- 探索Headless组件与Tailwind CSS的魔力——前端开发的
- Java实战:SpringBoot 业务操作日志功能设计
- Llama2模型本地部署(Mac M1 16G)
- uniapp+springboot 实现前后端分离的个人备忘录系统【超
- 简单易懂:Axios 如何取消请求的两种方法
- uni-app的页面中使用uni-map-common的地址解析(地址
- Rust面试宝典第7题:单词接龙
- Spring AI与大模型Ollama如何集成整合?
- SpringBoot整合参数校验
- 已解决com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.Com
- idea 2023版本创建maven管理的Scala项目教程
- 反序列化渗透与防御之PHP
- 深度解析 Spring 源码:三级缓存机制探究
- 基于pear-admin-flask 的 flask 使用教程
- 使用SM4国密加密算法对Spring Boot项目数据库连接信息以及y
- 最新免费 ChatGPT、GPTs、AI换脸(Suno-AI音乐生成大
- 力扣习题+——单链表
- Node.js版本升级,修改模块默认的保存位置
- 【Linux】使用Jenkins + svn + springboot
- Postman测试金蝶云星空Webapi【协同开发云】
- MysqlOracle的DATE、DATETIME 和 TIMESTA
- 数据结构中的时间复杂度和空间复杂度基础
- 网络编程套接字(1)—网络编程基础
- 深度学习超参数调整介绍
- 五种方案图文并茂教你使用DBeaver,SQL文件导入数据库,插入数据
- Python赋能AI数据分析开启人工智能新时代
- Hadoop集群安装部署
- 解决mysql报错ERROR 1049 (42000): Unknow
- 【MySQL】MySQL数据库主键自增长删除后ID不连续的问题及其解决
- 输了,腾讯golang一面凉了
神经网络——循环神经网络(RNN)
文章目录
- 神经网络——循环神经网络(RNN)
- 一、循环神经网络(RNN)
- 二、循环神经网络结构
- 1、一对一(One to One)
- 2、一对多(One to Many)
- 3、多对多(Many to Many)
- 4、多对一(Many to One)
- 三、循环神经网络原理
- 四、RNN实战
- 1、时间序列预测
- 五、循环神经网络的弊端
一、循环神经网络(RNN)
循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network,简称RNN)是一种能够处理序列数据的神经网络模型。循环神经网络属于深度学习神经网络(DNN),与传统的前馈神经网络不同,RNN在处理每个输入时都会保留一个隐藏状态,该隐藏状态会被传递到下一个时间步,以便模型能够记忆之前的信息。
循环神经网络在自然语言处理、语音识别、机器翻译等任务上取得了很大的成功。它能够捕捉到输入序列的上下文信息,从而能够更好地处理序列数据的特点。
二、循环神经网络结构
1、一对一(One to One)
特征:由一个输入到模型中,获得一个输出。
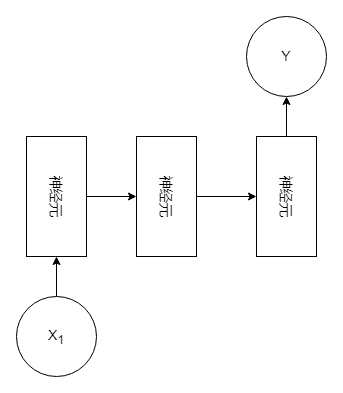
2、一对多(One to Many)
特征:由一个输入到模型中,获得多个输出。
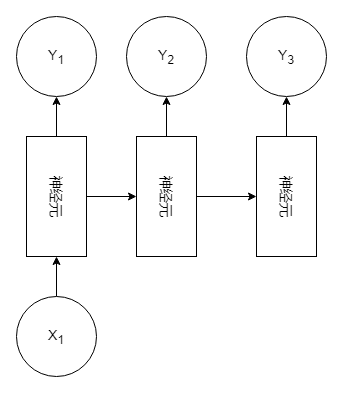
3、多对多(Many to Many)
特征:由多个输入到模型中,获得多个输出。
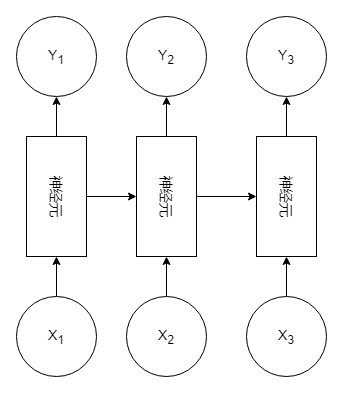
其他变形:
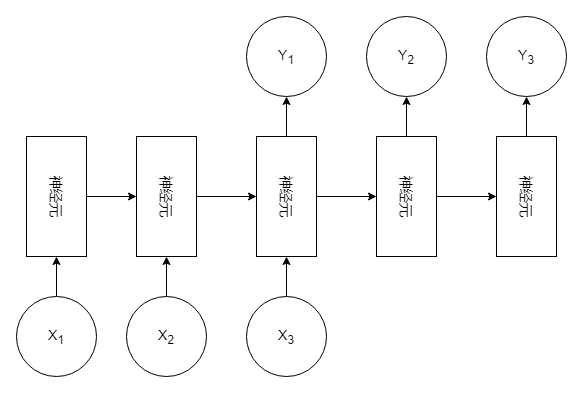
4、多对一(Many to One)
特征:由多个输入到模型中,获得一个输出。
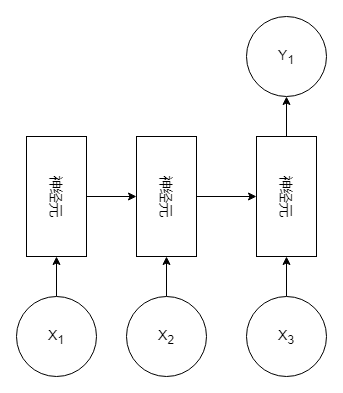
三、循环神经网络原理
符号说明:
符号 说明 X n X_n Xn 输入内容 Y n Y_n Yn 输出内容 U 、 V 、 W U、V、W U、V、W 权重 S n S_n Sn 神经元 c c c 输出的个数 循环神经网络的一个特性是上一次的结果将会作为下一次的输入
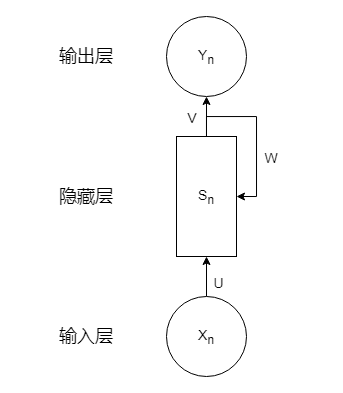
在输出层,通常使用 s o f t m a x softmax softmax函数对数据进行归一化处理。
Y n = s o f t m a x ( S n ) = e S n ∑ c = 1 c e S c \begin{aligned} Y_n&=softmax(S_n)\\ &= \frac{e^{S_n}}{\sum_{c= 1}^{c}e^{S_c}} \end{aligned} Yn=softmax(Sn)=∑c=1ceSceSn
由函数可知,此函数将数据限制在 [ 0 , 1 ] [0,1] [0,1]且和为 1 1 1。
在隐藏层中,常用 t a n h tanh tanh作为激活函数。根据循环神经网络的性质可以分析出
S n = t a n h ( U X n + W S n − 1 ) S_n=tanh(UX_n+WS_{n-1}) Sn=tanh(UXn+WSn−1)
根据公式可以得知
Y n = s o f t m a x ( ∑ n = 1 n t a n h ( U X n + W S n − 1 ) ) = e ∑ n = 1 n t a n h ( U X n + W S n − 1 ) ∑ c = 1 c e S c \begin{aligned} Y_n&=softmax(\sum_{n=1}^{n}tanh(UX_n+WS_{n-1}))\\ &=\frac{e^{\sum_{n=1}^{n}tanh(UX_n+WS_{n-1})}}{\sum_{c=1}^{c}e^{Sc}} \end{aligned} Yn=softmax(n=1∑ntanh(UXn+WSn−1))=∑c=1ceSce∑n=1ntanh(UXn+WSn−1)
四、RNN实战
1、时间序列预测
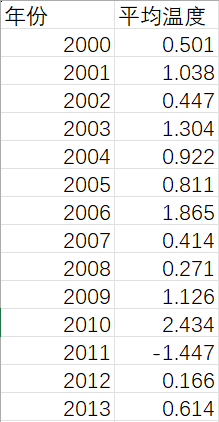
现在有2000-2013年成都一月份的平均温度数据,现在即将预测2014年的温度。
MATLAB代码如下:
% 日期数据 years = 2000:2013; target_year = 2014; % 温度数据 temperatures = [0.501, 1.038, 0.447, 1.304, 0.922, 0.811, 1.865, 0.414, 0.271, 1.126, 2.434, -1.447, 0.166, 0.614]; % 利用数据进行训练 training_years = years(1:14); training_temperatures = temperatures(1:14); % 创建简单的递归神经网络 (RNN) 模型 net = layrecnet(1,10); % 调整输入数据的维度 input_seq = con2seq(training_temperatures'); target_seq = con2seq(training_temperatures'); % 在训练数据上训练模型 net = train(net, input_seq, target_seq); % 预测2014年的温度 predicted_temperatures = sim(net, input_seq); % 将 cell 类型的预测结果转换为数组类型 predicted_temperature_2014 = cell2mat(predicted_temperatures); % 输出预测结果 disp(['2014年的预测温度为: ', num2str(predicted_temperature_2014(end))]); figure; hold on; plot(training_years, training_temperatures, 'o-', 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'MarkerSize', 8, 'DisplayName', 'Training Data'); plot(target_year, predicted_temperature_2014(end), 'ro', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'DisplayName', 'Prediction'); xlabel('Year'); ylabel('Temperature'); legend('Location', 'best'); title('Temperature Prediction'); hold off;最后得到2014年的预测温度,并获得一个预测图像。
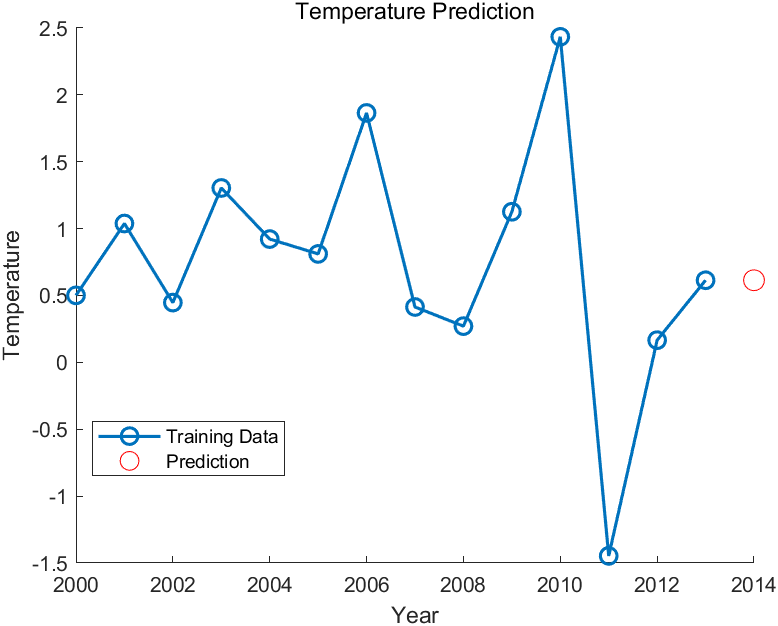
有时候我们不一定只预测一年的数据。我们还可以预测2014-2018年每年的数据。
MATLAB代码如下:
% 温度数据 temperature = [0.501, 1.038, 0.447, 1.304, 0.922, 0.811, 1.865, 0.414, 0.271, 1.126, 2.434, -1.447, 0.166, 0.614]; % 准备训练数据 X = temperature(1:end-1); Y = temperature(2:end); % 数据预处理 X = X'; Y = Y'; % 构建RNN模型 hiddenUnits = 10; % 隐藏单元数量 net = layrecnet(1, hiddenUnits); % 配置训练参数 net.trainParam.showWindow = false; % 不显示训练进度窗口 net.trainParam.epochs = 100; % 迭代次数 % 修改输入数据尺寸 X = con2seq(X); Y = con2seq(Y); % 转换数据为二维矩阵形式 X = cell2mat(X); Y = cell2mat(Y); % 将数据转换为时间序列数据 inputSize = size(X, 2); outputSize = size(Y, 2); X = num2cell(X', 1); Y = num2cell(Y', 1); % 训练RNN模型 net = train(net, X, Y); % 预测并显示2014至2018年的温度和误差值 futureYears = 2014:2018; predictedTemperature = []; errors = []; for i = 1:numel(futureYears) % 预测下一年的温度 prediction = round(sim(net, lastInput), 3, 'significant'); % 计算误差值 error = abs(prediction - Y{i}); % 添加到预测结果和误差列表 predictedTemperature = [predictedTemperature, prediction]; errors = [errors, error]; % 更新输入 lastInput = [lastInput(:, 2:end), prediction]; % 显示当前年份、温度和误差值 disp(['年份:' num2str(futureYears(i)) ',温度:' num2str(prediction) ',误差值:' num2str(error)]); end % 绘制训练集和预测结果 figure hold on plot(2000:2013, temperature, 'b') plot(futureYears, predictedTemperature, 'r') xlabel('年份') ylabel('温度') legend('训练数据', '预测数据') % 计算平均绝对误差MAE MAE = mean(errors); % 输出平均绝对误差MAE disp(['平均绝对误差MAE:' num2str(MAE)]);根据MAE,选择误差合理的数据作为预测值。我选取一个MAE值为0.2422的预测值。图像如下:
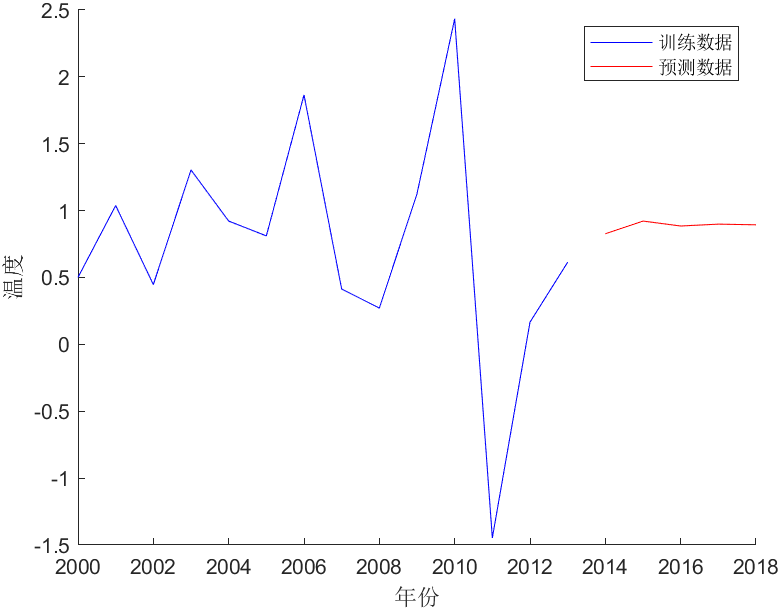
五、循环神经网络的弊端
存在问题:
1、计算复杂度高:RNN的推理过程是逐步进行的,每一步都需要依赖前一步的结果。这导致了计算量较大,特别是在处理长序列时,时间和空间复杂度都会显著增加。
2、信息丢失:RNN的隐藏状态只能通过有限个时间步骤传递信息。长时间序列中重要的历史信息可能会被遗忘或丢失,从而影响预测的准确性。
解决方法:
采用长短期记忆网络(LSTM)、门控循环单元(GRU)等RNN变体。














