- Nginx 长连接keep
- 首游南京,AI科技大事件分享:百度智能云宣布国内首家支持Llama3全
- AI小说推文工具,一键生成AI视频推文助手
- Springboot JPA打印SQL语句及参数(2024最新版)
- SpringBlade dict-bizlist SQL 注入漏洞复现
- Mac安装及配置MySql及图形化工具MySQLworkbench安装
- 【经典算法】LeetCode 64. 最小路径和(JavaCPytho
- 【JavaScript+自然语言处理+HTML+CSS】实现Web端的
- 【MySQL】内外连接——内连接、外连接、左外连接、右外连接、内外连接
- 【CSDN活动】人工智能:前沿科技中的创业机遇与挑战
- 高级Java开发工程师手把手教你用AI人工智能帮你写JAVA代码实际案
- MySql005——使用SQL创建数据库和表(创建、选择、删除、插入)
- 12.Mysql 多表数据横向合并和纵向合并
- K8S--安装metrics-server,解决error: Metr
- SpringBoot集成WebSocket,实现后台向前端推送信息
- SpringBoot整合Minio的详细步骤
- Spring Cloud Alibaba 面试题及答案整理,最新面试题
- Nginx系列:windows10系统下安装nginx的安装并配置!
- 【爬虫实战】python文本分析库——Gensim
- 分享 GoLand 2024.1 激活的方案,支持JetBrains全
- 蓝禾,三七互娱,顺丰,康冠科技,金证科技24春招内推
- 阿里面试总结 一
- 【每日一题】LeetCode——链表的中间结点
- Docker - 基本概念、与虚拟机的区别、架构、镜像操作、容器操作、
- Java Spring Boot 写 API 接口
- 【粉丝福利社】《AIGC重塑金融:AI大模型驱动的金融变革与实践》(文
- Linux【OSMCTools 02】OpenStreetMap数据处
- 云计算——ACA学习 阿里云云计算服务概述
- 自然语言处理NLP:文本预处理Text Pre-Processing
- springboot整合支付宝沙箱支付和退款
一、问题重述
电商物流网络在订单履约中由多个环节组成,图1是一个简化的物流网络示意图。其中,分拣中心作为网络的中间环节,需要将包裹按照不同流向进行分拣并发往下一个场地,最终使包裹到达消费者手中。分拣中心管理效率的提升,对整体网络的履约效率和运作成本起着十分重要的作用。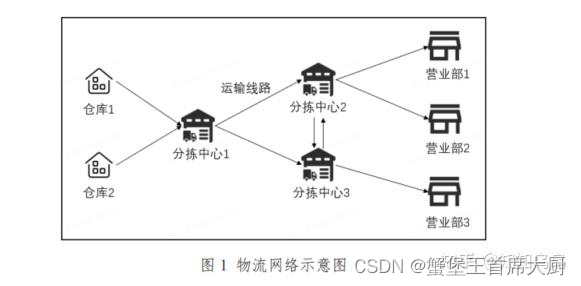 整体网络的履
整体网络的履
分拣中心的货量预测是电商物流网络重要的研究问题,对分拣中心货量的精准预测是后续管理及决策的基础,如果管理者可以提前预知之后一段时间各个分拣中心需要操作的货量,便可以提前对资源进行安排。在此场景下的货量预测目标一般有两个:一是根据历史货量、物流网络配置等信息,预测每个分拣中心每天的货量;二是根据历史货量小时数据,预测每个分拣中心每小时的货量。
分拣中心的货量预测与网络的运输线路有关,通过分析各线路的运输货量,可以得出各分拣中心之间的网络连接关系。当线路关系调整时,可以参考线路的调整信息,得到各分拣中心货量更为准确的预测。
基于分拣中心货量预测的人员排班是接下来要解决的重要问题,分拣中心的人员包含正式工和临时工两种:正式工是场地长期雇佣的人员,工作效率较高:临时工是根据货量情况临时招募的人员,每天可以任意增减但工作效率相对较低、雇佣成本较高。根据货量预测结果合理安排人员,旨在完成工作的情况下尽可能降低人员成本。针对当前物流网络,其人员安排班次及小时人效指标情况如下:
1)对于所有分拣中心,每天分为6个班次,分别为:00:00-08:00,05:00-13:00,08:00-16:00、12:00-20:00,14:00-22:00. 16:00-24:00.每个人员(正式工或临时工)每天只能出勤一个班次;2)小时人效指标为每人每小时完成分拣的包裹量(包裹量即货量),正式工的最高小时人效为 25 包裹/小时,临时工的最高小时人效为 20包裹1小时。
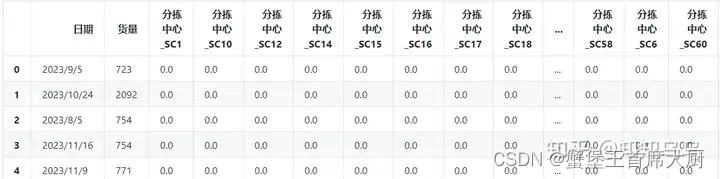
该物流网络包括57个分拣中心,每个分拣中心过去4个月的每天货量如附件1所示,过去30天的每小时货量如附件2所示。基于以上数据,请完成以下问题:
问题 1
建立货量预测模型,对57 个分拣中心未来 30 天每天及每小时的货量进行预测,将预测结果写入结果表1和表2中。
解题思路
使用了深度学习中的长短期记忆(LSTM)神经网络来进行时间序列的预测
数据加载和预处理:
1、使用Pandas库加载CSV文件,并将日期列转换为日期时间格式。
2、对数据进行预处理,包括选择特定的分拣中心,对货量数据进行归一化处理。
3、将时间序列数据转换为适用于LSTM模型的输入格式。这里使用了一个滑动窗口的方法,将过去一段时间的数据作为输入,然后使用下一时刻的数据作为输出。
4、使用Keras库构建一个简单的LSTM模型,包括一个LSTM层和一个全连接层。
5、编译模型,并使用训练数据进行模型训练。
6、使用训练好的模型进行未来30天每小时的预测。在每次预测时,将最近的24小时数据传递给模型,并预测下一个时刻的货量。
7、使用逆变换将归一化的预测结果转换回原始货量值。
8、将预测结果写入CSV文件,包括分拣中心、日期、小时和预测货量。
解题代码(python)
import pandas as pd
file_paths = ['附件1.csv', '附件2.csv', '附件3.csv', '附件4.csv']
data_frames_gb2312 = [pd.read_csv(file_path, encoding='GB2312') for file_path in file_paths]
for i, df in enumerate(data_frames_gb2312, start=1):
print(f"Data from 附件{i} :")
print(df.head(), "\n")
#%%
from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder
data = pd.read_csv('附件1.csv', encoding='GB2312')
encoder = OneHotEncoder()
center_encoded = encoder.fit_transform(data[['分拣中心']]).toarray() # 使用.toarray()将稀疏矩阵转换为密集矩阵
# 将编码后的数据转换为DataFrame,并添加回原始数据集
center_encoded_df = pd.DataFrame(center_encoded, columns=encoder.get_feature_names_out())
data = data.reset_index(drop=True)
data_encoded = pd.concat([data.drop('分拣中心', axis=1), center_encoded_df], axis=1)
# 显示处理后的数据前几行
data_encoded.head()
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 数据加载
data = pd.read_csv('附件1.csv', encoding='GB2312')
data['日期'] = pd.to_datetime(data['日期'])
data = data.sort_values('日期')
# 仅使用SC48分拣中心的数据作为示例
data_example = data[data['分拣中心'] == 'SC48'].groupby('日期')['货量'].sum().reset_index()
# 数据标准化
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
data_example['货量'] = scaler.fit_transform(data_example[['货量']])
# 将时间序列数据转换为监督学习问题
def create_dataset(dataset, look_back=1):
X, Y = [], []
for i in range(len(dataset)-look_back-1):
a = dataset[i:(i+look_back)]
X.append(a)
Y.append(dataset[i + look_back])
return np.array(X), np.array(Y)
look_back = 1
scaled = data_example['货量'].values
X, Y = create_dataset(scaled, look_back)
X = np.reshape(X, (X.shape[0], 1, X.shape[1]))
# 构建LSTM模型
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(4, input_shape=(1, look_back)))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(loss='mean_squared_error', optimizer='adam')
# 模型训练
model.fit(X, Y, epochs=100, batch_size=1, verbose=2)
# 进行预测
train_predict = model.predict(X)
# 反转预测值以便可视化
train_predict = scaler.inverse_transform(train_predict)
Y_inverse = scaler.inverse_transform([Y])
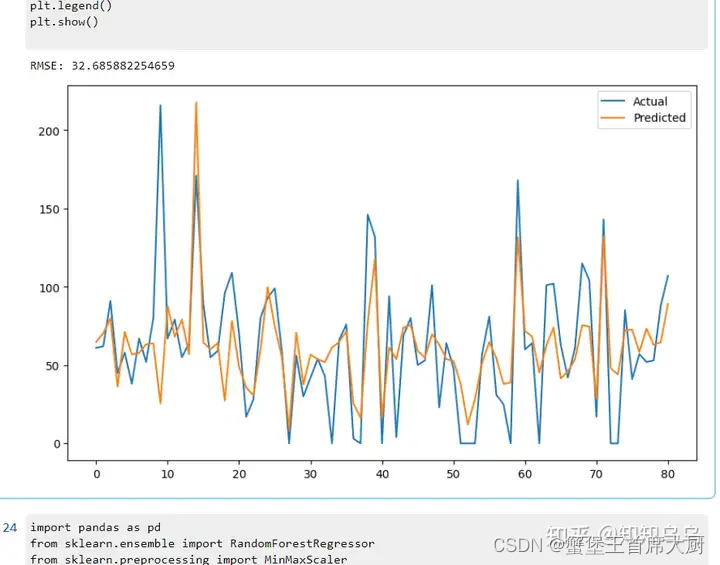
# 计算性能指标
train_score = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(Y_inverse[0], train_predict[:,0]))
print('Train Score: %.2f RMSE' % (train_score))
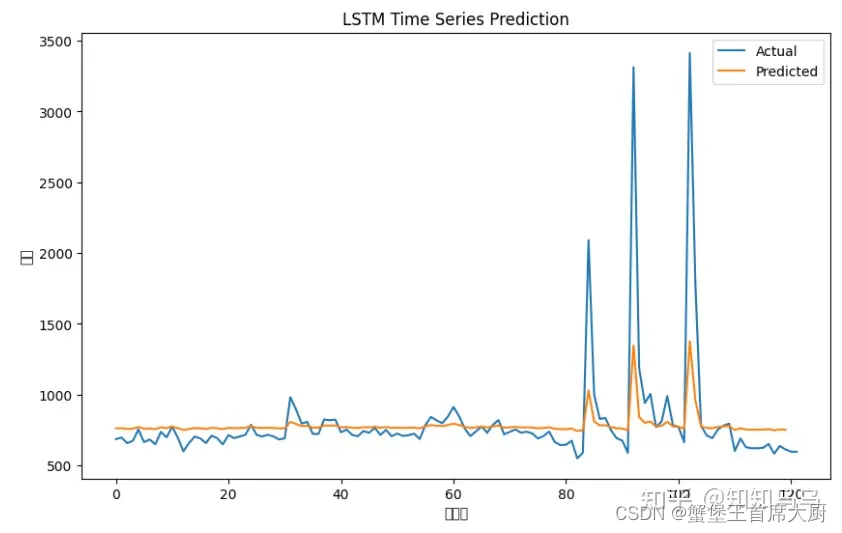
# 可视化展示
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
plt.plot(scaler.inverse_transform(scaled.reshape(-1,1)))
plt.plot(train_predict)
plt.title('LSTM Time Series Prediction')
plt.ylabel('货量')
plt.xlabel('时间点')
plt.legend(['Actual', 'Predicted'], loc='upper right')
plt.show()

问题 2
过去 90天各分拣中心之间的各运输线路平均货量如附件3所示。若未来 30 天分拣中心之间的运输线路发生了变化,具体如附件4所示。根据附件 1-4,请对 57个分拣中心未来 30 天每天及每小时的货量进行预测,并将预测结果写入结果表3和表4中。
解题思路与代码
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime
# 加载数据
attachment_3_path = '附件3.csv'
attachment_4_path = '附件4.csv'
attachment_1_path = '附件1.csv'
attachment_3 = pd.read_csv(attachment_3_path, encoding='GB2312')
attachment_4 = pd.read_csv(attachment_4_path, encoding='GB2312')
attachment_1 = pd.read_csv(attachment_1_path, encoding='GB2312')
# 确定新增的运输线路
existing_routes_set = set(tuple(x) for x in attachment_3[['始发分拣中心', '到达分拣中心']].values)
future_routes_set = set(tuple(x) for x in attachment_4[['始发分拣中心', '到达分拣中心']].values)
added_routes = future_routes_set - existing_routes_set
# 估算新增运输线路的初始货量为附件3中的平均货量
average_cargo_volume = attachment_3['货量'].mean()
# 如果我们关注的是一个特定的分拣中心,例如SC31,我们可以按照以下方式整合这些信息
data_SC31 = attachment_1[attachment_1['分拣中心'] == 'SC31']
data_SC31['日期'] = pd.to_datetime(data_SC31['日期'])
data_SC31.sort_values('日期', inplace=True)
# 对于示例,我们不直接将新增运输线路的数据加入到模型中,
# 而是关注如何使用现有数据进行预测
# 数据预处理
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
data_SC31_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(data_SC31[['货量']])
look_back = 1
X_SC31, Y_SC31 = create_dataset(data_SC31_scaled, look_back)
X_SC31 = np.reshape(X_SC31, (X_SC31.shape[0], 1, X_SC31.shape[1]))
# 构建LSTM模型
model_SC31 = Sequential([
LSTM(4, input_shape=(1, look_back)),
Dense(1)
])
model_SC31.compile(loss='mean_squared_error', optimizer='adam')
# 训练模型
model_SC31.fit(X_SC31, Y_SC31, epochs=100, batch_size=1, verbose=2)
# 预测未来30天的货量
predictions_SC31 = predict_future(model_SC31, data_SC31_scaled, scaler, look_back, 30)
# 打印预测结果
print(predictions_SC31)
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
# 设置 matplotlib 支持中文显示
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 指定默认字体
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像时负号'-'显示为方块的问题
# 加载数据
data = pd.read_csv('附件4.csv', encoding='GBK')
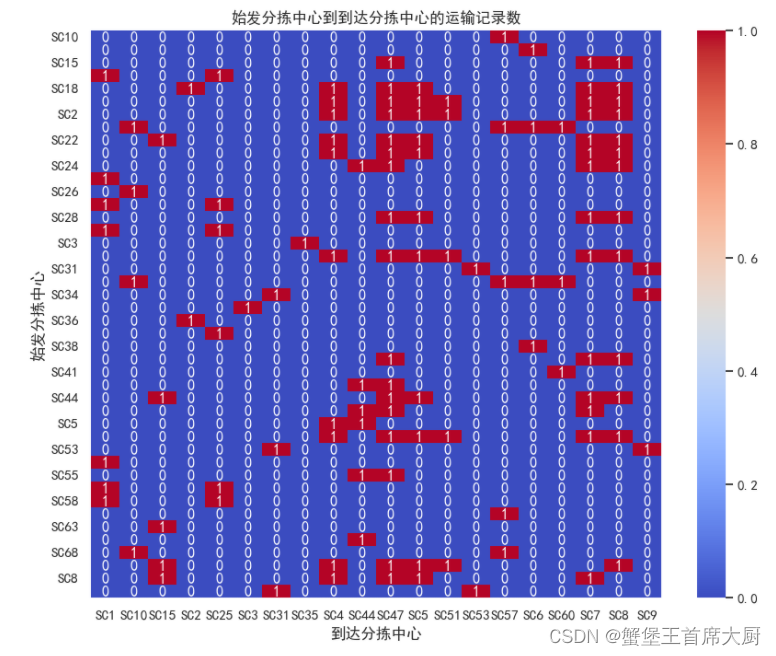
# 使用pandas的crosstab功能计算不同始发分拣中心到不同到达分拣中心的记录数
distribution_matrix = pd.crosstab(data['始发分拣中心'], data['到达分拣中心'])
# 使用Seaborn绘制热力图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
heatmap = sns.heatmap(distribution_matrix, annot=True, cmap='coolwarm', fmt='d')
plt.title('始发分拣中心到到达分拣中心的运输记录数')
plt.xlabel('到达分拣中心')
plt.ylabel('始发分拣中心')
plt.show()
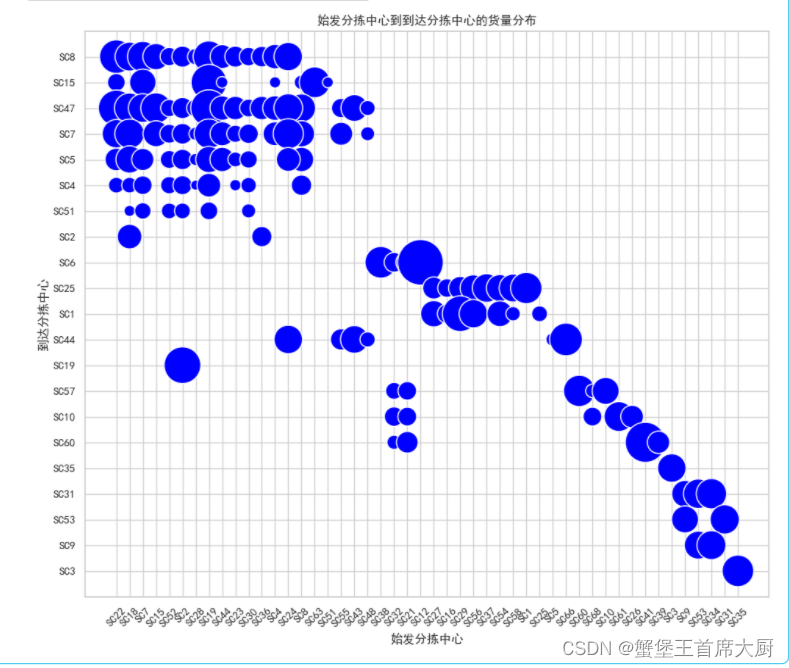
# 加载数据
data_new = pd.read_csv('附件3.csv', encoding='GBK') # 假设编码为GBK,根据之前的文件
# 使用Matplotlib和Seaborn绘制气泡图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
bubble_plot = sns.scatterplot(data=data_new, x='始发分拣中心', y='到达分拣中心', size='货量', sizes=(100, 2000), legend=None, color='blue')
plt.title('始发分拣中心到到达分拣中心的货量分布')
plt.xlabel('始发分拣中心')
plt.ylabel('到达分拣中心')
plt.grid(True)
# 调整x轴和y轴的标签显示以便更容易阅读
bubble_plot.set_xticklabels(bubble_plot.get_xticklabels(), rotation=45)
plt.show()
问题3
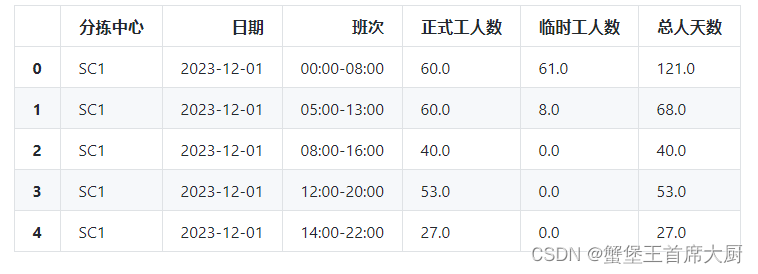
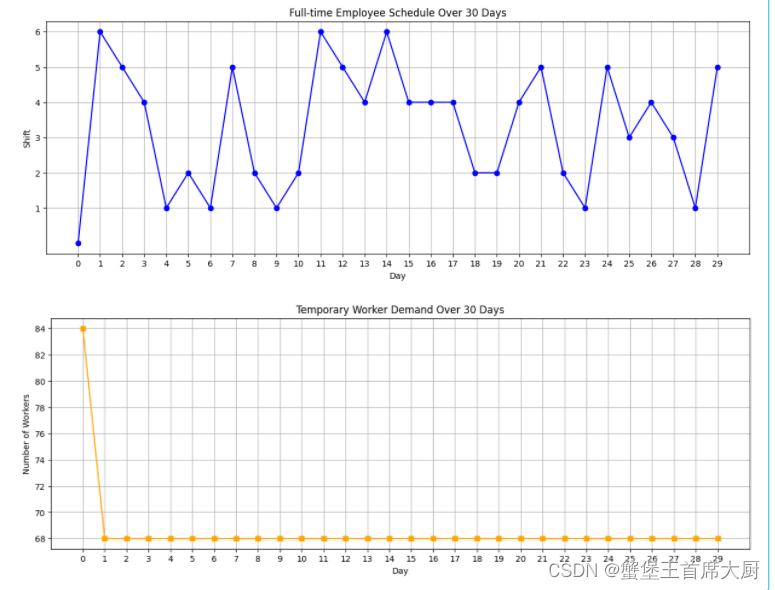
假设每个分拣中心有60名正式工,在人员安排时将优先使用正式工,若需额外人员将使用临时工。请基于问题2的预测结果建立模型,给出未来 30 天每个分拣中心每个班次的出勤人数,并写入结果表5中。要求在每天的货量处理完成的基础上,安排的人天数(例如30天每天出勤200名员工,则总人天数为6000)尽可能少,且每天的实际小时人效尽量均衡。
解题思路与代码
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
results_table_4 = pd.read_csv('结果表4.csv')
# 确认已加载数据的结构
results_table_4.head()
#%%
# 根据正确的数据集重新定义计算和处理步骤
# 定义将小时映射到班次的时间段
shift_times = {
'00:00-08:00': list(range(0, 8)),
'05:00-13:00': list(range(5, 13)),
'08:00-16:00': list(range(8, 16)),
'12:00-20:00': list(range(12, 20)),
'14:00-22:00': list(range(14, 22)),
'16:00-24:00': list(range(16, 24))
}
# 按日期、分拣中心和班次汇总数据
results_table_4['日期'] = pd.to_datetime(results_table_4['日期'])
results_table_4['班次'] = results_table_4['小时'].apply(lambda x: next((shift for shift, hours in shift_times.items() if x in hours), None))
shift_demand = results_table_4.groupby(['分拣中心', '日期', '班次'])['货量'].sum().reset_index()
# 定义绩效标准
full_time_efficiency = 25 # 每小时全职员工的最大包裹数量
temp_efficiency = 20 # 每小时临时员工的最大包裹数量
full_time_count = 60 # 每个分拣中心的全职员工数量
# 计算每个班次所需的最少员工数量
def calculate_staff_needs(row):
# 计算所需的全职员工数量
needed_full_time = np.ceil(row['货量'] / (full_time_efficiency * 8))
if needed_full_time <= full_time_count:
return needed_full_time, 0 # 不需要临时工人
else:
# 如果全职员工不足,则计算所需的临时工人数量
temp_needed = np.ceil((row['货量'] - full_time_count * full_time_efficiency * 8) / (temp_efficiency * 8))
return full_time_count, temp_needed
问题4
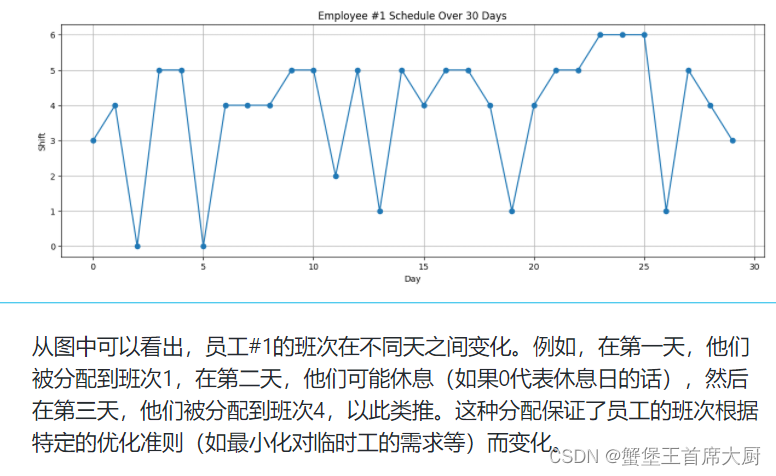
研究特定分拣中心的排班问题,这里不妨以SC60为例,假设分拣中心 SC60 当前有 200名正式工,请基于问题2的预测结果建立模型,确定未来 30 天每名正式工及临时工的班次出勤计划,即给出未来 30 天每天六个班次中,每名正式工将在哪些班次出勤,每个班次需要雇佣多少临时工,并写入结果表6中。每名正式工的出勤率(出勤的天数除以总天数30)不能高于 85%,且连续出勤天数不能超过7天。要求在每天货量处理完成的基础上,安排的人天数尽可能少,每天的实际小时人效尽量均衡,且正式工出勤率尽量均衡。
解题思路与代码
def assign_shift(hour):
if 0 <= hour < 8:
return 1 # 00:00-08:00
elif 5 <= hour < 13:
return 2 # 05:00-13:00
elif 8 <= hour < 16:
return 3 # 08:00-16:00
elif 12 <= hour < 20:
return 4 # 12:00-20:00
elif 14 <= hour < 22:
return 5 # 14:00-22:00
elif 16 <= hour < 24:
return 6 # 16:00-24:00
return None # 防止非预期的小时数
# 应用这个函数到 '小时' 列,创建新的 '班次' 列
sc60_data['班次'] = sc60_data['小时'].apply(assign_shift)
# 尝试创建数据透视表
try:
daily_demands = sc60_data.pivot_table(index='日期', columns='班次', values='货量', aggfunc='sum').fillna(0)
print("数据透视表创建成功,这里是部分数据:")
print(daily_demands.head())
except KeyError as e:
print(f"再次发生错误:{e}。请检查列名是否正确。")
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 加载数据
sc60_data = pd.read_csv('结果表4.csv')
# 确保数据仅包含SC60分拣中心的数据
sc60_data = sc60_data[sc60_data['分拣中心'] == 'SC60']
# 定义班次
def assign_shift(hour):
if 0 <= hour < 8:
return 1
elif 5 <= hour < 13:
return 2
elif 8 <= hour < 16:
return 3
elif 12 <= hour < 20:
return 4
elif 14 <= hour < 22:
return 5
elif 16 <= hour < 24:
return 6
return None
sc60_data['班次'] = sc60_data['小时'].apply(assign_shift)
# 聚合每天每班次的需求量
daily_demands = sc60_data.pivot_table(index='日期', columns='班次', values='货量', aggfunc='sum').fillna(0)
# 遗传算法的参数
population_size = 50
generations = 100
crossover_rate = 0.7
mutation_rate = 0.1
num_days = 30
num_shifts = 6
num_employees = 200 # 正式工人数
full_time_efficiency = 25 * 8 # 正式工每天最大处理量
temp_efficiency = 20 * 8 # 临时工每天最大处理量
# 根据需求初始化种群
def initialize_population(demands):
population = []
for _ in range(population_size):
schedules = np.zeros((num_employees, num_days), dtype=int)
for day in range(num_days):
daily_demand = demands.iloc[day]
for shift in range(1, num_shifts + 1):
# 根据需求分配正式工
demand = daily_demand.get(shift, 0)
required_employees = min(num_employees, int(np.ceil(demand / full_time_efficiency)))
employees = np.random.choice(range(num_employees), required_employees, replace=False)
for emp in employees:
schedules[emp, day] = shift
population.append(schedules)
return population
# 运行遗传算法
def genetic_algorithm(demands):
population = initialize_population(demands)
best_fitness = float('-inf') # 最佳适应度初始化为负无穷
best_individual = None
for generation in range(generations):
fitness_scores = [fitness(individual, demands.to_dict('index')) for individual in population]
current_best_index = np.argmax(fitness_scores)
current_best_fitness = fitness_scores[current_best_index]
print(f"Generation {generation}: Best fitness = {current_best_fitness}") # 输出当前代的最佳适应度
if current_best_fitness > best_fitness:
best_fitness = current_best_fitness
best_individual = population[current_best_index]
new_population = []
while len(new_population) < population_size:
indices = np.random.choice(len(population), 2, replace=False)
parent1, parent2 = population[indices[0]], population[indices[1]]
child1, child2 = crossover(parent1, parent2)
mutate(child1)
mutate(child2)
new_population.extend([child1, child2])
population = new_population
return best_individual
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 加载数据
sc60_data = pd.read_csv('结果表4.csv')
# 选择SC60分拣中心的数据
sc60_data = sc60_data[sc60_data['分拣中心'] == 'SC54']
# 根据小时数指定班次
def assign_shift(hour):
if 0 <= hour < 5:
return 1 # 00:00-05:00, 班次1
elif 5 <= hour < 8:
return 2 # 05:00-08:00, 班次2
elif 8 <= hour < 12:
return 3 # 08:00-12:00, 班次3
elif 12 <= hour < 14:
return 4 # 12:00-14:00, 班次4
elif 14 <= hour < 16:
return 5 # 14:00-16:00, 班次5
elif 16 <= hour < 24:
return 6 # 16:00-24:00, 班次6
else:
return None
sc60_data['班次'] = sc60_data['小时'].apply(assign_shift)
# 确定每天每个班次的货量
daily_demands = sc60_data.pivot_table(index='日期', columns='班次', values='货量', aggfunc='sum').fillna(0)
# 遗传算法参数
population_size = 50
generations = 100
crossover_rate = 0.7
mutation_rate = 0.1
num_days = 30
num_shifts = 6
num_employees = 200 # 正式工数量
full_time_efficiency = 25 * 8 # 正式工每天的最大处理量
temp_efficiency = 20 * 8 # 临时工每天的最大处理量
# 初始化种群
def initialize_population():
population = []
for _ in range(population_size):
# 随机生成每名员工的班次表,0表示不工作,1-6表示班次
schedules = np.random.randint(0, num_shifts + 1, size=(num_employees, num_days))
population.append(schedules)
return population
# 适应度函数
def fitness(individual, demands):
total_temp_workers = 0
for day in range(num_days):
for shift in range(1, num_shifts + 1):
demand = demands.iloc[day][shift] if shift in demands.columns else 0
num_full_workers = np.sum(individual[:, day] == shift)
total_work = num_full_workers * full_time_efficiency
temp_workers_needed = max(0, np.ceil((demand - total_work) / temp_efficiency))
total_temp_workers += temp_workers_needed
return -total_temp_workers # 适应度为负的临时工总数,越少越好
# 交叉操作
def crossover(parent1, parent2):
if np.random.rand() < crossover_rate:
point = np.random.randint(1, num_days)
new1 = np.hstack((parent1[:, :point], parent2[:, point:]))
new2 = np.hstack((parent2[:, :point], parent1[:, point:]))
return new1, new2
else:
return parent1.copy(), parent2.copy()
# 变异操作
def mutate(individual):
for i in range(num_employees):
for j in range(num_days):
if np.random.rand() < mutation_rate:
individual[i, j] = np.random.randint(0, num_shifts + 1)
# 运行遗传算法
def genetic_algorithm(demands):
population = initialize_population()
best_fitness = float('inf')
best_individual = None
for generation in range(generations):
fitness_scores = [fitness(individual, demands) for individual in population]
best_index = np.argmax(fitness_scores)
if fitness_scores[best_index] < best_fitness:
best_fitness = fitness_scores[best_index]
best_individual = population[best_index]
new_population = []
while len(new_population) < population_size:
indices = np.random.choice(len(population), 2, replace=False)
parent1, parent2 = population[indices[0]], population[indices[1]]
child1, child2 = crossover(parent1, parent2)
mutate(child1)
mutate(child2)
new_population.extend([child1, child2])
population = new_population
return best_individual
# 使用算法计算最优排班
best_schedule = genetic_algorithm(daily_demands)
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# 路径配置
input_file_path = '结果表4.csv'
output_file_path = '结果表6gai.csv'
# 加载数据
df = pd.read_csv(input_file_path)
# 定义班次
def assign_shift(hour):
if 0 <= hour < 5:
return 1
elif 5 <= hour < 8:
return 2
elif 8 <= hour < 12:
return 3
elif 12 <= hour < 14:
return 4
elif 14 <= hour < 16:
return 5
elif 16 <= hour < 24:
return 6
return None
# 应用班次分配规则
df['班次'] = df['小时'].apply(assign_shift)
# 聚合每天每班次的货量
daily_demands = df.pivot_table(index='日期', columns='班次', values='货量', aggfunc='sum').fillna(0)
# 遗传算法参数配置
population_size = 50
generations = 100
num_days = 30
num_shifts = 6
num_employees = 200
full_time_efficiency = 25
temp_efficiency = 20
# 初始化种群
def initialize_population(pop_size, num_emps, num_days):
return np.random.randint(0, num_shifts+1, size=(population_size, num_employees, num_days))
# 适应度函数
def fitness(individual, demands):
penalty = 0
for day in range(num_days):
for shift in range(1, num_shifts+1):
shift_demand = demands.iloc[day, shift-1] if shift in demands.columns else 0
workers_in_shift = np.sum(individual[:, day] == shift)
work_done = workers_in_shift * full_time_efficiency
shortage = max(0, shift_demand - work_done)
penalty += shortage
return penalty
# 选择操作
def selection(population, fitness_scores):
probabilities = fitness_scores / fitness_scores.sum()
selected_indices = np.random.choice(range(population_size), size=population_size, replace=True, p=probabilities)
return population[selected_indices]
# 交叉操作
def crossover(parent1, parent2, crossover_rate=0.7):
if np.random.rand() < crossover_rate:
crossover_point = np.random.randint(1, num_days-1)
child1 = np.hstack((parent1[:, :crossover_point], parent2[:, crossover_point:]))
child2 = np.hstack((parent2[:, :crossover_point], parent1[:, crossover_point:]))
return child1, child2
else:
return parent1.copy(), parent2.copy()
# 变异操作
def mutation(individual, mutation_rate=0.1):
for employee in range(num_employees):
for day in range(num_days):
if np.random.rand() < mutation_rate:
individual[employee, day] = np.random.randint(0, num_shifts+1)
# 遗传算法主体函数
def genetic_algorithm(population, demands):
for _ in range(generations):
# 计算适应度
fitness_scores = np.array([fitness(individual, demands) for individual in population])
# 选择
selected = selection(population, 1 / (1 + fitness_scores)) # 适应度越低,选择概率越高
# 交叉和变异
next_population = []
for i in range(0, population_size, 2):
parent1, parent2 = selected[i], selected[i+1]
child1, child2 = crossover(parent1, parent2)
mutation(child1)
mutation(child2)
next_population.extend([child1, child2])
population = np.array(next_population)
# 返回适应度最高的个体
best_fitness_idx = np.argmin(fitness_scores)
return population[best_fitness_idx]
# 初始化种群
population = initialize_population(population_size, num_employees, num_days)
# 执行遗传算法
best_individual = genetic_algorithm(population, daily_demands)
# 将最优排班结果转换为DataFrame
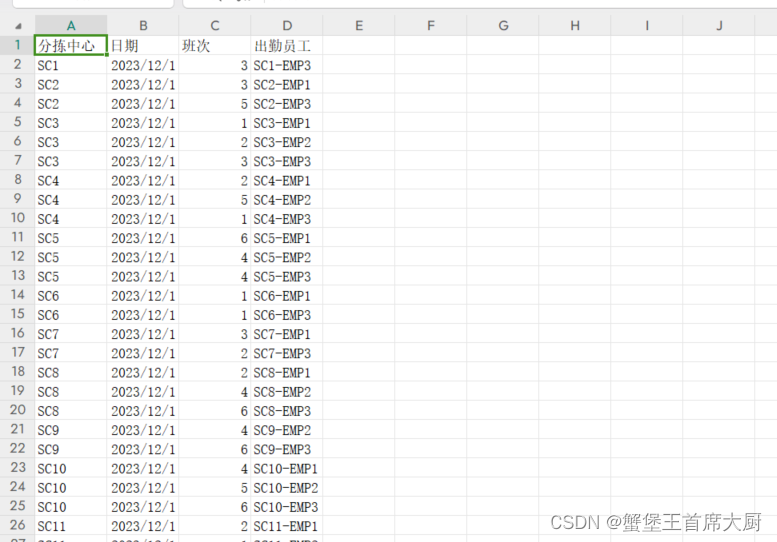
result_data = []
for day in range(num_days):
for employee in range(num_employees):
shift = best_individual[employee, day]
if shift != 0:
sorting_center = f"SC{employee // 3 + 1}"
# 确保分拣中心编号在SC1到SC57之间
sorting_center_id = min(employee // 3 + 1, 57)
# 确保员工编号在1到3之间
employee_id = (employee % 3) + 1
result_data.append({'分拣中心': sorting_center, '日期': f'2023-12-{day + 1}', '班次': shift, '出勤员工': f'SC{sorting_center_id}-EMP{employee_id}'})
result_df = pd.DataFrame(result_data)
# 保存结果到CSV文件
result_df.to_csv(output_file_path, index=False)
print(f'排班结果已保存至 {output_file_path}')
资料获取
提供2024MathorCupBC题的思路分析与代码,欢迎进群讨论:953799264
C题目思路代码获取:http://app.niucodata.com/mianbaoduo/recommend.php?id=59187
C题目成品论文获取:http://app.niucodata.com/mianbaoduo/recommend.php?id=59181