- 云计算时代的运维: 职业发展方向与岗位选择
- 使用 Docker 部署 Nacos 并配置 MySQL 数据源
- 我们该如何看待AIGC(人工智能)
- SpringBoot+Vue入门并实现前后端分离和数据库查询(入门笔记
- vue前端简单实现无缝循环滚动自动播放,滚动条上下滚动,鼠标悬停,从鼠
- com.mysql.cj.exceptions.CJCommunica
- 基于JSP+Mysql+HTml+Css仓库出入库管理系统设计与实现
- Java八股文(Spring Boot)
- 使用PySpider进行IP代理爬虫的技巧与实践
- nginx如何配置ws(websocket)代理服务?
- Aivis:AI语音模仿系统
- JavaWeb项目:航班信息管理系统(tomcat+jsp)
- org.apache.tomcat.util.http.fileupl
- HCIA | WLAN二层旁挂组网实验
- 剑指offer刷题笔记-链表
- 【vue加载16秒优化到2秒】Vue3加载慢的性能优化,打包后页面静态
- tomcat默认最大线程数、等待队列长度、连接超时时间
- 华为ensp中nat server 公网访问内网服务器
- 前端Vue日常工作中--Watch数据监听
- SpringBoot 解决跨域问题的 5 种方案!
- 智慧工地管理平台APP源码基于物联网、云计算、大数据等技术
- Java面试八股文(JVM篇)(❤❤)
- 深入理解深度学习:LabML AI注解实现库
- 【微服务】spring状态机模式使用详解
- IntelliJ IDEA 2023.3 的 AI Assistant
- 云计算——ACA学习 阿里云云计算服务概述
- 解决mysql:2059 -Authentication plugin
- Vue实例挂载的过程
- SpringMVC运行时出现404错误(解决办法汇总,基本包含所有错误
- 【Consul】基于Golang实现Consul服务的注册、注销、修改

📋 前言
🌈hello! 各位铁铁们大家好啊,栈和队列我们都学过了那么试试用队列实现栈你会嘛?。
⛳️本篇文章就来给大家来篇如何用队列来实现栈的全部解析让你彻底拿捏队列。
📚本期文章收录在《数据结构&算法》,大家有兴趣可以看看呐!
⛺️ 欢迎铁汁们 ✔️ 点赞 👍 收藏 ⭐留言 📝!
文章目录
- 📋 前言
- 一、队列实现栈的具体功能
- 二、队列实现栈的具体思路
- 2.1 实现栈区的具体方法
- 2.1 栈区的插入思路
- 2.1 栈区的删除思路
- 三、队列实现栈(具体代码)
- 3.1 队列的准备
- 3.2 栈区的初始化
- 3.3 栈区的插入
- 3.4 栈区的删除
- 3.5 栈区的判空
- 3.6 获取栈区的头元素
- 3.7 栈区的销毁
- 三、全部实现代码
- 📝全篇总结
一、队列实现栈的具体功能

二、队列实现栈的具体思路
我们先来总结一下队列的特点 先进先出 ,队列的特点 是 后进先出 :
- 具体我们可以看一下下图来快速了解
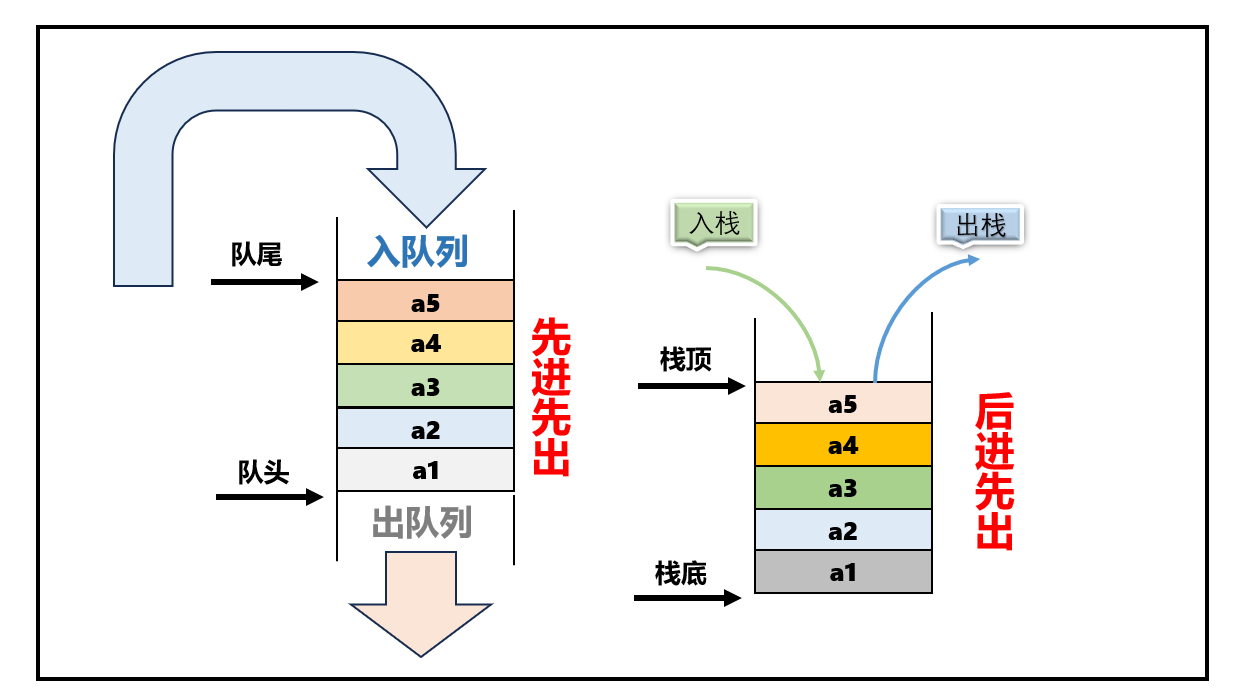
- 队列的特点是先进先出
- 我们要实现栈的功能是后进先出
2.1 实现栈区的具体方法
我们是不是可以具体这样想,队列既然是先进先出,栈是后进先出,的意识就是我们需要每次获取的栈区数据是队列的最后一个:
- ⁉️那可以不可以这样呢?
- 开辟俩个队列空间,每次让其中一个为空
- 另外一个不为空,这样就可以解决删除的问题了。
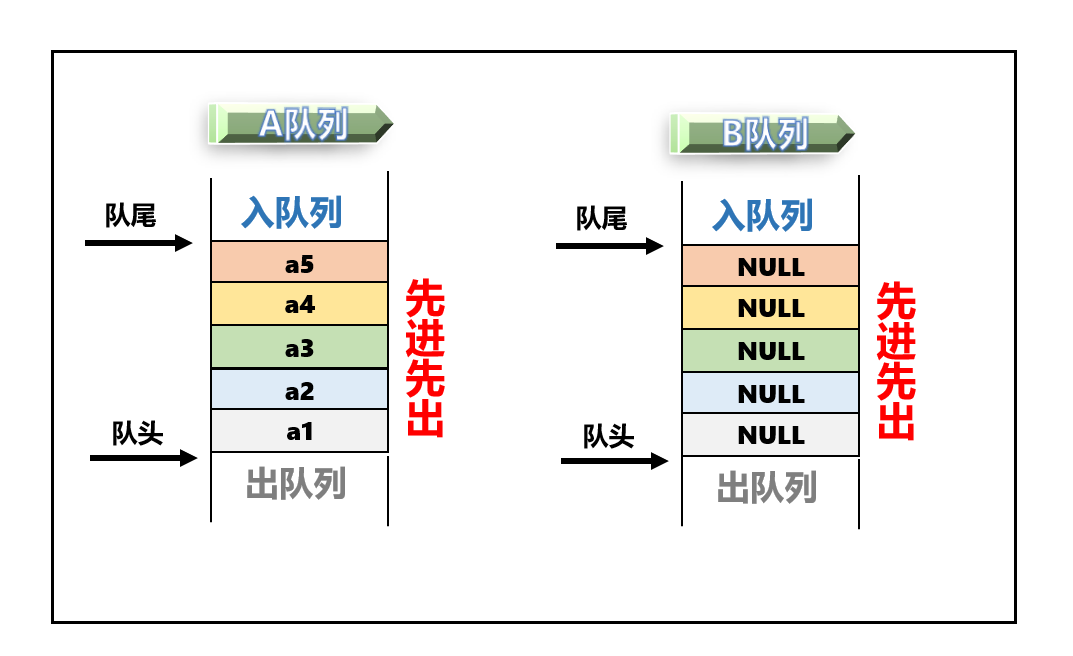
2.1 栈区的插入思路
这思路就很简单如果使用俩个指针来管理队列,那么插入就非常简单了,只需要考虑俩种情况:
- 第一种当然是俩个栈区都为空的情况,还没开始插数据
- 第二种就是已经插入数据了,那么插入的时候直接往不为空的栈区插入就好了。
2.1 栈区的删除思路
大家看如何我们使用俩个指针来管理队列,来实现栈的话那么来删除就非常简单了为什么这样说呢?
- 既然一个队列永远为空,一个不为空
- 那么删除的时候直接把不为空的队列插入到为空的队列
- 留下最后一个元素用来删除就好了
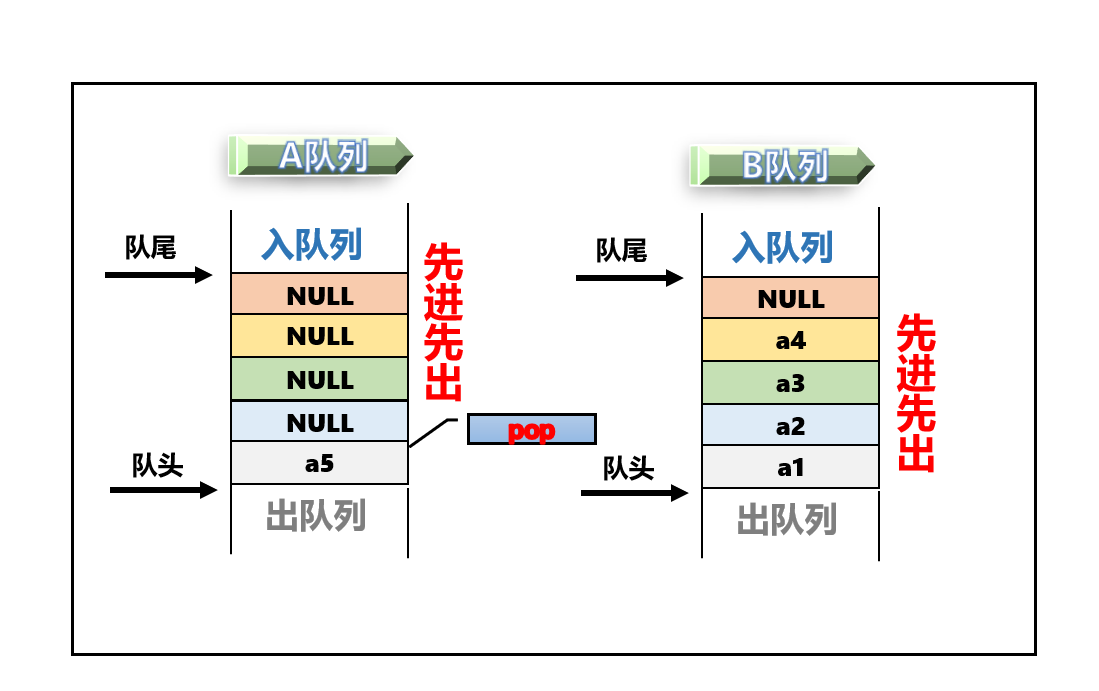
三、队列实现栈(具体代码)
好了以上就是队列实现栈的核心思想了,只要核心思想掌握了,那么其他就是小菜了。下面我们就来快速实现一下吧:
3.1 队列的准备
这里是队列的实现代码,由于C语言库里面并没有队列这个数据结构我们就只能手动实现了:
- 如果有想了解队列的可以看这篇文章:
#include
#include #include #include typedef int QueDataType; typedef struct QueueType { QueDataType data; struct QueueType* next; }QueueNode; typedef struct Queue { struct QueueType* head; struct QueueType* tail; int size; }Que; //初始化队列 void QueueInit(Que* ps); //销毁队列 void QueueDestroy(Que* ps); //插入数据 void QueuePush(Que* ps, QueDataType x); //删除数据 void QueuePop(Que* ps); //获取头数据 QueDataType QueueFront(Que* ps); //获取尾数据 QueDataType QueueBack(Que* ps); //获取队列长度 int QueueSize(Que* ps); //判断是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Que* ps); //初始化队列 void QueueInit(Que* ps) { assert(ps); ps->head = NULL; ps->tail = NULL; ps->size = 0; } //销毁队列 void QueueDestroy(Que* ps) { assert(ps); QueueNode* cur = ps->head; while (cur) { QueueNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } ps->head = ps->tail = NULL; ps->size = 0; } //插入数据 void QueuePush(Que* ps, QueDataType x) { assert(ps); QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); exit(-1); } newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (ps->head == NULL) { ps->head = ps->tail = newnode; } else { ps->tail->next = newnode; ps->tail = newnode; } ps->size++; } //删除数据 void QueuePop(Que* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); if (pq->head->next == NULL) { free(pq->head); pq->head = pq->tail = NULL; } else { QueueNode* next = pq->head->next; free(pq->head); pq->head = next; } pq->size--; } //获取头数据 QueDataType QueueFront(Que* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!QueueEmpty(ps)); return ps->head->data; } //获取尾数据 QueDataType QueueBack(Que* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!QueueEmpty(ps)); return ps->tail->data; } //获取队列长度 int QueueSize(Que* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->size; } //判断是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Que* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->head == NULL; } 3.2 栈区的初始化
好了思路我们理清楚了接下来就是看看具体队列实现栈的代码到底如何实现:
- 前面我们说过了使用俩个指针来管理队列就好了
- 然后进行 malloc 申请空间就好了
📚 代码演示:
typedef struct { Que q1; Que q2; } MyStack; MyStack* myStackCreate() { MyStack* obj = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack)); QueueInit(&obj->q1); QueueInit(&obj->q2); return obj; }3.3 栈区的插入
插入的话我们思想已经都知道,下面就是考验你的代码能力了:
- 如果俩个队列为空随便插入一个就好了
- 否则就插入另一个队列
-
📚 代码演示:
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) { assert(obj); if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { QueuePush(&obj->q1,x); } else { QueuePush(&obj->q2,x); } }3.4 栈区的删除
删除的思想很简单,每次搬运一下队列就好了:
- 这里使用了一个非常实用的判定方法大家可以去看看
- 先假设一个为空一个不为空
- 然后如果错了就换过来
📚 代码演示:
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) { assert(obj); Que* empty = &obj->q1; Que* noempty = &obj->q2; if(!QueueEmpty(empty)) { empty = &obj->q2; noempty = &obj->q1; } while(QueueSize(noempty) > 1) { QueuePush(empty, QueueFront(noempty)); QueuePop(noempty); } int top = QueueFront(noempty); QueuePop(noempty); return top; }3.5 栈区的判空
这个就简单了只要栈中管理俩个队列的的都为空那当然都没有数据了:
- QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2)
📚 代码演示:
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) { return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2); }3.6 获取栈区的头元素
既然我们使用了俩个队列来实现栈,并且只有一个队列存放数据。
- 那么只需要看哪个队列不为取出队尾数据就好了。
📚 代码演示:
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) { if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { return QueueBack(&obj->q1); } else { return QueueBack(&obj->q2); } }3.7 栈区的销毁
老样子了,先把栈区里面的 malloc 里面的空间释放了,然后再释放栈就好了。
📚 代码演示:
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) { QueueDestroy(&obj->q1); QueueDestroy(&obj->q2); free(obj); }三、全部实现代码
📚 代码演示:
#include
#include #include #include typedef int QueDataType; typedef struct QueueType { QueDataType data; struct QueueType* next; }QueueNode; typedef struct Queue { struct QueueType* head; struct QueueType* tail; int size; }Que; //初始化队列 void QueueInit(Que* ps); //销毁队列 void QueueDestroy(Que* ps); //插入数据 void QueuePush(Que* ps, QueDataType x); //删除数据 void QueuePop(Que* ps); //获取头数据 QueDataType QueueFront(Que* ps); //获取尾数据 QueDataType QueueBack(Que* ps); //获取队列长度 int QueueSize(Que* ps); //判断是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Que* ps); //初始化队列 void QueueInit(Que* ps) { assert(ps); ps->head = NULL; ps->tail = NULL; ps->size = 0; } //销毁队列 void QueueDestroy(Que* ps) { assert(ps); QueueNode* cur = ps->head; while (cur) { QueueNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } ps->head = ps->tail = NULL; ps->size = 0; } //插入数据 void QueuePush(Que* ps, QueDataType x) { assert(ps); QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); exit(-1); } newnode->data = x; newnode->next = NULL; if (ps->head == NULL) { ps->head = ps->tail = newnode; } else { ps->tail->next = newnode; ps->tail = newnode; } ps->size++; } //删除数据 void QueuePop(Que* pq) { assert(pq); assert(!QueueEmpty(pq)); if (pq->head->next == NULL) { free(pq->head); pq->head = pq->tail = NULL; } else { QueueNode* next = pq->head->next; free(pq->head); pq->head = next; } pq->size--; } //获取头数据 QueDataType QueueFront(Que* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!QueueEmpty(ps)); return ps->head->data; } //获取尾数据 QueDataType QueueBack(Que* ps) { assert(ps); assert(!QueueEmpty(ps)); return ps->tail->data; } //获取队列长度 int QueueSize(Que* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->size; } //判断是否为空 bool QueueEmpty(Que* ps) { assert(ps); return ps->head == NULL; } typedef struct { Que q1; Que q2; } MyStack; MyStack* myStackCreate() { MyStack* obj = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack)); QueueInit(&obj->q1); QueueInit(&obj->q2); return obj; } void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) { assert(obj); if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { QueuePush(&obj->q1,x); } else { QueuePush(&obj->q2,x); } } int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) { assert(obj); Que* empty = &obj->q1; Que* noempty = &obj->q2; if(!QueueEmpty(empty)) { empty = &obj->q2; noempty = &obj->q1; } while(QueueSize(noempty) > 1) { QueuePush(empty, QueueFront(noempty)); QueuePop(noempty); } int top = QueueFront(noempty); QueuePop(noempty); return top; } int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) { if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)) { return QueueBack(&obj->q1); } else { return QueueBack(&obj->q2); } } bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) { return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2); } void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) { QueueDestroy(&obj->q1); QueueDestroy(&obj->q2); free(obj); } /** * Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such: * MyStack* obj = myStackCreate(); * myStackPush(obj, x); * int param_2 = myStackPop(obj); * int param_3 = myStackTop(obj); * bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj); * myStackFree(obj); */ 📝全篇总结
☁️ 好了以上就是队列实现栈的全部细节与过程来,大家不要忘记练习哦!
看到这里了还不给博主扣个:
⛳️ 点赞☀️收藏 ⭐️ 关注!
💛 💙 💜 ❤️ 💚💓 💗 💕 💞 💘 💖
拜托拜托这个真的很重要!
你们的点赞就是博主更新最大的动力!
有问题可以评论或者私信呢秒回哦。

- 那么只需要看哪个队列不为取出队尾数据就好了。
- QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2)
- 如果有想了解队列的可以看这篇文章:
- 具体我们可以看一下下图来快速了解
上一篇:求组合数的三种算法














