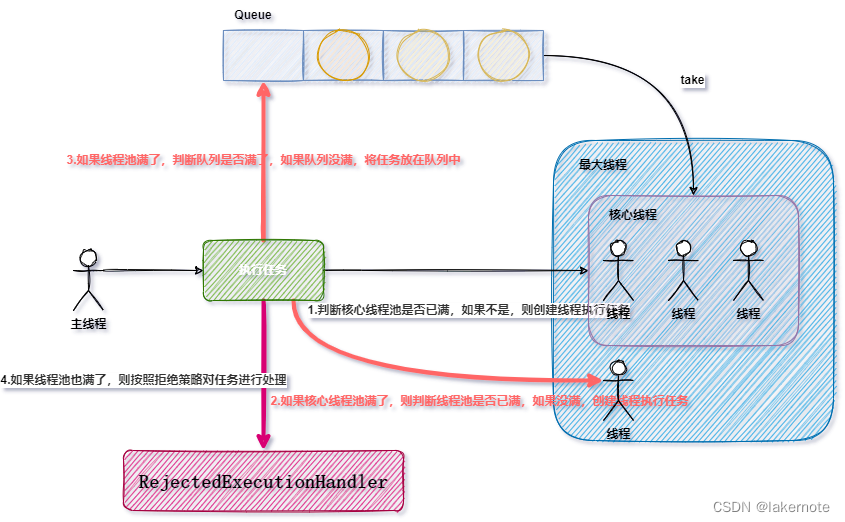
// 与 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor 相同,但实现了更高效的getSubmittedCount()方法,用于正确处理工作队列。 // 如果未指定 RejectedExecutionHandler,将配置一个默认的,并且该处理程序将始终抛出 RejectedExecutionException public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor { // 已提交但尚未完成的任务数。这包括队列中的任务和已交给工作线程但后者尚未开始执行任务的任务。 // 这个数字总是大于或等于getActiveCount() 。 private final AtomicInteger submittedCount = new AtomicInteger(0); @Override protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) { if (!(t instanceof StopPooledThreadException)) { submittedCount.decrementAndGet(); } @Override public void execute(Runnable command){ // 提交任务的数量+1 submittedCount.incrementAndGet(); try { // 线程池内部方法,真正执行的方法。就是JDK线程池原生的方法。 super.execute(command); } catch (RejectedExecutionException rx) { // 再次把被拒绝的任务放入到队列中。 if (super.getQueue() instanceof TaskQueue) { final TaskQueue queue = (TaskQueue)super.getQueue(); try { //强制的将任务放入到阻塞队列中 if (!queue.force(command, timeout, unit)) { //放入失败,则继续抛出异常 submittedCount.decrementAndGet(); throw new RejectedExecutionException(sm.getString("threadPoolExecutor.queueFull")); } } catch (InterruptedException x) { //被中断也抛出异常 submittedCount.decrementAndGet(); throw new RejectedExecutionException(x); } } else { //不是这种队列,那么当任务满了之后,直接抛出去。 submittedCount.decrementAndGet(); throw rx; } } }/** * 实现Tomcat特有逻辑的自定义队列 */ public class TaskQueue extends LinkedBlockingQueue
{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private transient volatile ThreadPoolExecutor parent = null; private static final int DEFAULT_FORCED_REMAINING_CAPACITY = -1; /** * 强制遗留的容量 */ private int forcedRemainingCapacity = -1; /** * 队列的构建方法 */ public TaskQueue() { } public TaskQueue(int capacity) { super(capacity); } public TaskQueue(Collection c) { super(c); } /** * 设置核心变量 */ public void setParent(ThreadPoolExecutor parent) { this.parent = parent; } /** * put:向阻塞队列填充元素,当阻塞队列满了之后,put时会被阻塞。 * offer:向阻塞队列填充元素,当阻塞队列满了之后,offer会返回false。 * * @param o 当任务被拒绝后,继续强制的放入到线程池中 * @return 向阻塞队列塞任务,当阻塞队列满了之后,offer会返回false。 */ public boolean force(Runnable o) { if (parent == null || parent.isShutdown()) { throw new RejectedExecutionException("taskQueue.notRunning"); } return super.offer(o); } /** * 带有阻塞时间的塞任务 */ @Deprecated public boolean force(Runnable o, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { if (parent == null || parent.isShutdown()) { throw new RejectedExecutionException("taskQueue.notRunning"); } return super.offer(o, timeout, unit); //forces the item onto the queue, to be used if the task is rejected } /** * 当线程真正不够用时,优先是开启线程(直至最大线程),其次才是向队列填充任务。 * * @param runnable 任务 * @return false 表示向队列中添加任务失败, */ @Override public boolean offer(Runnable runnable) { if (parent == null) { return super.offer(runnable); } //若是达到最大线程数,进队列。 if (parent.getPoolSize() == parent.getMaximumPoolSize()) { return super.offer(runnable); } //当前活跃线程为10个,但是只有8个任务在执行,于是,直接进队列。 if (parent.getSubmittedCount() < (parent.getPoolSize())) { return super.offer(runnable); } //当前线程数小于最大线程数,那么直接返回false,去创建最大线程 if (parent.getPoolSize() < parent.getMaximumPoolSize()) { return false; } //否则的话,将任务放入到队列中 return super.offer(runnable); } /** * 获取任务 */ @Override public Runnable poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { Runnable runnable = super.poll(timeout, unit); //取任务超时,会停止当前线程,来避免内存泄露 if (runnable == null && parent != null) { parent.stopCurrentThreadIfNeeded(); } return runnable; } /** * 阻塞式的获取任务,可能返回null。 */ @Override public Runnable take() throws InterruptedException { //当前线程应当被终止的情况下: if (parent != null && parent.currentThreadShouldBeStopped()) { long keepAliveTime = parent.getKeepAliveTime(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); return poll(keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } return super.take(); } /** * 返回队列的剩余容量 */ @Override public int remainingCapacity() { if (forcedRemainingCapacity > DEFAULT_FORCED_REMAINING_CAPACITY) { return forcedRemainingCapacity; } return super.remainingCapacity(); } /** * 强制设置剩余容量 */ public void setForcedRemainingCapacity(int forcedRemainingCapacity) { this.forcedRemainingCapacity = forcedRemainingCapacity; } /** * 重置剩余容量 */ void resetForcedRemainingCapacity() { this.forcedRemainingCapacity = DEFAULT_FORCED_REMAINING_CAPACITY; } } JDK线程池架构图
Tomcat线程架构
测试
如下配置举例
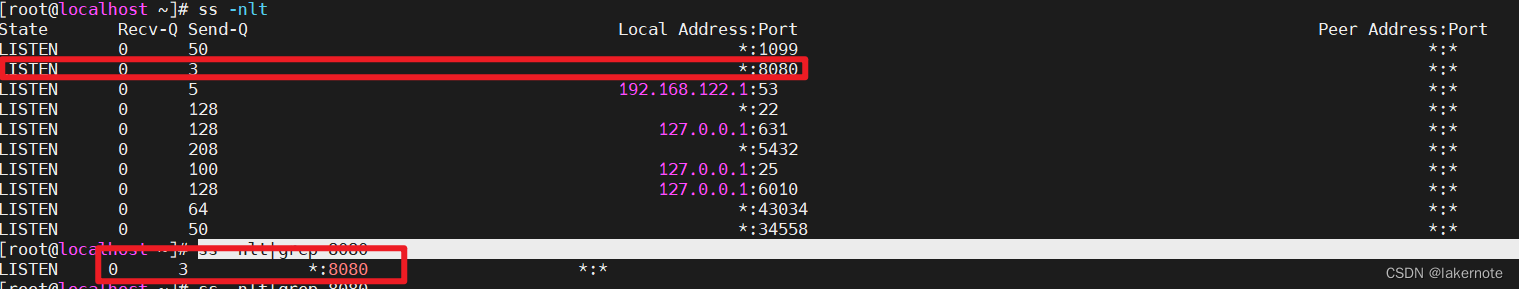
server: port: 8080 tomcat: accept-count: 3 max-connections: 6 threads: min-spare: 2 max: 3使用ss -nlt查看全连接队列容量。
ss -nltp ss -nlt|grep 8080 - Recv-Q表示(acceptCount)全连接队列目前长度 - Send-Q表示(acceptCount)全连接队列的容量。
静默状态
6个并发连接
结果同上
9个并发连接

10个并发连接
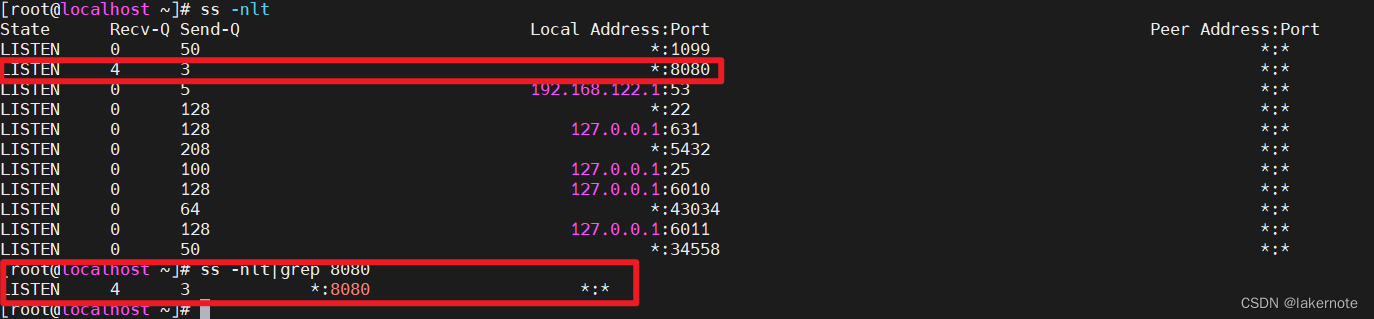
11个并发连接
结果同上
使用ss -nt查看连接状态。
ss -ntp ss -nt|grep 8080 - Recv-Q表示客户端有多少个字节发送但还没有被服务端接收 - Send-Q就表示为有多少个字节未被客户端接收。
静默状态

6个并发连接
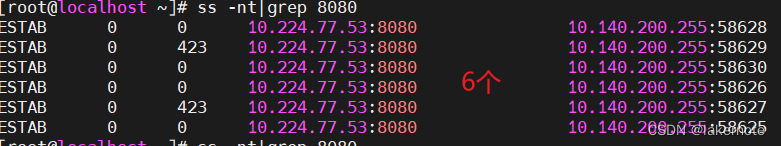
9个并发连接
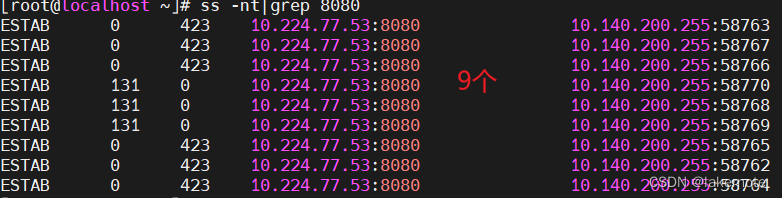
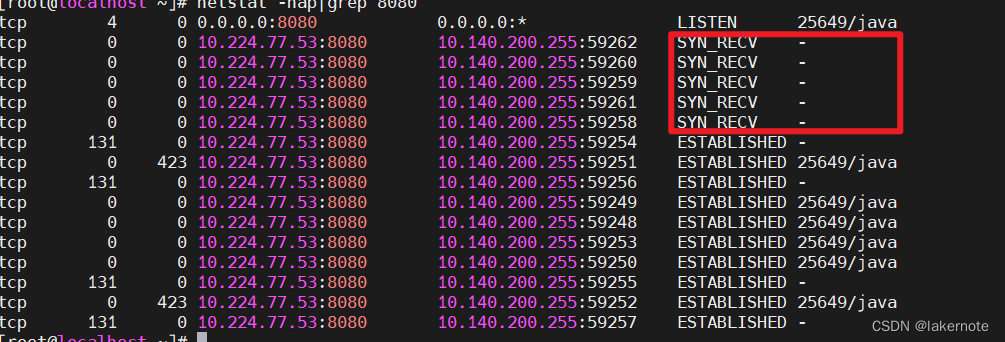
补充个netstat
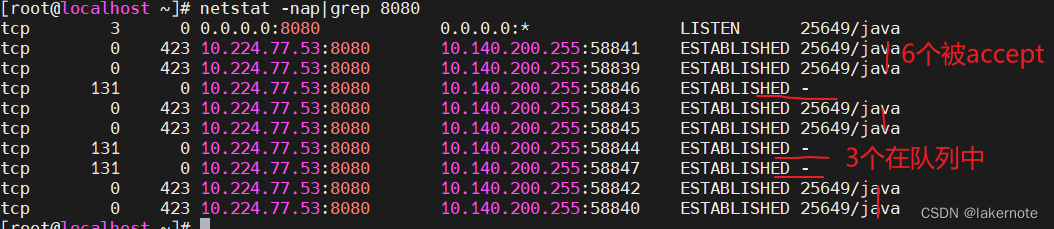
10个并发连接
结果同上,队列中多加了个
11个并发连接
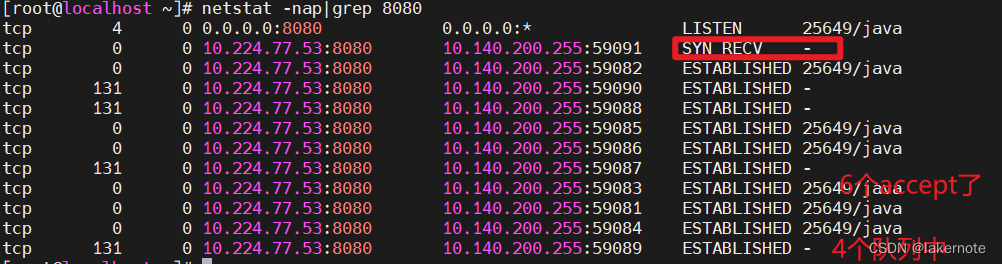
超出连接后,会有个连接一直停留在SYN_RECV状态,不会完成3次握手了。
超出连接后客户端一直就停留在SYN-SENT状态,服务端不会再发送SYN+ACK,直到客户端超时(20s内核控制)断开。
客户端请求超时(需要等待一定时间(20s))。
这里如果客户端设置了超时时间,要和服务端3次握手超时时间对比小的为准。
12个并发连接
参考
- https://www.zhangbj.com/p/1105.html
- https://www.eginnovations.com/blog/tomcat-monitoring-metrics/














