- 华为eNSP配置MSTP实验
- ping命令使用示例解析
- 淘宝电商用户行为数据分析及可视化-基于MySQLTableau
- 超简单的正则表达式从入门到精通
- 微信小程序使用PHP调用后台mysql数据库-小白版
- springboot整合支付宝沙箱支付和退款
- 如何在CentOS安装SQL Server数据库并实现无公网IP远程连
- 开源浏览器Firefox:使用Docker本地部署并远程访问进行测试
- java.sql.SQLIntegrityConstraintViol
- C++项目工程(包含opencv库以及项目的依赖库移植)编译成andr
- 使用Navicat导出导出 MySQL 数据库表结构、表数据到Exce
- k8s中,kubelet 出现问题, k8s-master node
- AI大模型探索之路-实战篇2:基于CVP架构-企业级知识库实战落地
- Nginx使用教程
- 图论(算法竞赛、蓝桥杯)--Dijkstra算法最短路
- 华为ensp中链路聚合两种(lacp-static)模式配置方法
- 在VBA中使用SQL
- SpringBoot中集成LiteFlow(轻量、快速、稳定可编排的组
- Spring AOP—深入动态代理 万字详解(通俗易懂)
- Spring Boot如何彻底解决跨域问题,五种方案来看看吧
- MySQL:ERROR 1698 (28000): Access de
- 多模态之ALBEF—先对齐后融合,利用动量蒸馏学习视觉语言模型表征,学
- AI大模型探索之路-应用篇17:GLM大模型-大数据自助查询平台架构实
- 21、Lua 面向对象
- Nginx快速入门:访问日志access.log参数详解 |访问日志记
- 新零售门店、商品、会员管理指标体系总览
- 基于在线学习的分布式流量实时分析系统设计与实现
- 【Consul】基于Golang实现Consul服务的注册、注销、修改
- 实验一 关系数据库标准语言SQL 课后习题头歌
- IntelliJ IDEA 2023.3 的 AI Assistant
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、栈
- 1、栈的基本概念
- 2、栈的实现(数组实现)
- 3、栈的基本操作
- 3.1 栈的结构设计
- 3.2 栈常见的基本函数接口
- 4、栈的实现
- 4.1 初始化栈
- 4.2 栈的销毁
- 4.3 入栈
- 4.4 出栈
- 4.5 判空
- 4.6 长度
- 4.7 获取栈顶元素
- 完整代码
- Stack.h
- Stack.c
- Test.c
- 二、队列
- 1、队列的结构及概念
- 2、队列的实现(单链表实现)
- 1、队列的链式结构设计
- 2、常用的功能接口
- 2.1、初始化队列
- 2.2、销毁队列
- 2.3、入队列
- 2.4、出队列
- 2.5、获取队列头部元素
- 2.6、获取队列尾部元素
- 2.7、判空
- 2.8、获取有效元素个数
- 完整代码
- Queue.h
- Queue.c
- Test.c
前言

一、栈
1、栈的基本概念
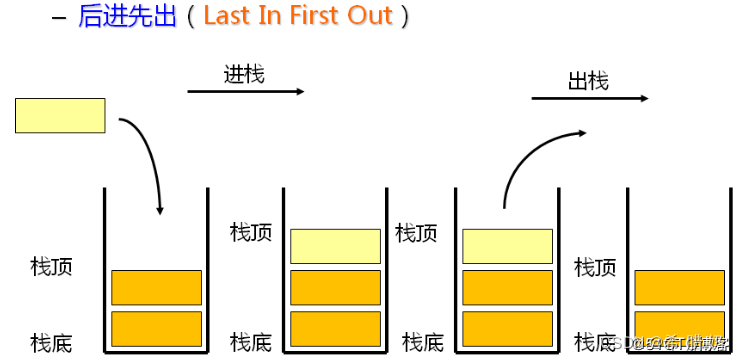
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶
2、栈的实现(数组实现)
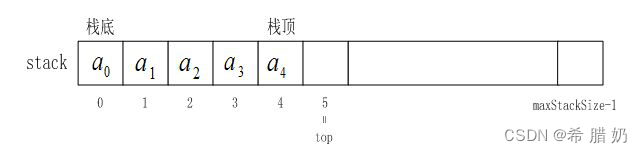
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小
3、栈的基本操作
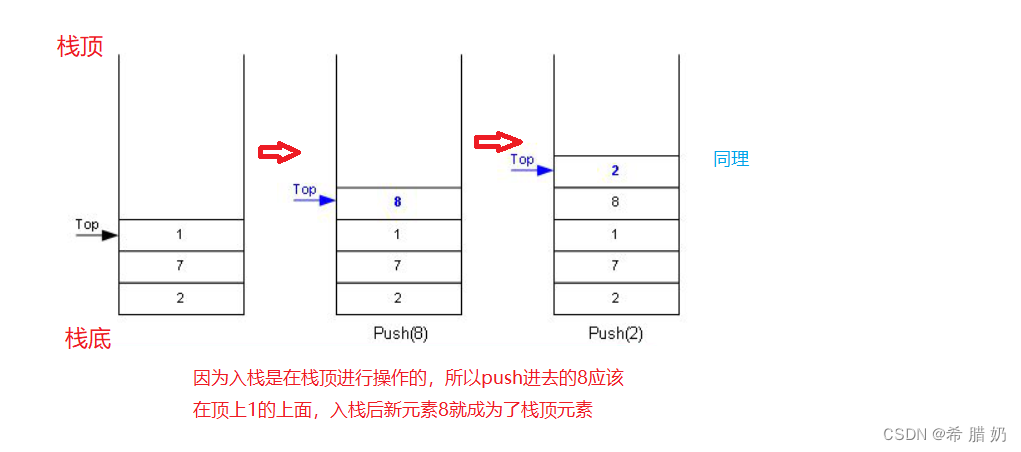
压栈:栈的插入操作,也叫进栈/入栈/压栈,在栈顶进行数据操作。
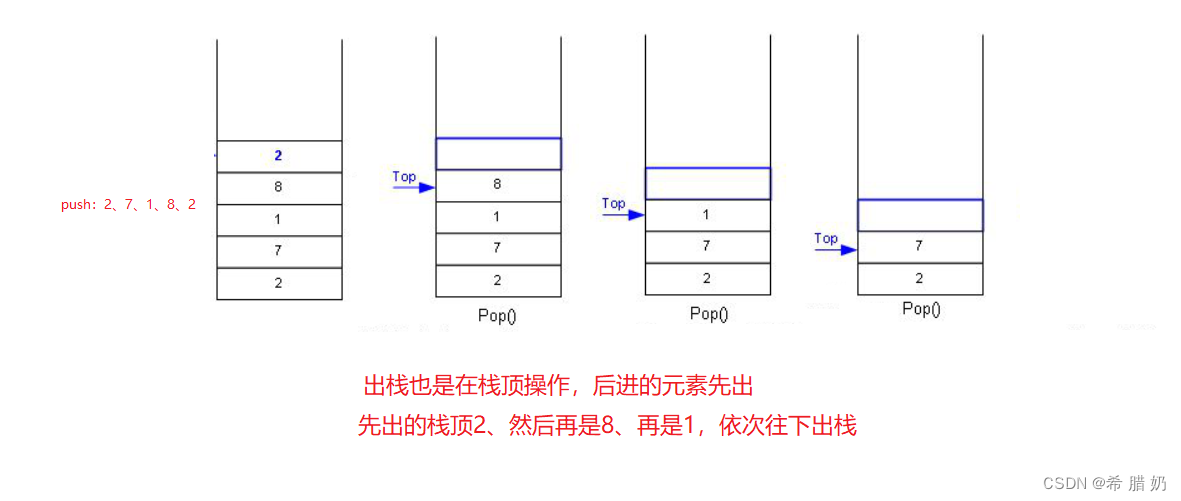
出栈:栈的删除操作,也是在栈顶进行数据删除的。
3.1 栈的结构设计
typedef int STDataType;//方便修改类型 typedef struct Stack { STDataType* a; int top; int capacity; }ST;3.2 栈常见的基本函数接口
//初始化 void STInit(ST* pst); //销毁栈 void STDestroy(ST* pst); //入栈 void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x); //出栈 void STPop(ST* pst); //判空 bool STEmpty(ST* pst); //长度 int STSize(ST* pst); //栈顶 STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
4、栈的实现
4.1 初始化栈
//初始化 void STInit(ST* pst) { assert(pst); pst->a = NULL; pst->top = 0;//指向栈顶下一个元素,若等于-1则指向栈顶元素,两种任选 pst->capacity = 0; }4.2 栈的销毁
//销毁栈 void STDestroy(ST* pst) { assert(pst); tree(pst->a); pst->a = NULL; pst->top = 0; pst->capacity = 0; }4.3 入栈
代码:
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x) { assert(pst); //判断栈是否已满,满了就扩容 if (pst->top == pst->capacity) { //使用三目运算符进行第一次开辟空间和后续扩容空间 int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2; STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity); //判断realloc是否开辟成功 if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc fail"); return; } //赋新值 pst->a = tmp; pst->capacity = newcapacity; } //插入 pst->a[pst->top] = x; pst->top++; }4.4 出栈
代码:
//出栈 void STPop(ST* pst) { assert(pst); assert(pst->top > 0); pst->top--; }4.5 判空
//判空 bool STEmpty(ST* pst) { assert(pst); //返回值为0为假,非零为真 return pst->top == 0; }4.6 长度
//长度 int STSize(ST* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top; }4.7 获取栈顶元素
注意:若栈顶指针初始化为pst->top = 0,即栈顶指针指向栈顶元素的下一个位置,则入栈操作变为pst->a[pst->top++],出栈操作为pst->a[- -pst->top]。因为栈顶指针若初始化为 0 时,则栈顶指针始终指向顺序栈将要入栈的位置,也就是栈顶指针的下标就是入栈元素的下标。
//栈顶 STDataType STTop(ST* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->a[pst->top - 1]; }完整代码
Stack.h
#include
#include #include #include typedef int STDataType; typedef struct Stack { STDataType* a; int top; int capacity; }ST; //初始化 void STInit(ST* pst); //销毁栈 void STDestroy(ST* pst); //入栈 void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x); //出栈 void STPop(ST* pst); //判空 bool STEmpty(ST* pst); //长度 int STSize(ST* pst); //栈顶 STDataType STTop(ST* pst); Stack.c
#include"Stack.h" //初始化 void STInit(ST* pst) { assert(pst); pst->a = NULL; pst->top = 0;//指向栈顶下一个元素 pst->capacity = 0; } //销毁栈 void STDestroy(ST* pst) { assert(pst); tree(pst->a); pst->a = NULL; pst->top = 0; pst->capacity = 0; } //入栈 void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x) { assert(pst); if (pst->top == pst->capacity) { int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2; STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity); if (tmp == NULL) { perror("realloc fail"); return; } pst->capacity = newcapacity; pst->a = tmp; } pst->a[pst->top] = x; pst->top++; } //出栈 void STPop(ST* pst) { assert(pst); assert(pst->top > 0); pst->top--; } //判空 bool STEmpty(ST* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top == 0; } //长度 int STSize(ST* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->top; } //栈顶 STDataType STTop(ST* pst) { assert(pst); return pst->a[pst->top - 1]; }Test.c
#include"Stack.h" int main() { ST st; //初始化 STInit(&st); //插入+删除 STPush(&st, 1); STPush(&st, 2); STPush(&st, 3); STPush(&st, 4); STPush(&st, 5); STPop(&st); STPop(&st); //长度 STSize(&st); //栈顶 STTop(&st); //销毁 STDestroy(&st); return 0; }二、队列
1、队列的结构及概念
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
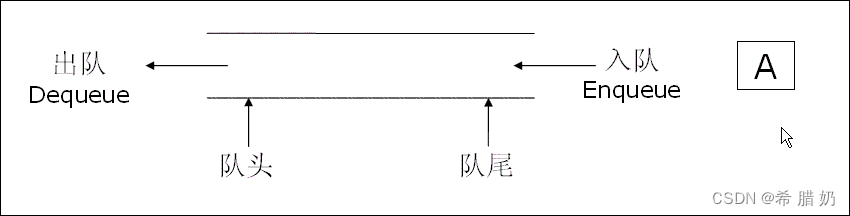
2、队列的实现(单链表实现)
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
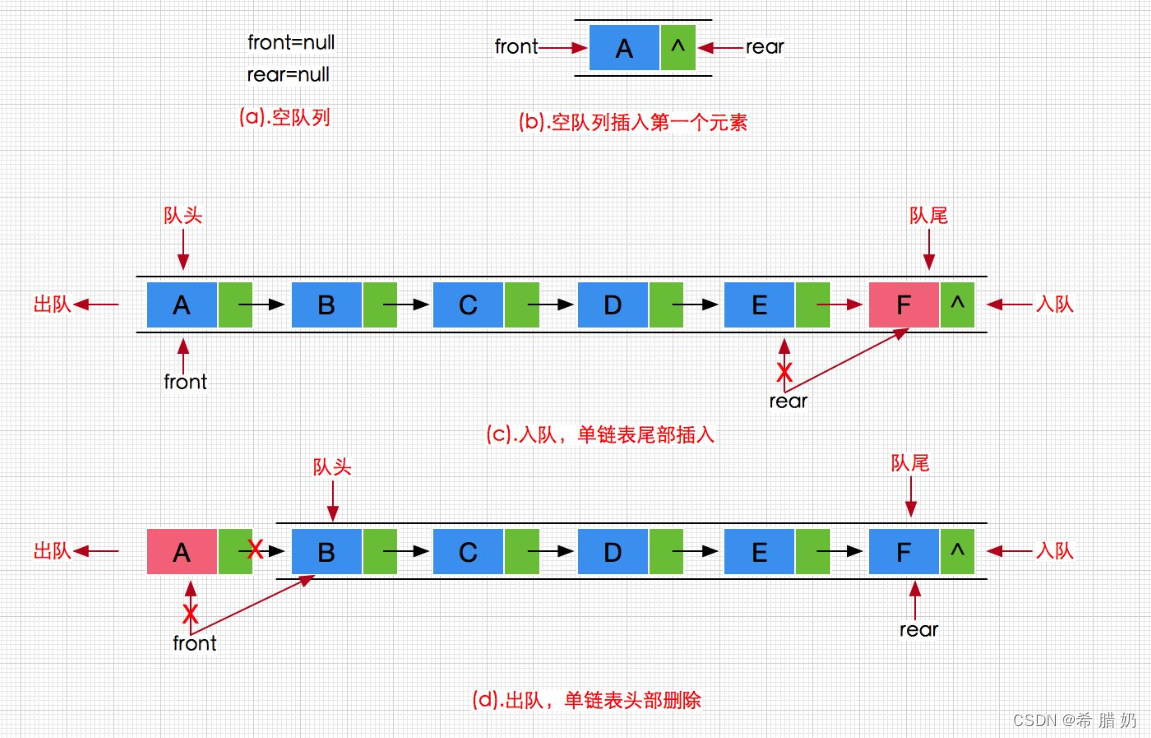
下面话不多说,直接开始代码实现
1、队列的链式结构设计
//链式结构 表示队列 typedef int QDataType; typedef struct QueueNode { struct QueueNode* next; QDataType val; }QNode; //队列的结构 typedef struct Queue { QNode* phead; QNode* ptail; int size; }Queue;2、常用的功能接口
//初始化 void QueueInit(Queue* pq); //销毁队列 void QueueDeatroy(Queue* pq); //队尾入列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x); //队头出列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq); //获取队列头部元素 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq); //获取队列尾部元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq); //检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq); //获取队列中有效元素个数 int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
2.1、初始化队列
只需要将头尾指针都指向空即可,元素个数为零
//初始化 void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->phead = NULL; pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }2.2、销毁队列
遍历链表,从头到尾依次删除结点,最后将头尾指针指向空,元素个数为0。
//销毁队列 void QueueDeatroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QNode* cur = pq->phead; while (cur) { QNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->phead = NULL; pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }2.3、入队列
创建新节点,若队列为空,则将头指针和尾指针都指向新创建的节点,若不为空,则尾插,因为是链式存储,所以和单链表的尾插一样,将尾指针的next指向该节点,再把该节点设为新的尾节点
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } newnode->val = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (pq->ptail == NULL) { pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode; } else { pq->ptail->next = newnode; pq->ptail = newnode; } pq->size++; }2.4、出队列
注意:出列要考虑队列是空还是只有一个结点又或者有多个结点,为空则在代码第一步就报错,若只有一个结点,则直接删除该结点,并将头尾俩指针指向空,若不止一个结点,可以创建一个临时指针来记录当前头指针,然后尾指针往后遍历,再free掉创建的临时指针,并置空
void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); QNode* del = pq->phead; pq->phead = pq->phead->next; free(del); del = NULL; if (pq->phead == NULL) pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size--; }2.5、获取队列头部元素
断言,然后直接返回队头指针指向的节点元素
//获取队列头部元素 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); return pq->phead->val; }2.6、获取队列尾部元素
也是一样的,直接返回队尾指针指向的节点元素
//获取队列尾部元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); return pq->ptail->val; }2.7、判空
检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->phead == NULL; }2.8、获取有效元素个数
//获取队列中有效元素个数 int QueueSize(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; }完整代码
Queue.h
#include
#include #include #include //链式结构 表示队列 typedef int QDataType; typedef struct QueueNode { struct QueueNode* next; QDataType val; }QNode; //队列的结构 typedef struct Queue { QNode* phead; QNode* ptail; int size; }Queue; //初始化 void QueueInit(Queue* pq); //销毁队列 void QueueDeatroy(Queue* pq); //队尾入列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x); //队头出列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq); //获取队列头部元素 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq); //获取队列尾部元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq); //检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq); //获取队列中有效元素个数 int QueueSize(Queue* pq); Queue.c
#include"Queue.h" //初始化 void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->phead = NULL; pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; } //销毁队列 void QueueDeatroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QNode* cur = pq->phead; while (cur) { QNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->phead = NULL; pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; } //队尾入列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); exit(-1); } newnode->next = NULL; newnode->val = x; if (pq->ptail == NULL) { pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode; } else { //现在newnode是新的尾结点 pq->ptail->next = newnode; pq->ptail = newnode; } pq->size++; } //队头出列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); //保存当前节点 QNode* tmp = pq->phead; //phead往下走 pq->phead = pq->phead->next; free(tmp); tmp = NULL; if (pq->phead = NULL) { pq->ptail = NULL; } pq->size--; } //获取队列头部元素 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); return pq->phead->val; } //获取队列尾部元素 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); return pq->ptail; } //检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->phead == NULL; } //获取队列中有效元素个数 int QueueSize(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; }Test.c
#include"Queue.h" int main() { Queue q; QueueInit(&q); QueuePush(&q, 1); QueuePush(&q, 2); QueuePush(&q, 3); while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) { printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q)); QueuePop(&q); } QueueDeatroy(&q); return 0; }
上一篇:初级数据结构(七)——二叉树














