- [MySQL报错]关于发生net start mysql 服务无法启动
- Spring之 国际化:i18n
- 基于大模型的Text2SQL微调的实战教程(二)
- 最详细的Keycloak教程(建议收藏):Keycloak实现手机号、
- MySQL- 创建可以远程访问的root账户
- 学习使用在mysql中查询指定字段字符串包含多个字符串的方法
- 从零开始实现C++ TinyWebServer(九)---- 项目知识
- Lua语法(四)——协程
- Mysql SQL优化
- Spring Boot学习随笔- 集成MyBatis-Plus(二)条
- mysql中varchar长度为多少
- 伪分布式hadoop+spark+scala 超详细搭建
- 二刷大数据(一)- Hadoop
- SpringBoot整合Druid数据库连接池&多数据源&am
- lua学习笔记20(lua中一些自带库的学习)
- Text2SQL研究(一)-Chat2DB体验与剖析
- AI大模型引领金融创新变革与实践【文末送书】
- 21、Lua 面向对象
- eNSP防火墙配置实验(trust、DMZ、untrust)
- 推荐系统算法 协同过滤算法详解(三)Springboot 实现基于用户
- 深入理解 SQL UNION 运算符及其应用场景
- 人大金仓国产数据库与PostgreSQL
- Python Flask-Mail实现邮件发送
- mysql 内存缓冲池innodb
- 漫途水产养殖水质智能监测方案,科技助力养殖业高效生产!
- 【Rust】——项目实例:——命令行实例(一)
- SpringBoot集成WebSocket,实现后台向前端推送信息
- 数据库的基本知识(mysql)
- [运行报错] Maven打包SpringBoot项目,运行报错:no
- Spring Cloud Gateway负载均衡
文章目录
- 🐱👓数据库的操作
- 📌显示当前的数据库
- 📌创建数据库
- 🎈语法:
- 🎈语法说明
- 🎈示例:
- 🌴使用数据库
- 🎋删除数据库
- 🐱🏍语法
- 🚨说明
- 🐱👤常用数据类型
- 🌳数值类型
- 🧭内容扩展:
- 🎄字符串类型
- 🌲日期类型
- 🐱🐉表的操作
- 🚩查看表结构
- 🚩创建表
- ⚾语法:
- ⚾示例:
- 🚩删除表
- 🏀语法格式
- 🏀示例
- 🎡内容重点总结
- 🍀练习
- ⭕总结
🎄本节目标:
🐱👓数据库的操作
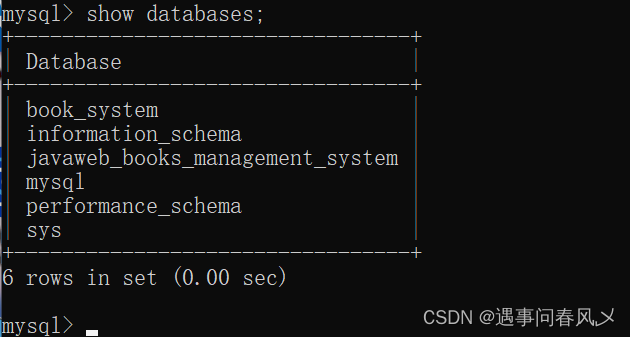
📌显示当前的数据库
SHOW DATABASES;
使用如下:
📌创建数据库
🎈语法:
CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] db_name [create_specification [, create_specification] ...] create_specification: [DEFAULT] CHARACTER SET charset_name [DEFAULT] COLLATE collation_name
🎈语法说明
-
大写的表示关键字
-
[] 是可选项
-
CHARACTER SET: 指定数据库采用的字符集
-
COLLATE: 指定数据库字符集的校验规则
🎈示例:
- 🛫创建名为 db_test1 的数据库
CREATE DATABASE db_test1;
说明:
说明:当我们创建数据库没有指定字符集和校验规则时,系统使用默认字符集:utf8,校验规则是:
utf8_ general_ ci
-
🛫如果系统没有 db_test2 的数据库,则创建一个名叫 db_test2 的数据库,如果有则不创建
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS db_test2;
-
🛫如果系统没有 db_test 的数据库,则创建一个使用utf8mb4字符集的 db_test 数据库,如果有则
不创建
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS db_test CHARACTER SET utf8mb4
说明:
MySQL的utf8编码不是真正的utf8,没有包含某些复杂的中文字符。
MySQL真正的utf8是使用utf8mb4,建议大家都使用utf8mb4
🌴使用数据库
use 数据库名;
🎋删除数据库
🐱🏍语法
DROP DATABASE [IF EXISTS] db_name;
🚨说明
数据库删除以后,内部看不到对应的数据库,里边的表和数据全部被删除
drop database if exists db_test1; drop database if exists db_test2;
🐱👤常用数据类型
🌳数值类型
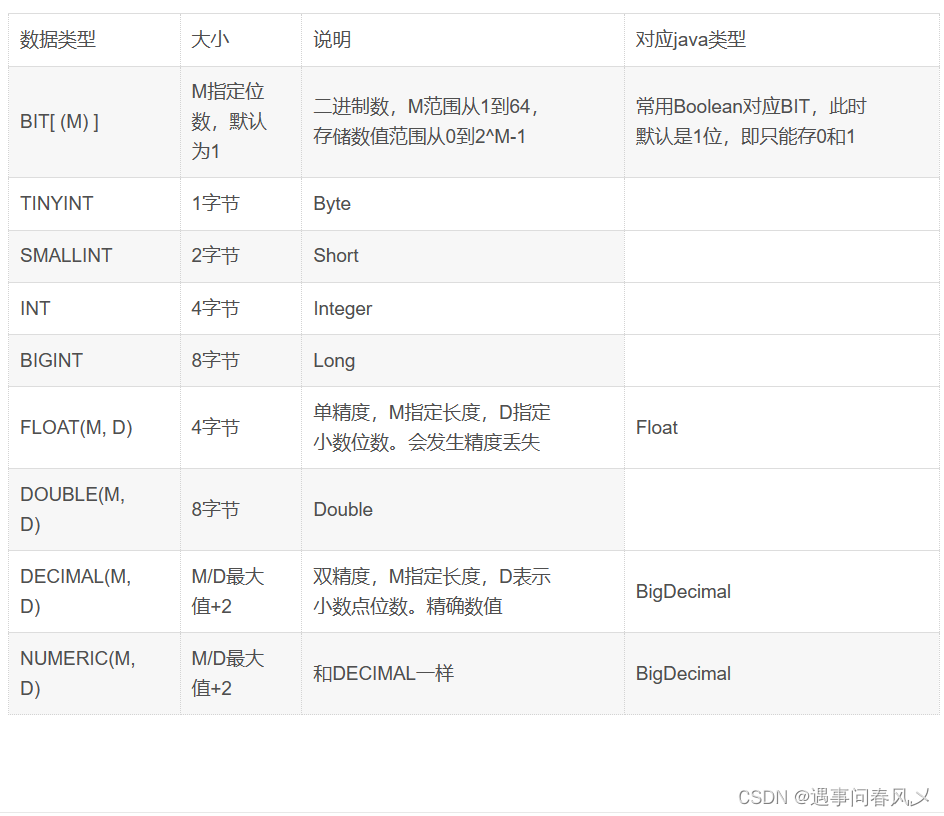
🧭内容扩展:
数值类型可以指定为无符号(unsigned),表示不取负数
1字节(bytes)= 8bit。
对于整型类型的范围:
- 有符号范围:-2(类型字节数*8-1)到2(类型字节数*8-1)-1,如int是4字节,就
是-231到231-1
- 无符号范围:0到2(类型字节数*8)-1,如int就是232-1
尽量不使用unsigned,对于int类型可能存放不下的数据,int unsigned同样可能存放不下,与其
如此,还不如设计时,将int类型提升为bigint类型。
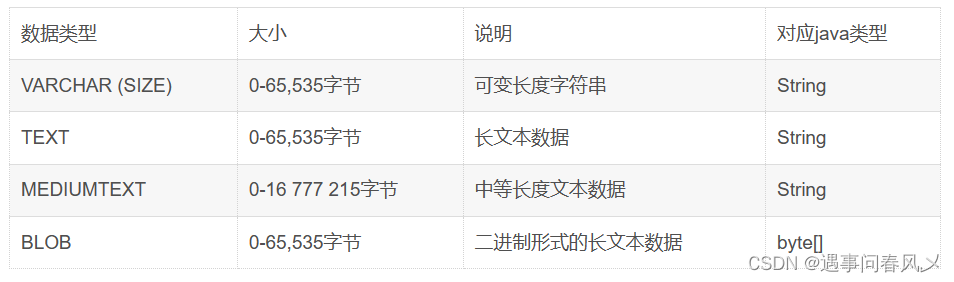
🎄字符串类型
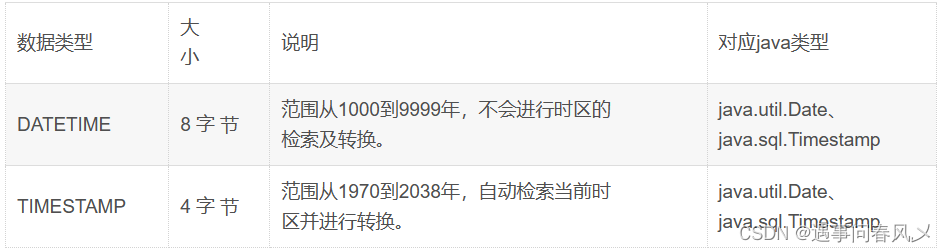
🌲日期类型
🐱🐉表的操作
需要操作数据库中的表时,需要先使用该数据库
🚩查看表结构
desc 表名;
示例:
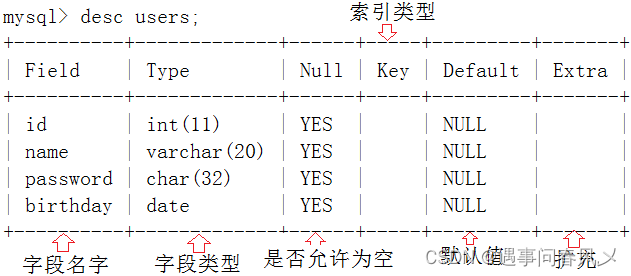
🚩创建表
⚾语法:
CREATE TABLE table_name ( field1 datatype, field2 datatype, field3 datatype );
⚾示例:
可以使用comment增加字段说明
create table stu_test ( id int, name varchar(20) comment '姓名', password varchar(50) comment '密码', age int, sex varchar(1), birthday timestamp, amout decimal(13,2), resume text );
结果展示:
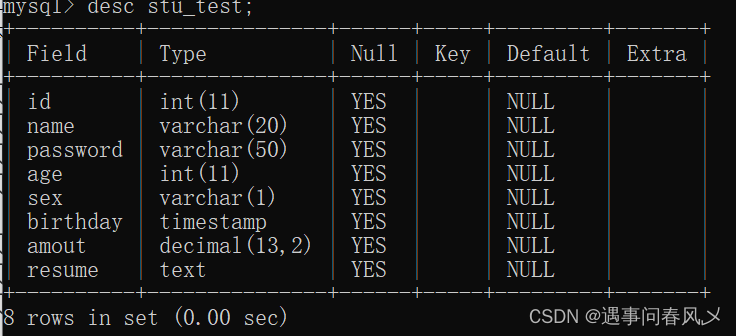
补充说明:comment这个注释并不好用
更推荐使用 --加空格来表示注释
create table student(name varchar(20)); -- 创建学生表
🚩删除表
🏀语法格式
DROP [TEMPORARY] TABLE [IF EXISTS] tbl_name [, tbl_name] ...
🏀示例
-- 删除 stu_test 表 drop table stu_test; -- 如果存在 stu_test 表,则删除 stu_test 表 drop table if exists stu_test;
🎡内容重点总结
- 操作数据库
– 显示
show databases;
– 创建
create database xxx;
– 使用
use xxx;
– 删除
drop database xxx;
- 常用数据类型:
INT:整型
DECIMAL(M, D):浮点数类型
VARCHAR(SIZE):字符串类型
TIMESTAMP:日期类型
- 操作表:
-- 查看 show 表; -- 创建 create table 表名( 字段1 类型1, 字段2 类型2, ... ); -- 删除 drop talbe 表名;
🍀练习
有一个商店的数据,记录客户及购物情况,有以下三个表组成:
-
商品goods(商品编号goods_id,商品名goods_name, 单价unitprice, 商品类别category, 供
应商provider)
-
客户customer(客户号customer_id,姓名name,住址address,邮箱email,性别sex,身份证
card_id)
-
购买purchase(购买订单号order_id,客户号customer_id,商品号goods_id,购买数量nums)
SQL语句如下:
-- 创建数据库 create database bit32mall; -- 选择数据库 use bit32mall; -- 创建数据库表 -- 商品 create table if not exists goods ( goods_id int -- '商品编号', goods_name varchar(32) -- '商品名称', unitprice int -- '单价,单位分', category varchar(12) -- '商品分类', provider varchar(64) -- '供应商名称' ); -- 客户 create table if not exists customer ( customer_id int -- '客户编号', name varchar(32) -- '客户姓名', address varchar(256) -- '客户地址', email varchar(64) -- '电子邮箱', sex bit -- '性别', card_id varchar(18) -- '身份证' ); -- 购买 create table if not exists purchase ( order_id int -- '订单号', customer_id int -- '客户编号', goods_id int -- '商品编号', nums int -- '购买数量' );
⭕总结
关于《【MySQL】 MySQL数据库基础》就讲解到这儿,感谢大家的支持,欢迎各位留言交流以及批评指正,如果文章对您有帮助或者觉得作者写的还不错可以点一下关注,点赞,收藏支持一下!
-
- 操作表:
- 常用数据类型:
- 有符号范围:-2(类型字节数*8-1)到2(类型字节数*8-1)-1,如int是4字节,就
-
- 🛫创建名为 db_test1 的数据库
-
上一篇:Spring 事务管理详解及使用














